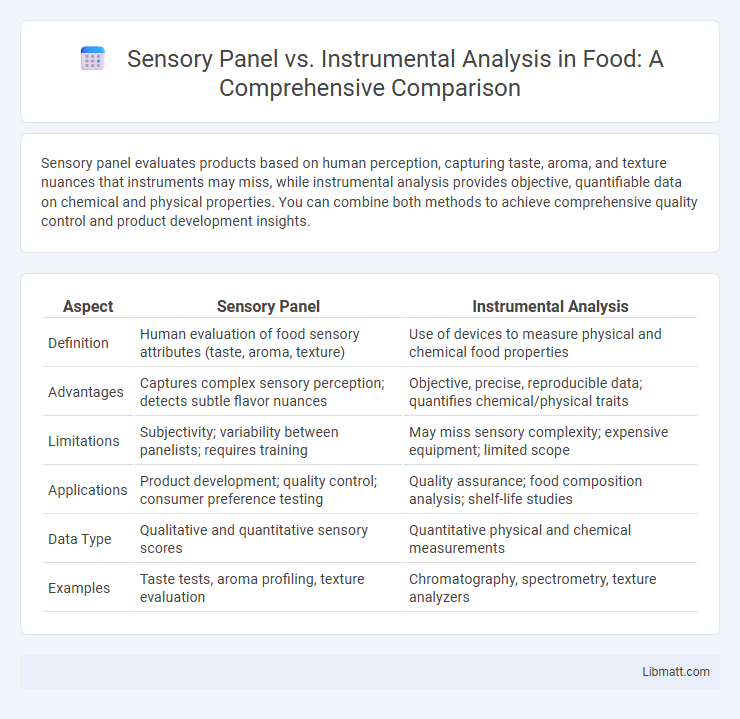
Sensory panel evaluates products based on human perception, capturing taste, aroma, and texture nuances that instruments may miss, while instrumental analysis provides objective, quantifiable data on chemical and physical properties. You can combine both methods to achieve comprehensive quality control and product development insights.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Sensory Panel | Instrumental Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Human evaluation of food sensory attributes (taste, aroma, texture) | Use of devices to measure physical and chemical food properties |
| Advantages | Captures complex sensory perception; detects subtle flavor nuances | Objective, precise, reproducible data; quantifies chemical/physical traits |
| Limitations | Subjectivity; variability between panelists; requires training | May miss sensory complexity; expensive equipment; limited scope |
| Applications | Product development; quality control; consumer preference testing | Quality assurance; food composition analysis; shelf-life studies |
| Data Type | Qualitative and quantitative sensory scores | Quantitative physical and chemical measurements |
| Examples | Taste tests, aroma profiling, texture evaluation | Chromatography, spectrometry, texture analyzers |
Introduction to Sensory Panel and Instrumental Analysis
Sensory panel testing involves trained human assessors who evaluate product attributes such as taste, aroma, texture, and appearance to capture complex sensory perceptions that instruments may not detect. Instrumental analysis uses precise scientific equipment to measure physical and chemical properties, providing objective and quantifiable data that supports product quality control and consistency. Combining sensory panel results with instrumental data enhances your understanding of product characteristics, ensuring more accurate and comprehensive quality assessments.
Defining Sensory Panel Evaluation
Sensory panel evaluation involves trained human assessors who use their senses to analyze and describe product attributes such as taste, aroma, texture, and appearance. Unlike instrumental analysis, which relies on machines for objective measurements of physical and chemical properties, sensory panels capture subjective human responses and preferences crucial for product development. Your insights and feedback through sensory panels provide vital information that instruments alone cannot fully replicate.
Understanding Instrumental Analysis Techniques
Instrumental analysis techniques use precise devices like gas chromatographs, spectrophotometers, and texture analyzers to quantify sensory attributes such as flavor compounds, color, and texture with objective data. These methods provide reproducible and consistent results that complement the subjective responses collected from a sensory panel. By integrating instrumental analysis with sensory evaluations, Your product development gains a comprehensive understanding of sensory quality and consumer perception.
Key Differences Between Sensory Panels and Instrumental Analysis
Sensory panels rely on human perception to evaluate product characteristics such as taste, aroma, texture, and appearance, capturing subjective qualities that instruments cannot detect. Instrumental analysis uses precise scientific tools to quantify physical and chemical attributes like composition, color, and viscosity, providing objective and reproducible data. The key difference lies in sensory panels assessing experiential factors through trained or consumer judges, while instrumental analysis focuses on measurable and consistent parameters for quality control and research.
Advantages of Sensory Panel Testing
Sensory panel testing offers advantages by capturing human perceptions of aroma, flavor, texture, and appearance that instrumental analysis cannot replicate. It provides nuanced insights into product acceptability and consumer preferences, directly reflecting real-world experiences. Your feedback from trained panelists ensures a comprehensive understanding of sensory qualities pivotal for product development and quality control.
Benefits of Instrumental Analysis Methods
Instrumental analysis methods provide precise, objective, and reproducible data critical for quality control and product development in food, pharmaceuticals, and materials science. Unlike sensory panels, these methods reduce human error and variability by using advanced devices such as spectrometers, chromatographs, and texture analyzers to measure chemical composition, texture, color, and flavor profiles accurately. This technological approach enables rapid, consistent analysis essential for compliance with regulatory standards and optimization of formulation processes.
Limitations of Sensory Panels
Sensory panels face limitations including variability in human perception, which leads to inconsistent data due to individual differences in taste, smell, and sensitivity. Fatigue and adaptation effects reduce accuracy over prolonged sessions, while training requirements and subjective bias impact reproducibility and reliability of results. Environmental factors and psychological influences further constrain the objectivity of sensory evaluations compared to instrumental analysis.
Drawbacks of Instrumental Analysis
Instrumental analysis often lacks the ability to fully capture the complexity of human sensory perception, missing nuances like aroma and mouthfeel that a sensory panel can detect. These methods may also be limited by high equipment costs, maintenance requirements, and the need for specialized operators, making them less accessible for some testing environments. Your product evaluations can miss critical quality attributes without integrating sensory panel feedback alongside instrumental data.
Applications in Food Quality Assessment
Sensory panel evaluation provides subjective insights into food quality by assessing taste, aroma, texture, and appearance using human senses, crucial for understanding consumer preferences. Instrumental analysis offers objective, quantifiable data through techniques like gas chromatography, spectrophotometry, and texture profiling to measure chemical composition and physical properties. Combining sensory panels with instrumental methods enhances accuracy in detecting quality variations, ensuring comprehensive assessment in food product development and quality control.
Choosing Between Sensory Panel and Instrumental Analysis
Choosing between sensory panel and instrumental analysis depends on the specific goals of quality assessment and product development. Sensory panels provide detailed human perception insights into aroma, flavor, and texture, essential for consumer preference studies, while instrumental analysis offers objective, reproducible data on chemical composition and physical properties. Combining both methods often yields the most comprehensive evaluation, balancing subjective experience with precise measurement.
sensory panel vs instrumental analysis Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com