Forward logistics in the food industry focuses on the efficient movement of products from manufacturers to consumers, ensuring freshness and timely delivery. Reverse logistics involves the management of food returns, recycling, and waste reduction to minimize environmental impact and enhance sustainability in your supply chain.
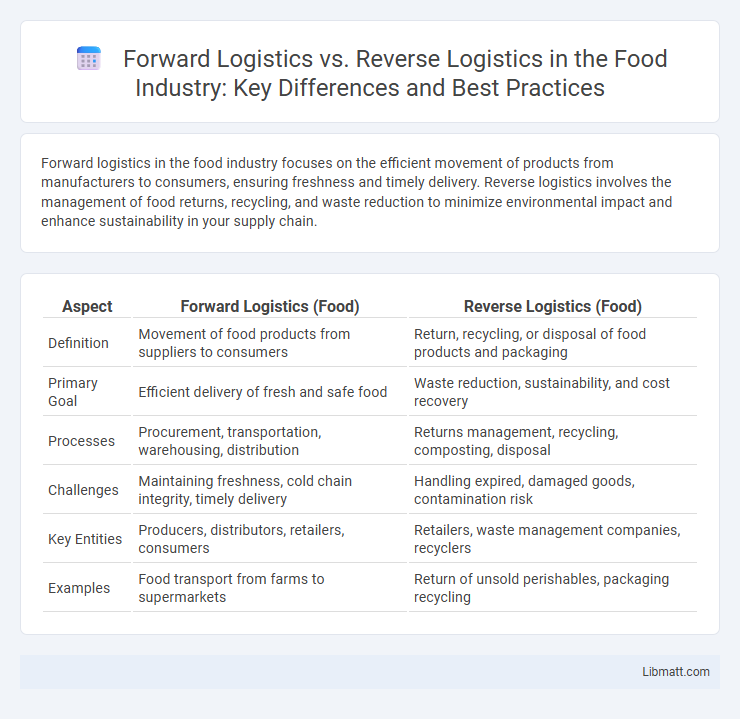
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Forward Logistics (Food) | Reverse Logistics (Food) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Movement of food products from suppliers to consumers | Return, recycling, or disposal of food products and packaging |
| Primary Goal | Efficient delivery of fresh and safe food | Waste reduction, sustainability, and cost recovery |
| Processes | Procurement, transportation, warehousing, distribution | Returns management, recycling, composting, disposal |
| Challenges | Maintaining freshness, cold chain integrity, timely delivery | Handling expired, damaged goods, contamination risk |
| Key Entities | Producers, distributors, retailers, consumers | Retailers, waste management companies, recyclers |
| Examples | Food transport from farms to supermarkets | Return of unsold perishables, packaging recycling |
Introduction to Forward and Reverse Logistics in the Food Industry
Forward logistics in the food industry involves the efficient movement of products from producers to consumers, ensuring freshness and safety throughout the supply chain. Reverse logistics focuses on managing returns, recycling, and waste reduction, helping companies minimize spoilage and environmental impact. Your ability to optimize both processes directly influences cost savings and sustainability outcomes in food distribution.
Key Differences Between Forward and Reverse Logistics
Forward logistics in the food industry involves the movement of products from suppliers to customers, emphasizing efficient distribution, quality maintenance, and timely delivery. Reverse logistics focuses on the return flow of food products, including returns, recycling, waste management, and handling expired or damaged goods to ensure sustainability and compliance with food safety regulations. Understanding these key differences helps optimize Your supply chain by balancing customer satisfaction with environmental responsibility.
The Importance of Forward Logistics in Food Supply Chains
Forward logistics in food supply chains ensures the efficient movement of perishable products from producers to consumers, maintaining freshness and safety through controlled transportation and storage. It involves critical processes such as inventory management, order fulfillment, and last-mile delivery, which directly impact product quality and customer satisfaction. Optimizing forward logistics reduces spoilage, minimizes costs, and strengthens supply chain reliability in the food industry.
Reverse Logistics: Managing Food Returns and Recalls
Reverse logistics in the food industry focuses on efficiently managing product returns and recalls to minimize waste, ensure safety, and comply with regulations. This process involves the collection, inspection, and proper disposal or reprocessing of returned food items to maintain quality and protect brand reputation. Optimizing your reverse logistics can reduce costs associated with food spoilage and enhance customer trust in your supply chain management.
Challenges Unique to Food Logistics
Food logistics faces unique challenges due to the perishable nature of products, requiring strict temperature control and timely delivery in both forward and reverse logistics. Forward logistics must ensure freshness and compliance with safety regulations, while reverse logistics involves efficient handling of expired or recalled items to minimize waste and health risks. Your supply chain must incorporate advanced tracking and rapid response systems to manage these complexities effectively.
Impact of Reverse Logistics on Food Waste Reduction
Reverse logistics in the food industry plays a critical role in reducing food waste by facilitating efficient return, recycling, and redistribution processes for unsold or expired products. Implementing robust reverse logistics systems enables companies to recover value from food items through donation, composting, or processing into alternative products, significantly lowering landfill contributions. This approach not only supports sustainability goals but also enhances supply chain efficiency and regulatory compliance related to food waste management.
Technology’s Role in Optimizing Food Logistics
Technology plays a crucial role in optimizing forward and reverse logistics within the food industry by enhancing traceability, inventory management, and demand forecasting. Advanced IoT sensors and blockchain systems ensure real-time monitoring of food quality and safety during transportation and returns, reducing spoilage and waste. Automated data analytics streamline reverse logistics processes such as returns, recycling, and disposal, promoting sustainability while minimizing operational costs.
Sustainability in Forward vs. Reverse Food Logistics
Sustainability in forward food logistics emphasizes reducing waste through efficient transportation, optimized storage, and minimizing carbon emissions from farm to consumer. Reverse food logistics enhances sustainability by managing food recalls, redistributing surplus food to reduce landfill waste, and facilitating recycling or composting of organic materials. Both systems contribute to a circular food supply chain, but reverse logistics plays a critical role in closing the loop and improving resource recovery for sustainable food management.
Best Practices for Efficient Food Logistics Operations
Optimizing food logistics operations requires distinct best practices for forward and reverse logistics to ensure freshness, safety, and sustainability. Forward logistics emphasizes streamlined supply chain coordination, temperature-controlled transportation, and real-time tracking to minimize spoilage and delivery delays. Reverse logistics focuses on effective handling of returns, food waste management, and compliance with health regulations, helping your business reduce losses and improve environmental impact.
Future Trends in Food Logistics Management
Future trends in food logistics management emphasize the integration of advanced technologies like IoT, AI, and blockchain to enhance traceability and efficiency in both forward and reverse logistics. Sustainable practices such as reducing food waste through reverse logistics and utilizing eco-friendly packaging are gaining momentum to meet consumer demand for environmentally responsible supply chains. Your logistics strategy will benefit from adaptive systems that optimize delivery routes, monitor product conditions in real-time, and facilitate seamless returns or recycling processes.
Forward Logistics vs Reverse Logistics (food) Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com