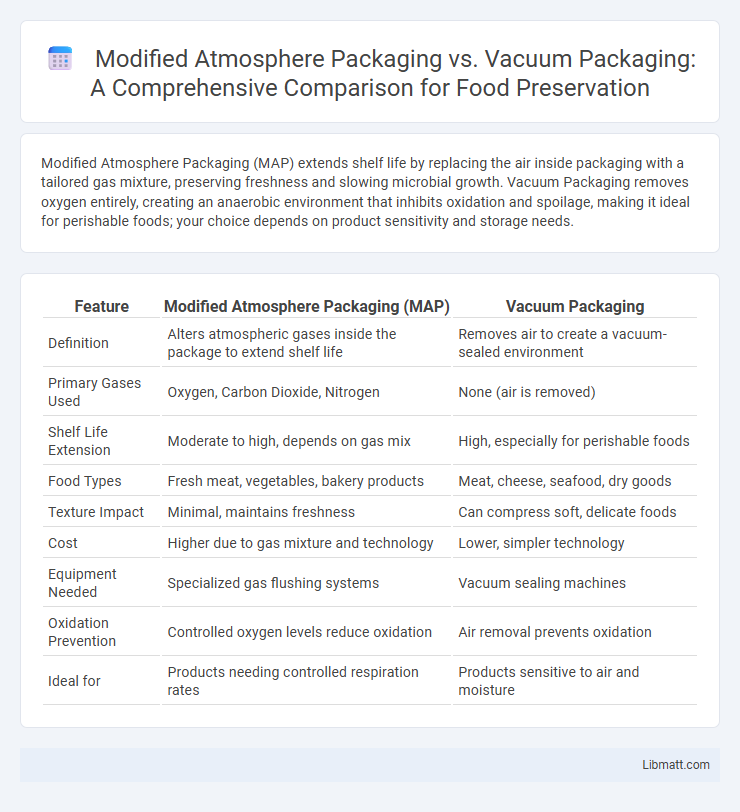
Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP) extends shelf life by replacing the air inside packaging with a tailored gas mixture, preserving freshness and slowing microbial growth. Vacuum Packaging removes oxygen entirely, creating an anaerobic environment that inhibits oxidation and spoilage, making it ideal for perishable foods; your choice depends on product sensitivity and storage needs.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP) | Vacuum Packaging |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Alters atmospheric gases inside the package to extend shelf life | Removes air to create a vacuum-sealed environment |
| Primary Gases Used | Oxygen, Carbon Dioxide, Nitrogen | None (air is removed) |
| Shelf Life Extension | Moderate to high, depends on gas mix | High, especially for perishable foods |
| Food Types | Fresh meat, vegetables, bakery products | Meat, cheese, seafood, dry goods |
| Texture Impact | Minimal, maintains freshness | Can compress soft, delicate foods |
| Cost | Higher due to gas mixture and technology | Lower, simpler technology |
| Equipment Needed | Specialized gas flushing systems | Vacuum sealing machines |
| Oxidation Prevention | Controlled oxygen levels reduce oxidation | Air removal prevents oxidation |
| Ideal for | Products needing controlled respiration rates | Products sensitive to air and moisture |
Introduction to Modified Atmosphere Packaging and Vacuum Packaging
Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP) involves altering the internal gas composition of packaging to extend the shelf life of perishable foods by slowing microbial growth and oxidation. Vacuum Packaging removes air from the package before sealing, significantly reducing oxygen and inhibiting aerobic bacteria and mold proliferation. Both methods are widely used in food preservation to maintain freshness, texture, and flavor while preventing spoilage.
How Modified Atmosphere Packaging Works
Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP) works by altering the composition of gases within the package to extend the shelf life of perishable foods. Typically, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and nitrogen levels are adjusted to slow microbial growth and oxidative spoilage, thereby preserving freshness and quality. This method is widely used for fresh meats, produce, and bakery products to maintain texture, color, and taste during storage and transportation.
How Vacuum Packaging Works
Vacuum packaging works by removing air from the package before sealing, which significantly slows down the growth of aerobic bacteria and mold, thereby extending the shelf life of perishable foods. This method creates an oxygen-free environment that preserves freshness, flavor, and nutritional value by minimizing oxidation and moisture loss. Your food stays protected from contamination and spoilage, making vacuum packaging ideal for meats, cheeses, and other sensitive products.
Key Differences Between MAP and Vacuum Packaging
Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP) replaces the air inside the package with a specific gas mixture tailored to extend the shelf life of perishable foods, whereas Vacuum Packaging removes all air to create a tight seal around the product. MAP is ideal for products like fresh produce and meats that require controlled oxygen and carbon dioxide levels, while Vacuum Packaging is better suited for items sensitive to oxidation and microbial growth. Your choice between MAP and Vacuum Packaging depends on the food type and desired shelf life, optimizing freshness and quality preservation.
Advantages of Modified Atmosphere Packaging
Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP) extends the shelf life of perishable foods by altering the gas composition surrounding the product, typically reducing oxygen levels and increasing carbon dioxide or nitrogen to inhibit microbial growth and oxidative damage. This technology preserves freshness, color, and texture more effectively than Vacuum Packaging, which compresses the product and removes air but can sometimes cause texture deformation. MAP is widely used for fresh meat, seafood, and produce, offering better visual appeal and longer marketability, supporting supply chain efficiency and reducing food waste.
Benefits of Vacuum Packaging
Vacuum packaging removes air from the package to extend shelf life by slowing oxidation and inhibiting aerobic bacteria growth, preserving freshness and flavor more effectively than Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP). It reduces freezer burn and moisture loss, making it ideal for meat, cheese, and delicate food items. Your food stays safer and more nutrient-rich with vacuum packaging due to its airtight seal and prevention of contamination.
Food Types Best Suited for MAP
Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP) is ideal for fresh produce, meats, and baked goods due to its ability to extend shelf life by altering gas composition around the product. MAP maintains oxygen, carbon dioxide, and nitrogen levels tailored to slow microbial growth and oxidation in fruits, vegetables, poultry, and seafood. This packaging method preserves texture and freshness in delicate food items that are sensitive to vacuum compression, making it preferable over vacuum packaging for breathable and aerobic products.
Products Ideal for Vacuum Packaging
Vacuum packaging is ideal for products like fresh meats, seafood, cheese, and coffee, where oxygen removal is crucial to prevent spoilage and extend shelf life. This method is highly effective for preserving the texture, flavor, and nutritional quality of perishable items by reducing oxidation and microbial growth. Foods with high moisture content benefit significantly from vacuum packaging, maintaining freshness longer compared to Modified Atmosphere Packaging.
Cost and Equipment Considerations
Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP) typically incurs higher initial equipment costs due to specialized gas flushing systems and precise atmosphere control technology, whereas Vacuum Packaging requires simpler, often less expensive machinery focused on air removal. Operating expenses for MAP may be elevated because of ongoing gas supply costs, while Vacuum Packaging mainly involves maintenance of vacuum pumps and sealing components. Cost-effectiveness depends on product type, shelf-life requirements, and production scale, with Vacuum Packaging favored for lower-volume or cost-sensitive operations and MAP preferred for preserving delicate or highly perishable items.
Choosing the Right Packaging Solution for Your Needs
Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP) extends shelf life by adjusting gas compositions inside the package, preserving freshness and color, while Vacuum Packaging removes air to inhibit microbial growth and oxidation. Your choice depends on product type, desired shelf life, and preservation goals; MAP suits fresh produce and meats needing controlled atmospheres, whereas Vacuum Packaging is ideal for airtight sealing of dry or cooked foods. Evaluate factors such as product sensitivity, storage conditions, and cost-effectiveness to determine the most efficient packaging solution for your needs.
Modified Atmosphere Packaging vs Vacuum Packaging Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com