Canning preserves food by heating it in sealed metal containers, which sterilizes and extends shelf life, while bottling typically involves sealing liquids or preserves in glass jars to maintain freshness and flavor. Your choice depends on the type of food and storage preferences, with canning offering more durability and bottling providing better visibility of contents.
Table of Comparison
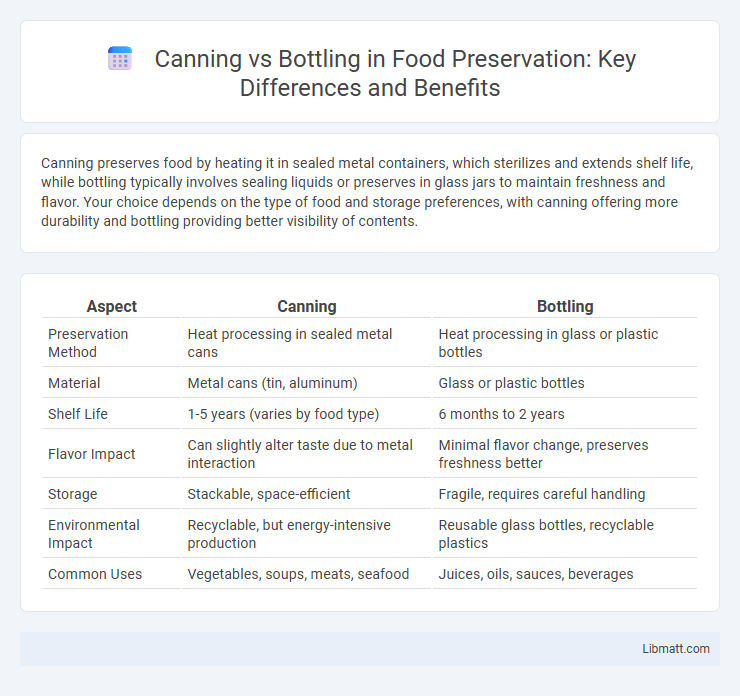
| Aspect | Canning | Bottling |
|---|---|---|
| Preservation Method | Heat processing in sealed metal cans | Heat processing in glass or plastic bottles |
| Material | Metal cans (tin, aluminum) | Glass or plastic bottles |
| Shelf Life | 1-5 years (varies by food type) | 6 months to 2 years |
| Flavor Impact | Can slightly alter taste due to metal interaction | Minimal flavor change, preserves freshness better |
| Storage | Stackable, space-efficient | Fragile, requires careful handling |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable, but energy-intensive production | Reusable glass bottles, recyclable plastics |
| Common Uses | Vegetables, soups, meats, seafood | Juices, oils, sauces, beverages |
Introduction to Canning and Bottling
Canning preserves food by sealing it in airtight metal containers, preventing spoilage through heat processing that kills bacteria. Bottling typically involves glass jars, offering visibility of contents and reuse potential but often requires careful handling to avoid breakage. Your choice between canning and bottling depends on storage needs, shelf life, and the type of food being preserved.
Key Differences Between Canning and Bottling
Canning involves sealing food in metal cans using heat to preserve and prevent spoilage, while bottling typically uses glass or plastic containers sealed with lids or caps. Canning offers superior protection against light and air, extending shelf life, whereas bottling allows for easier resealing and reuse of containers. Differences in sterilization processes, container materials, and preservation methods impact product quality and storage duration significantly.
Pros and Cons of Canning
Canning preserves food by sealing it in airtight containers and heating to destroy bacteria, extending shelf life up to several years without refrigeration. Pros include long-term storage, retention of nutrients, and protection against spoilage, while cons involve potential nutrient loss from heat processing, risk of contamination if not done properly, and the need for specialized equipment and time. Compared to bottling, canning offers greater durability but less convenience for direct consumption.
Pros and Cons of Bottling
Bottling preserves the flavor and aroma of beverages better than canning due to its airtight seal, making it ideal for wines and craft oils. Glass bottles are recyclable and reusable but are heavier and more fragile, increasing shipping costs and risk of breakage. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize product quality and presentation or convenience and durability.
Preservation Methods Compared
Canning and bottling are preservation methods that extend the shelf life of food and beverages by preventing microbial growth and oxidation. Canning uses heat to sterilize sealed metal containers, creating a vacuum that blocks bacteria and molds, ideal for high-acid and low-acid foods. Bottling, often used for liquids like juices and sauces, relies on sterilized glass or plastic containers and may require refrigeration after opening to maintain freshness and prevent spoilage.
Safety Considerations in Canning vs Bottling
Canning offers superior safety through airtight seals that prevent contamination and spoilage, significantly reducing the risk of bacterial growth compared to bottling. Bottling, especially with glass containers, requires thorough sterilization and proper storage to avoid unsafe conditions such as mold or yeast development. Properly executed canning processes, including pressure canning for low-acid foods, provide reliable long-term preservation and food safety assurances.
Cost Analysis: Canning vs Bottling
Canning typically offers lower packaging costs compared to bottling due to cheaper raw materials and faster production speeds, making it ideal for large-scale operations. Bottling incurs higher expenses from glass production, transportation, and breakage, but can enhance perceived product value and shelf appeal. Evaluating cost efficiency requires analyzing factors like initial investment, material prices, and expected shelf life relative to target market demands.
Impact on Flavor and Quality
Canning preserves flavor by sealing food under heat, which can slightly alter taste but ensures long-term freshness and safety. Bottling often retains more natural flavors, especially in products like sauces and juices, due to gentler heat treatments or cold preservation methods. Both methods impact texture and nutrient retention differently, with bottling generally better for delicate flavors and canning offering more robust preservation.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Canning offers a lower environmental footprint due to its lightweight aluminum, which is highly recyclable and requires less energy to transport compared to glass bottles. Glass bottling, while reusable, demands more energy during production and has a heavier weight that increases transportation emissions. Sustainability efforts favor cans for their closed-loop recycling process and reduced carbon emissions throughout the supply chain.
Choosing the Best Method for Your Needs
Choosing between canning and bottling depends on factors such as the type of food or beverage, shelf life requirements, and storage conditions. Canning provides airtight sealing ideal for high-acid foods and longer preservation, while bottling is preferred for liquids like juices and wines where clarity and flavor retention are crucial. Evaluating convenience, processing equipment, and intended use ensures selecting the best preservation method tailored to your needs.
canning vs bottling Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com