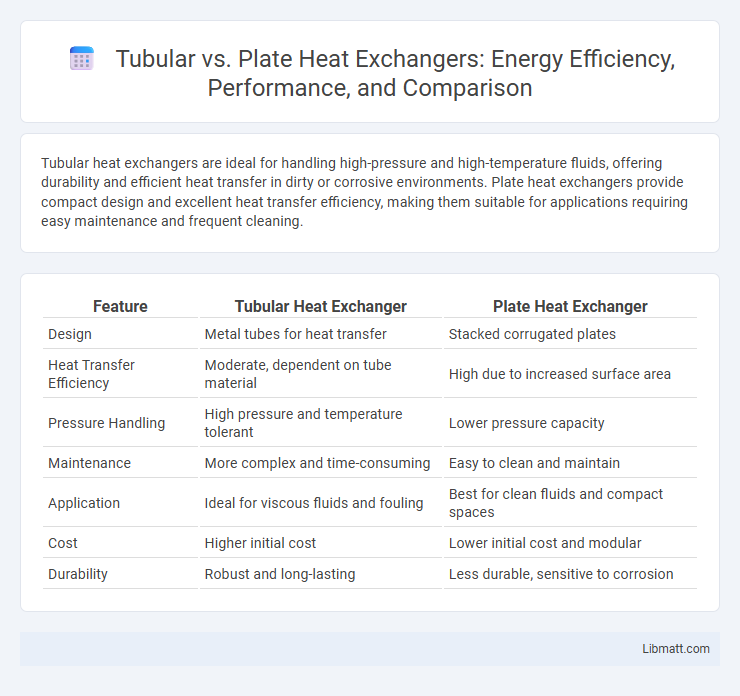
Tubular heat exchangers are ideal for handling high-pressure and high-temperature fluids, offering durability and efficient heat transfer in dirty or corrosive environments. Plate heat exchangers provide compact design and excellent heat transfer efficiency, making them suitable for applications requiring easy maintenance and frequent cleaning.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Tubular Heat Exchanger | Plate Heat Exchanger |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Metal tubes for heat transfer | Stacked corrugated plates |
| Heat Transfer Efficiency | Moderate, dependent on tube material | High due to increased surface area |
| Pressure Handling | High pressure and temperature tolerant | Lower pressure capacity |
| Maintenance | More complex and time-consuming | Easy to clean and maintain |
| Application | Ideal for viscous fluids and fouling | Best for clean fluids and compact spaces |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower initial cost and modular |
| Durability | Robust and long-lasting | Less durable, sensitive to corrosion |
Introduction to Heat Exchangers
Heat exchangers are devices designed to transfer heat between two or more fluids efficiently while preventing direct contact. Tubular heat exchangers utilize cylindrical tubes to facilitate heat transfer, often favored for handling high-pressure or corrosive fluids, while plate heat exchangers consist of multiple thin, corrugated plates that provide a large surface area for rapid heat transfer and are ideal for compact installations with moderate pressure requirements. The selection between tubular and plate heat exchangers depends on factors such as fluid properties, temperature ranges, pressure differences, and maintenance needs.
Overview of Tubular Heat Exchangers
Tubular heat exchangers consist of a series of tubes where one fluid flows inside the tubes and another fluid flows outside them, enabling efficient heat transfer through the tube walls. They are ideal for handling high-pressure, high-temperature applications and fluids with high fouling tendencies due to their robust design and ease of cleaning. Commonly used in industries such as chemical processing, power generation, and oil refining, tubular heat exchangers provide superior durability compared to plate heat exchangers.
Overview of Plate Heat Exchangers
Plate heat exchangers consist of multiple corrugated metal plates stacked together, creating a compact design that offers high heat transfer efficiency by maximizing surface area and turbulence. Their modular construction allows easy maintenance and expansion, making them ideal for industries such as HVAC, food processing, and chemical manufacturing. Compared to tubular heat exchangers, plate heat exchangers provide superior heat transfer rates and space-saving benefits, but they may have limitations in handling high-pressure or high-temperature fluids.
Working Principles: Tubular vs Plate Heat Exchangers
Tubular heat exchangers transfer heat through the walls of cylindrical tubes, allowing fluids to flow inside the tubes and around the shell, promoting efficient heat exchange via conduction and convection. Plate heat exchangers consist of thin, corrugated plates stacked together, creating multiple parallel channels where fluids flow in alternate passages, enhancing heat transfer through a larger surface area with turbulent flow. Your choice depends on factors like fluid properties and maintenance ease, as tubular designs handle high pressures and fouling better, while plate exchangers excel in compactness and heat transfer efficiency.
Efficiency Comparison: Tubular vs Plate Designs
Plate heat exchangers demonstrate higher thermal efficiency due to their large surface area and turbulent flow, promoting better heat transfer rates compared to tubular designs. Tubular heat exchangers offer robustness and are favored for handling high-pressure and fouling applications but typically exhibit lower heat transfer coefficients. Optimizing efficiency depends on the application, with plate designs excelling in compactness and heat transfer performance, while tubular designs are preferred for durability in harsh operating conditions.
Maintenance and Cleaning Considerations
Tubular heat exchangers offer easier maintenance with their straightforward design, allowing for simple cleaning by mechanical or chemical methods, especially in applications with fouling fluids. Plate heat exchangers require regular disassembly for cleaning, as their compact plates can trap debris, but their gasketed construction enables quick cleaning and inspection. Your choice depends on the cleaning frequency and ease of access needed to ensure optimal performance and minimize downtime.
Cost Analysis: Installation and Operation
Tubular heat exchangers generally incur higher initial installation costs due to their robust design and complex assembly, while plate heat exchangers offer lower upfront expenses because of their compact, modular construction. Operational costs for tubular models tend to be higher, driven by increased maintenance and cleaning requirements, whereas plate heat exchangers benefit from easier maintenance and enhanced thermal efficiency, leading to reduced energy consumption. Your choice should balance the higher durability and suitability of tubular exchangers for high-pressure, high-temperature applications against the cost-effective, efficient operation of plate heat exchangers in moderate conditions.
Space and Design Flexibility
Tubular heat exchangers offer significant design flexibility, accommodating high-pressure and high-temperature applications with customizable tube lengths and diameters, which optimizes space in complex installations. Plate heat exchangers provide a compact footprint, maximizing heat transfer efficiency within limited spaces through their modular, stackable plate design ideal for applications requiring easy maintenance and scalability. Your choice depends on space constraints and design requirements, with tubular exchangers suited for rugged conditions and plate exchangers excelling in compact, efficient layouts.
Industrial Applications and Suitability
Tubular heat exchangers excel in industrial applications requiring high-pressure handling and superior heat transfer for viscous fluids, often found in chemical and petrochemical industries. Plate heat exchangers are ideal for processes demanding compact design and efficient heat transfer with easy maintenance, commonly used in food processing and HVAC systems. Your choice between tubular and plate heat exchangers depends on the specific industrial conditions, such as fluid type, pressure, and space constraints.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Heat Exchanger
Selecting the right heat exchanger depends on application specifics such as temperature range, pressure, and maintenance needs. Tubular heat exchangers excel in handling high pressures, corrosive fluids, and fouling conditions, making them suitable for heavy-duty industrial processes. Plate heat exchangers offer higher thermal efficiency and compact design, ideal for applications requiring frequent cleaning and moderate operating conditions.
Tubular vs Plate Heat Exchanger Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com