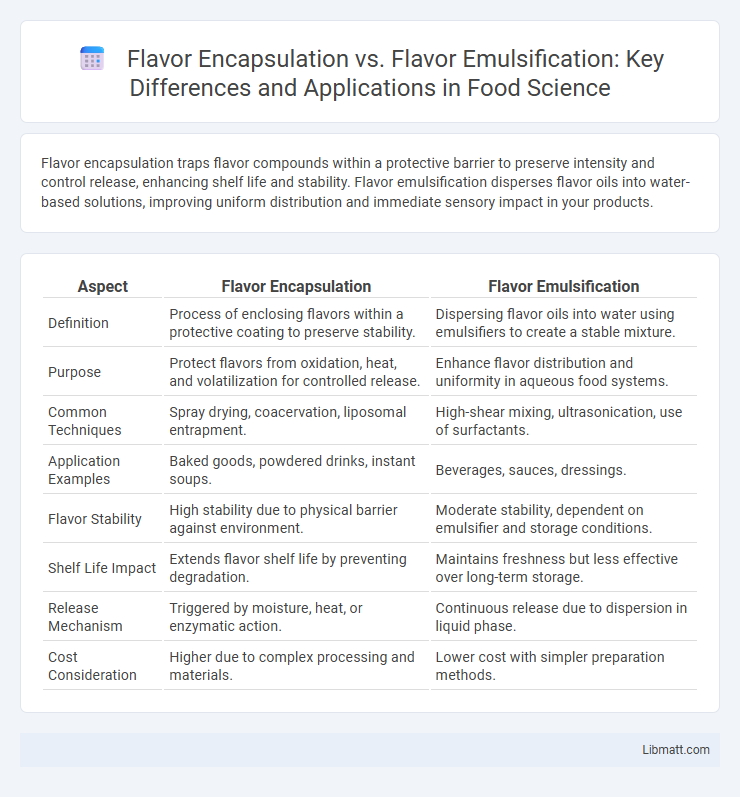
Flavor encapsulation traps flavor compounds within a protective barrier to preserve intensity and control release, enhancing shelf life and stability. Flavor emulsification disperses flavor oils into water-based solutions, improving uniform distribution and immediate sensory impact in your products.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Flavor Encapsulation | Flavor Emulsification |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of enclosing flavors within a protective coating to preserve stability. | Dispersing flavor oils into water using emulsifiers to create a stable mixture. |
| Purpose | Protect flavors from oxidation, heat, and volatilization for controlled release. | Enhance flavor distribution and uniformity in aqueous food systems. |
| Common Techniques | Spray drying, coacervation, liposomal entrapment. | High-shear mixing, ultrasonication, use of surfactants. |
| Application Examples | Baked goods, powdered drinks, instant soups. | Beverages, sauces, dressings. |
| Flavor Stability | High stability due to physical barrier against environment. | Moderate stability, dependent on emulsifier and storage conditions. |
| Shelf Life Impact | Extends flavor shelf life by preventing degradation. | Maintains freshness but less effective over long-term storage. |
| Release Mechanism | Triggered by moisture, heat, or enzymatic action. | Continuous release due to dispersion in liquid phase. |
| Cost Consideration | Higher due to complex processing and materials. | Lower cost with simpler preparation methods. |
Introduction to Flavor Encapsulation and Emulsification
Flavor encapsulation involves trapping flavor compounds in a protective coating, enhancing stability and controlled release during food processing and consumption. Flavor emulsification disperses flavor oils into fine droplets within a water-based medium, improving flavor distribution and sensory perception in beverages and sauces. Your choice between encapsulation and emulsification depends on the desired flavor longevity, release profile, and application in the final product.
Definition and Principles of Flavor Encapsulation
Flavor encapsulation is a method used to enclose flavor compounds within a protective coating to preserve their volatility and stability during processing and storage. This technique relies on principles such as microencapsulation, where tiny droplets or particles of flavor are trapped within a matrix material, preventing premature release and degradation. You benefit from enhanced flavor retention and controlled release by choosing encapsulation over emulsification, which disperses flavors in a continuous phase without the protective barrier.
Definition and Principles of Flavor Emulsification
Flavor emulsification involves the dispersion of flavor oils into a stable mixture with water or another aqueous phase, creating fine droplets that enhance flavor delivery and stability. This process relies on emulsifiers, such as lecithin or gum arabic, which reduce surface tension and prevent the separation of oil and water phases. Unlike flavor encapsulation, which traps flavors within a solid or gel matrix, emulsification focuses on forming a homogenous, liquid-based system to improve flavor distribution and sensory experience.
Key Differences Between Encapsulation and Emulsification
Flavor encapsulation involves trapping flavor compounds within a protective matrix to enhance stability and controlled release, while flavor emulsification disperses flavor oils into a stable mixture with water using emulsifiers. Encapsulation offers prolonged flavor retention and protection from oxidation, whereas emulsification ensures uniform flavor distribution in aqueous products. Understanding these key differences helps your formulation achieve desired sensory profiles and shelf life.
Technologies Used in Flavor Encapsulation
Flavor encapsulation employs advanced technologies such as spray drying, coacervation, liposome entrapment, and freeze-drying to protect and control the release of flavor compounds in food products. These methods enhance flavor stability by shielding volatile ingredients from oxidation, evaporation, and degradation during processing and storage. Encapsulation techniques enable targeted flavor delivery, improving product shelf life and consumer sensory experiences.
Techniques Used in Flavor Emulsification
Flavor emulsification techniques primarily involve high-shear mixing, ultrasonic emulsification, and membrane emulsification to create stable oil-in-water or water-in-oil emulsions, ensuring even flavor distribution. High-pressure homogenizers produce fine droplets that enhance flavor retention and release, while ultrasonic emulsification uses sound waves to break droplets into nanoscale sizes, improving stability and sensory impact. Membrane emulsification allows precise control over droplet size and uniformity, essential for consistent flavor intensity in food and beverage formulations.
Advantages of Encapsulation in Food Applications
Flavor encapsulation offers superior protection against oxidation, evaporation, and degradation, ensuring the preservation of aroma and taste during processing and storage. It enables targeted and controlled release of flavors, enhancing product consistency and consumer experience. Your food formulations benefit from extended shelf life and improved stability compared to flavor emulsification methods.
Benefits of Emulsification for Flavor Delivery
Flavor emulsification enhances the stability and uniformity of flavor compounds within food matrices, ensuring consistent taste throughout consumption. This method improves the solubility of hydrophobic flavor molecules in aqueous environments, resulting in prolonged flavor release and intensified sensory perception. Emulsification also protects sensitive flavor ingredients from degradation during processing and storage, extending shelf life and preserving product quality.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Method
Flavor encapsulation faces challenges such as limited release control and potential degradation of sensitive compounds during drying or storage, which can impact overall flavor stability. Flavor emulsification struggles with maintaining long-term stability due to phase separation and potential off-flavor development caused by oxidation or hydrolysis of emulsified oils. Your choice between these methods depends on balancing stability needs with processing conditions and desired flavor release profiles.
Future Trends in Flavor Delivery Systems
Future trends in flavor delivery systems emphasize the integration of advanced microencapsulation techniques and nanoemulsion technologies to enhance flavor stability and controlled release. Innovations in biodegradable and edible encapsulating materials are driving sustainability while maintaining flavor integrity in diverse food matrices. Continued research into stimuli-responsive emulsions aims to provide dynamically adjustable flavor release tailored to consumer preferences and processing conditions.
Flavor Encapsulation vs Flavor Emulsification Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com