Natural flavor comes from real ingredients extracted from plants or animals, while artificial flavor is chemically synthesized to mimic the taste of natural substances. Your choice between natural and artificial flavors can impact the quality, healthiness, and taste of the food you consume.
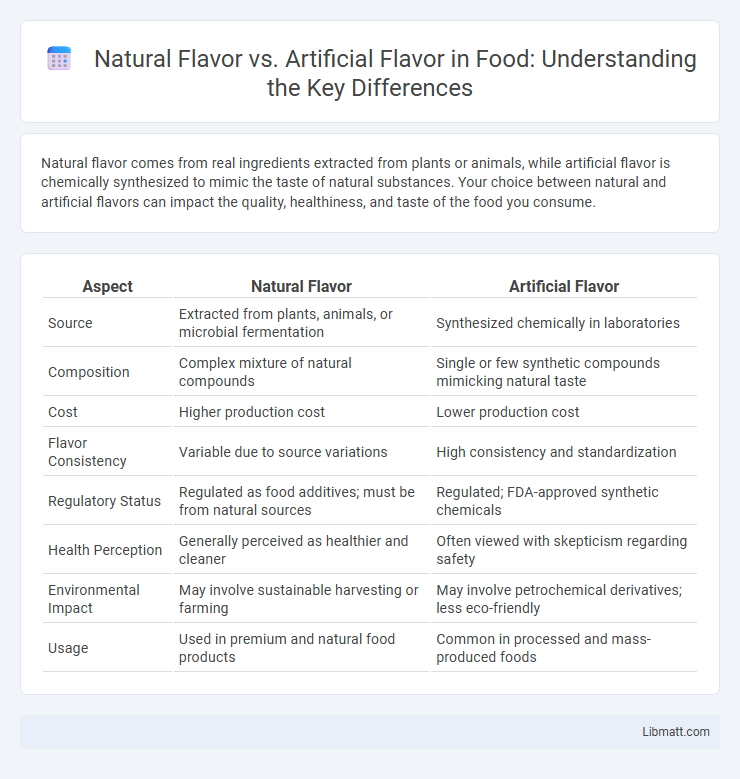
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Natural Flavor | Artificial Flavor |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Extracted from plants, animals, or microbial fermentation | Synthesized chemically in laboratories |
| Composition | Complex mixture of natural compounds | Single or few synthetic compounds mimicking natural taste |
| Cost | Higher production cost | Lower production cost |
| Flavor Consistency | Variable due to source variations | High consistency and standardization |
| Regulatory Status | Regulated as food additives; must be from natural sources | Regulated; FDA-approved synthetic chemicals |
| Health Perception | Generally perceived as healthier and cleaner | Often viewed with skepticism regarding safety |
| Environmental Impact | May involve sustainable harvesting or farming | May involve petrochemical derivatives; less eco-friendly |
| Usage | Used in premium and natural food products | Common in processed and mass-produced foods |
Understanding Natural vs Artificial Flavors
Natural flavors are derived from real food sources such as fruits, vegetables, or spices, using physical, enzymatic, or microbiological processes to extract their essence. Artificial flavors are chemically synthesized compounds designed to mimic natural flavor profiles, often providing more consistency and cost-effectiveness in food production. Understanding the key differences helps you make informed choices based on ingredient quality, taste preferences, and dietary considerations.
How Flavors Are Created
Natural flavors are extracted from plant or animal sources through processes such as distillation, solvent extraction, or fermentation, preserving key aromatic compounds. Artificial flavors are synthesized chemically to mimic natural flavor profiles using compounds like esters, aldehydes, and ketones. Both types focus on replicating specific taste sensations, but natural flavors rely on organic raw materials, whereas artificial flavors use lab-generated molecules.
Ingredient Sources: Natural and Synthetic Origins
Natural flavors originate from plant or animal sources through extraction, distillation, or fermentation, preserving authentic taste profiles derived from fruits, herbs, spices, or other botanical and animal materials. Artificial flavors are synthetically produced using chemical compounds designed to mimic natural taste, often created from petrochemicals or laboratory-synthesized ingredients. The key distinction lies in the source and processing method, where natural flavors are directly sourced from nature, while artificial flavors are the result of chemical synthesis.
Health Impacts of Natural and Artificial Flavors
Natural flavors are derived from plant or animal sources and generally contain fewer synthetic chemicals, potentially reducing exposure to harmful additives and allergens. Artificial flavors, synthesized from chemical compounds, may pose risks such as allergies or sensitivities and sometimes contain additives linked to negative health effects. Both natural and artificial flavors undergo regulatory evaluation, but natural flavors are often perceived as safer due to their origin, although comprehensive clinical studies on long-term health impacts are limited.
Regulatory Differences Between Natural and Artificial Flavors
Regulatory differences between natural and artificial flavors are primarily defined by agencies like the FDA, which requires natural flavors to be derived from plant or animal sources without synthetic processing. Artificial flavors are chemically synthesized and must be explicitly labeled as such, ensuring transparency for consumers. Understanding these distinctions helps you make informed choices about the flavors in your food products.
Consumer Perceptions and Preferences
Consumers often perceive natural flavors as healthier and safer compared to artificial flavors, associating them with cleaner labels and fewer synthetic chemicals. Preference trends reveal a growing demand for products labeled "natural," driven by increased awareness of ingredient origins and potential health impacts. Market studies indicate that these perceptions influence purchasing decisions, with a significant segment willing to pay premium prices for natural flavor options.
Flavor Labeling: What You Need to Know
Flavor labeling on food products indicates whether the taste comes from natural flavorings derived from plant or animal sources or from artificial flavorings created through chemical synthesis. Understanding these labels helps you make informed choices based on ingredient transparency, dietary restrictions, or preferences for clean eating. Natural flavors come from substances extracted directly from natural sources, while artificial flavors replicate the taste using synthetic compounds.
Environmental Impacts of Flavor Production
Natural flavor production relies heavily on agricultural resources, leading to considerable land and water use, and potentially contributing to deforestation and biodiversity loss. Artificial flavor manufacturing, often derived from petrochemicals, involves energy-intensive chemical synthesis processes that can generate hazardous waste and greenhouse gas emissions. Understanding these environmental impacts helps you make informed choices that support sustainable flavor sourcing.
Cost Differences in Production and Pricing
Natural flavors typically incur higher production costs due to the complex extraction processes from real plant or animal sources, resulting in a more expensive end product. Artificial flavors are synthesized from chemical compounds, allowing for lower manufacturing costs and cheaper pricing. Your choice between natural and artificial flavors will influence product cost, with natural options usually commanding a premium in the market.
Future Trends in the Flavor Industry
The flavor industry is rapidly advancing towards sustainable and clean-label solutions, with natural flavors gaining significant traction due to consumer demand for transparency and health-conscious products. Innovations in biotechnology and fermentation processes are enabling the creation of natural flavors that mimic complex profiles traditionally achieved by artificial means. Your choice between natural and artificial flavor options will increasingly depend on emerging regulatory standards and evolving market preferences prioritizing environmental impact and ingredient traceability.
natural flavor vs artificial flavor Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com