Hot-fill processes involve filling containers with liquid that has been heated to sterilize both the product and packaging, ensuring longer shelf life without preservatives. Cold-fill techniques rely on refrigeration or pasteurization after filling to maintain product freshness, ideal for heat-sensitive items like juices or dairy.
Table of Comparison
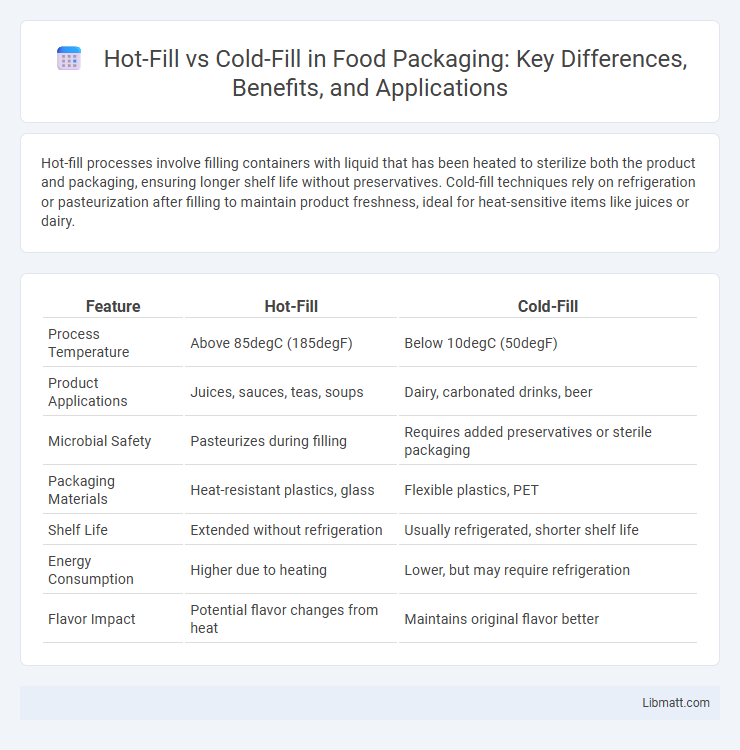
| Feature | Hot-Fill | Cold-Fill |
|---|---|---|
| Process Temperature | Above 85degC (185degF) | Below 10degC (50degF) |
| Product Applications | Juices, sauces, teas, soups | Dairy, carbonated drinks, beer |
| Microbial Safety | Pasteurizes during filling | Requires added preservatives or sterile packaging |
| Packaging Materials | Heat-resistant plastics, glass | Flexible plastics, PET |
| Shelf Life | Extended without refrigeration | Usually refrigerated, shorter shelf life |
| Energy Consumption | Higher due to heating | Lower, but may require refrigeration |
| Flavor Impact | Potential flavor changes from heat | Maintains original flavor better |
Introduction to Hot-Fill and Cold-Fill Processes
Hot-fill and cold-fill are two distinct packaging methods used in the beverage industry, where hot-fill involves filling containers with liquid heated above 85degC to ensure sterilization and extend shelf life, while cold-fill fills the beverage at ambient or refrigerated temperature, relying on preservatives or other sterilization methods. Hot-fill is ideal for acidic products like fruit juices and teas, as it eliminates microbial contamination through thermal processing, whereas cold-fill suits beverages sensitive to heat, such as carbonated drinks, maintaining flavor and carbonation. Understanding these processes helps you select the appropriate method based on product type, shelf stability, and packaging material compatibility.
How Hot-Fill Packaging Works
Hot-fill packaging involves heating the liquid product to approximately 85-95degC before filling, which sterilizes both the product and the container. This method eliminates the need for preservatives by killing bacteria and pathogens, ensuring extended shelf life. Your beverage or liquid is filled into heat-resistant containers while hot, then cooled to create a vacuum seal that maintains product freshness.
How Cold-Fill Packaging Works
Cold-fill packaging involves filling containers with products at refrigerated temperatures, typically between 35degF and 45degF (1.5degC to 7degC), to preserve freshness and extend shelf life. This method ensures minimal heat exposure, maintaining the product's taste, texture, and nutritional value while reducing energy consumption during packaging. Your product benefits from reduced microbial growth and less thermal degradation, making cold-fill ideal for beverages like juices, teas, and dairy-based drinks.
Key Differences Between Hot-Fill and Cold-Fill
Hot-fill uses elevated temperatures, typically above 185degF (85degC), to sterilize the product and container simultaneously, ensuring extended shelf life without preservatives. Cold-fill processes involve filling products at ambient or refrigerated temperatures, requiring pasteurization or preservatives to maintain safety and quality. Your selection depends on product type, packaging material, and desired shelf stability.
Advantages of Hot-Fill Technology
Hot-fill technology offers several advantages, including enhanced microbial safety by using high temperatures to sterilize both product and packaging, which extends shelf life without preservatives. This process improves product quality by preserving flavor and nutritional value through rapid heating and filling. Additionally, hot-fill packaging is highly effective for beverages such as juices and teas that require aseptic conditions, contributing to reduced contamination risks and longer storage periods.
Advantages of Cold-Fill Technology
Cold-fill technology offers significant advantages including improved product quality by preserving the freshness and nutritional content of beverages. Your packaging process benefits from reduced energy consumption compared to hot-fill, lowering operational costs and environmental impact. Additionally, cold-fill enables compatibility with a wider range of container types, enhancing packaging flexibility and shelf appeal.
Applications and Suitable Products for Each Method
Hot-fill techniques are ideal for packaging heat-stable products such as fruit juices, sauces, and soups that require pasteurization to ensure safety and extend shelf life. Cold-fill methods better suit beverages like carbonated drinks, dairy products, and sensitive juices that can degrade or lose carbonation when exposed to high temperatures. Understanding these applications enables you to choose the most effective filling process tailored to your product's composition and preservation needs.
Packaging Materials for Hot-Fill vs. Cold-Fill
Hot-fill packaging materials must withstand high temperatures typically between 85degC and 95degC, often involving heat-resistant glass or specially formulated polyethylene terephthalate (PET) with enhanced thermal stability. Cold-fill packaging, in contrast, uses standard PET, high-density polyethylene (HDPE), or glass that do not require thermal resistance since the contents are filled at ambient or refrigerated temperatures. Selecting appropriate materials ensures product safety, shelf-life stability, and prevents deformation or chemical leaching during the filling process.
Cost Considerations and Efficiency
Hot-fill processes often incur higher energy costs due to the need for heating liquids to sterilization temperatures, while cold-fill methods save on energy but may require additional preservatives or sterilization steps, impacting overall expenses. Equipment for hot-fill tends to be more specialized and costly, but it reduces cooling times and increases line throughput, enhancing production efficiency. Your choice between hot-fill and cold-fill should balance initial investment, operational costs, and desired production speed to optimize efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Choosing the Right Filling Method for Your Product
Choosing the right filling method depends on product type, packaging material, and shelf-life requirements, with hot-fill ideal for acidic beverages like juices and teas to ensure sterility and extended preservation. Cold-fill suits products sensitive to heat, such as dairy and some juices, preserving flavor and nutritional value while requiring refrigeration or pasteurization. Analyzing factors like pH level, container compatibility, and microbial stability helps optimize safety and quality in production processes.
hot-fill vs cold-fill Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com