Sous vide cooking preserves the natural flavors and nutrients by gently cooking food in a temperature-controlled water bath, ensuring even doneness and tender texture. Your meals achieve consistent results with enhanced moisture retention compared to conventional methods that often risk overcooking and uneven heat distribution.
Table of Comparison
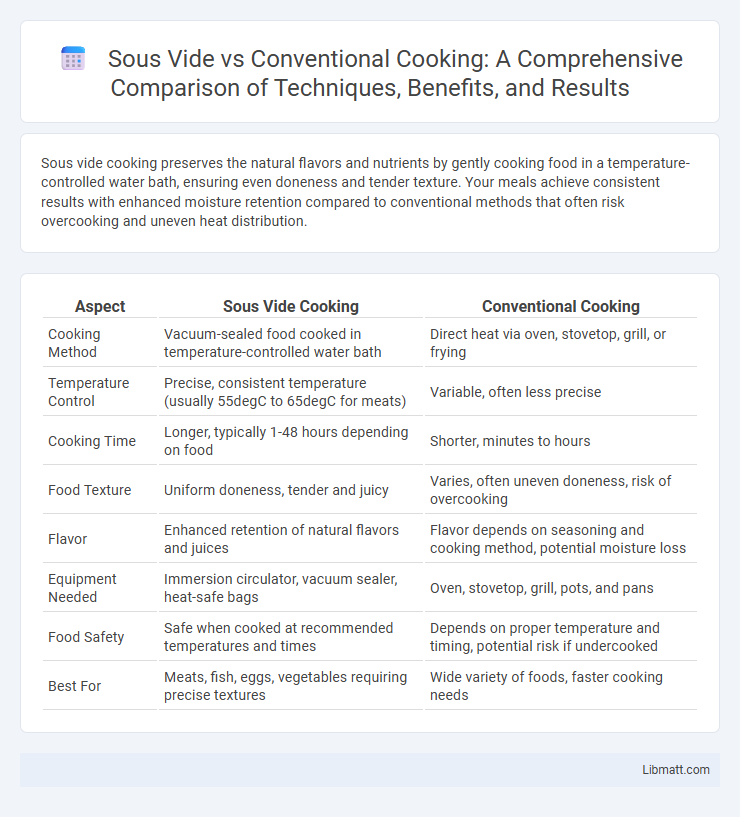
| Aspect | Sous Vide Cooking | Conventional Cooking |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | Vacuum-sealed food cooked in temperature-controlled water bath | Direct heat via oven, stovetop, grill, or frying |
| Temperature Control | Precise, consistent temperature (usually 55degC to 65degC for meats) | Variable, often less precise |
| Cooking Time | Longer, typically 1-48 hours depending on food | Shorter, minutes to hours |
| Food Texture | Uniform doneness, tender and juicy | Varies, often uneven doneness, risk of overcooking |
| Flavor | Enhanced retention of natural flavors and juices | Flavor depends on seasoning and cooking method, potential moisture loss |
| Equipment Needed | Immersion circulator, vacuum sealer, heat-safe bags | Oven, stovetop, grill, pots, and pans |
| Food Safety | Safe when cooked at recommended temperatures and times | Depends on proper temperature and timing, potential risk if undercooked |
| Best For | Meats, fish, eggs, vegetables requiring precise textures | Wide variety of foods, faster cooking needs |
Understanding Sous Vide Cooking
Sous vide cooking involves vacuum-sealing food and cooking it in a precisely controlled water bath, ensuring even heat distribution and consistent results. Unlike conventional cooking methods that rely on direct heat, sous vide maintains exact temperatures, preventing overcooking and preserving moisture, texture, and flavor. This technique is favored in professional kitchens for its ability to enhance food tenderness and nutritional retention.
What is Conventional Cooking?
Conventional cooking involves applying heat to food through direct methods such as baking, boiling, grilling, or frying, often resulting in faster cooking times but varying levels of moisture retention and flavor consistency. In contrast, sous vide cooking uses precise temperature control by sealing food in vacuum bags and immersing it in a water bath, ensuring even cooking and enhanced texture. Understanding conventional cooking techniques helps you appreciate sous vide's advantages in consistency and nutrient preservation.
Key Differences Between Sous Vide and Conventional Methods
Sous vide cooking uses precise temperature control by immersing vacuum-sealed food in a water bath, preserving texture and flavor better than conventional cooking, which relies on direct heat and faster cooking times that can lead to uneven results. Conventional methods often involve grilling, baking, or frying, which expose food to higher temperatures and may cause moisture loss or overcooking. Your choice between sous vide and conventional cooking will impact the tenderness, juiciness, and consistency of the final dish.
Temperature Control and Precision
Sous vide cooking offers unparalleled temperature control and precision by immersing food in a water bath maintained at a consistent, exact temperature, typically within 0.1degF (0.05degC) accuracy. Conventional cooking methods often rely on fluctuating heat sources such as stovetops or ovens, which can lead to uneven cooking and temperature spikes. By using sous vide, you ensure perfectly cooked meals with balanced textures and flavors, minimizing the risk of overcooking or undercooking.
Flavor and Texture Comparison
Sous vide cooking delivers precise temperature control that enhances flavor retention and produces consistently tender textures by evenly cooking food without overcooking edges. Conventional cooking methods often result in flavor loss and uneven textures due to higher heat exposure and variable cooking times. By maintaining moisture and intensifying natural flavors, sous vide offers superior juiciness and mouthfeel compared to traditional techniques.
Nutritional Value: Which Method Preserves More Nutrients?
Sous vide cooking preserves more nutrients compared to conventional cooking by using precise, lower temperatures and airtight vacuum sealing, which minimizes nutrient loss and oxidation. Conventional cooking methods, such as boiling or frying, expose food to higher heat and water, leading to significant leaching of water-soluble vitamins like vitamin C and B-complex. Studies show sous vide retains up to 30% more antioxidants and essential vitamins, enhancing the overall nutritional value of meals.
Equipment and Setup Requirements
Sous Vide cooking requires precise temperature-controlled water baths and vacuum sealers to ensure consistent results, whereas conventional cooking relies on standard kitchen appliances like ovens, stovetops, and pans. The setup for sous vide is more specialized, demanding additional tools such as immersion circulators and vacuum bags, which can be an upfront investment. Your choice of method affects not only the equipment needed but also the space and preparation time in your kitchen.
Cooking Time: Fast or Slow?
Sous vide cooking uses precise, low temperatures over an extended period, often several hours, to achieve even doneness and enhanced flavor, making it a slower but highly controlled method compared to conventional cooking. Conventional cooking relies on higher heat for shorter periods, delivering faster results but sometimes sacrificing uniformity and moisture retention. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize speed or the precise texture and flavor benefits sous vide offers.
Safety and Food Hygiene Considerations
Sous vide cooking offers enhanced safety by maintaining precise, consistent temperatures that effectively kill harmful bacteria without overcooking food, reducing the risk of undercooked meals common in conventional methods. Vacuum sealing in sous vide prevents cross-contamination and minimizes exposure to air, limiting bacterial growth and spoilage. Conventional cooking requires careful temperature monitoring to ensure food reaches safe internal temperatures, but uneven heating may lead to foodborne illnesses if not properly managed.
Which Method is Right for You?
Sous vide cooking offers precise temperature control for perfectly cooked meals, preserving nutrients and enhancing flavors with minimal effort. Conventional cooking provides flexibility and quicker preparation, ideal for spontaneous meals and diverse cooking techniques like sauteing or grilling. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize consistent results and convenience (sous vide) or speed and versatility (conventional cooking).
Sous Vide vs Conventional Cooking Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com