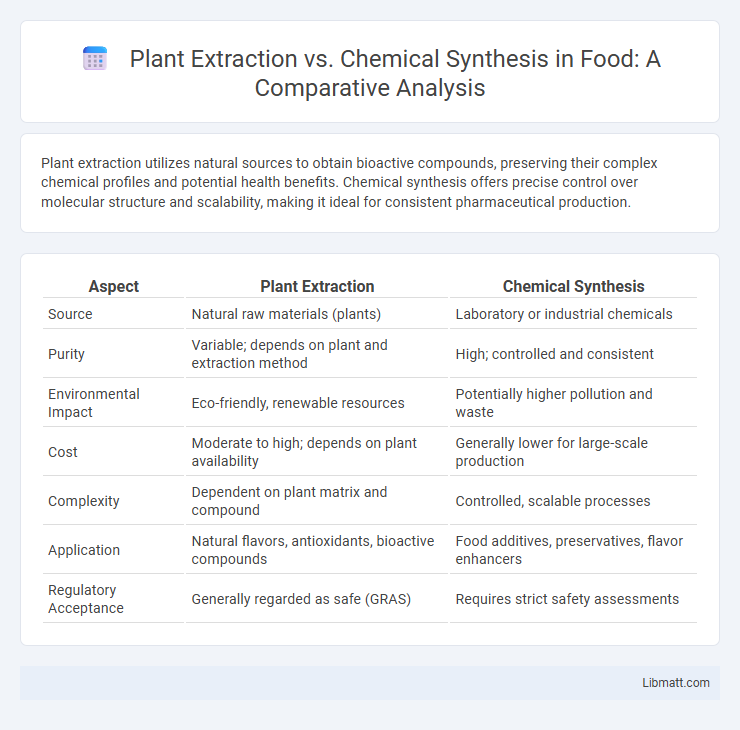
Plant extraction utilizes natural sources to obtain bioactive compounds, preserving their complex chemical profiles and potential health benefits. Chemical synthesis offers precise control over molecular structure and scalability, making it ideal for consistent pharmaceutical production.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Plant Extraction | Chemical Synthesis |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural raw materials (plants) | Laboratory or industrial chemicals |
| Purity | Variable; depends on plant and extraction method | High; controlled and consistent |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, renewable resources | Potentially higher pollution and waste |
| Cost | Moderate to high; depends on plant availability | Generally lower for large-scale production |
| Complexity | Dependent on plant matrix and compound | Controlled, scalable processes |
| Application | Natural flavors, antioxidants, bioactive compounds | Food additives, preservatives, flavor enhancers |
| Regulatory Acceptance | Generally regarded as safe (GRAS) | Requires strict safety assessments |
Introduction to Plant Extraction and Chemical Synthesis
Plant extraction involves isolating bioactive compounds directly from natural sources using solvents or mechanical methods, preserving complex phytochemical profiles crucial for pharmaceuticals and nutraceuticals. Chemical synthesis constructs molecules through controlled chemical reactions, enabling precise modification and large-scale production of compounds, often not readily available from plants. Both methods play essential roles in drug development, with plant extraction emphasizing natural diversity and chemical synthesis focusing on structural optimization.
Key Differences Between Plant Extraction and Chemical Synthesis
Plant extraction involves obtaining bioactive compounds directly from natural plant sources through physical or solvent-based methods, preserving complex molecular structures. Chemical synthesis, on the other hand, uses controlled laboratory reactions to create compounds from simpler substances, allowing for structural modifications and scalability. Key differences include the source origin, complexity of process, purity levels, and environmental impact, where plant extraction is eco-friendly but limited by plant availability, while chemical synthesis offers precision and mass production capabilities but may generate chemical waste.
Advantages of Plant Extraction Methods
Plant extraction methods offer a natural and sustainable approach to obtaining bioactive compounds, ensuring the preservation of complex phytochemicals that might be difficult to replicate synthetically. These methods often result in products with fewer harmful residues and environmental contaminants compared to chemical synthesis, enhancing purity and safety for your health. Moreover, plant extraction supports biodiversity and traditional knowledge, making it a valuable option in pharmaceutical and cosmetic industries.
Benefits of Chemical Synthesis Techniques
Chemical synthesis techniques offer precise control over molecular structure, enabling the production of consistent and high-purity compounds essential for pharmaceuticals and industrial applications. These methods allow for large-scale manufacturing with shorter production times compared to plant extraction, reducing costs and dependency on seasonal plant availability. Your ability to tailor chemical synthesis processes ensures scalable and sustainable production of complex molecules that might be difficult or impossible to extract naturally.
Environmental Impact: Natural vs Synthetic Approaches
Plant extraction methods generally have a lower environmental impact due to their reliance on renewable botanical resources and less energy-intensive processes. In contrast, chemical synthesis often involves petrochemical feedstocks, hazardous solvents, and high-energy consumption, contributing to pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. Sustainable plant extraction techniques combined with green chemistry principles offer a promising pathway to minimize ecological footprints while producing valuable bioactive compounds.
Quality and Purity of Extracted vs Synthesized Compounds
Plant extraction often yields compounds with complex mixtures, including beneficial secondary metabolites that enhance therapeutic effects but may reduce overall purity. Chemical synthesis provides high purity and consistency, enabling precise control over compound structure and concentration. However, synthetic compounds may lack the synergistic components found in natural plant extracts that contribute to efficacy.
Cost Comparison: Plant Extraction vs Chemical Synthesis
Plant extraction generally incurs higher costs due to lengthy cultivation periods, seasonal variability, and extensive processing required to isolate target compounds. Chemical synthesis often offers more cost-effective scalability with consistent yields and reduced dependency on natural resource availability. However, initial investments in synthetic pathways and raw materials can be significant, impacting the overall economic balance between the two methods.
Application Areas for Natural vs Synthetic Compounds
Natural compounds extracted from plants are widely applied in pharmaceuticals, nutraceuticals, cosmetics, and food industries due to their bioactive properties and biocompatibility. Synthetic compounds, produced via chemical synthesis, dominate in industrial chemicals, agricultural pesticides, and high-purity pharmaceutical intermediates because of their consistency and scalability. Your choice between plant extraction and chemical synthesis should consider the intended application area, balancing factors like efficacy, sustainability, and production cost.
Regulatory Considerations for Extraction and Synthesis
Regulatory considerations for plant extraction emphasize compliance with sustainable harvesting practices, purity standards, and documentation of natural source origin under agencies like the FDA or EMA. Chemical synthesis requires rigorous validation of synthetic pathways, impurity profiles, and adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure reproducibility and safety. Your regulatory strategy should balance these factors to meet legal requirements and facilitate product approval.
Future Trends in Plant Extraction and Chemical Synthesis
Emerging trends in plant extraction focus on eco-friendly techniques such as supercritical fluid extraction and microwave-assisted extraction, enhancing yield and preserving bioactive compounds. Chemical synthesis is moving towards green chemistry principles, utilizing renewable feedstocks and biocatalysts to reduce environmental impact and improve sustainability. Integration of machine learning and automation promises to accelerate both plant extraction optimization and synthetic pathway development, driving innovation in pharmaceuticals and natural product industries.
Plant Extraction vs Chemical Synthesis Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com