Seaming joins two materials together, creating a continuous connection essential for structural integrity, while sealing focuses on preventing leaks by filling gaps and protecting against moisture, air, or contaminants. Your choice between seaming and sealing depends on whether the priority is strength and durability or airtightness and impermeability.
Table of Comparison
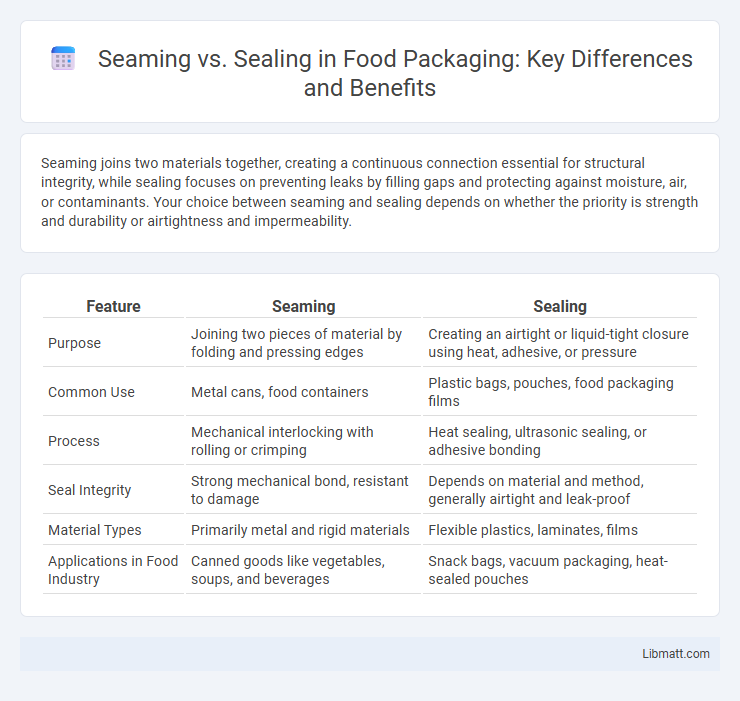
| Feature | Seaming | Sealing |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Joining two pieces of material by folding and pressing edges | Creating an airtight or liquid-tight closure using heat, adhesive, or pressure |
| Common Use | Metal cans, food containers | Plastic bags, pouches, food packaging films |
| Process | Mechanical interlocking with rolling or crimping | Heat sealing, ultrasonic sealing, or adhesive bonding |
| Seal Integrity | Strong mechanical bond, resistant to damage | Depends on material and method, generally airtight and leak-proof |
| Material Types | Primarily metal and rigid materials | Flexible plastics, laminates, films |
| Applications in Food Industry | Canned goods like vegetables, soups, and beverages | Snack bags, vacuum packaging, heat-sealed pouches |
Introduction to Seaming and Sealing
Seaming and sealing are essential techniques in manufacturing and packaging, ensuring product integrity and durability. Seaming refers to the process of joining two or more materials by folding, stitching, or welding, creating a physical bond. Sealing involves closing or securing an opening to prevent leakage, contamination, or environmental damage, often achieved using adhesives, heat, or pressure.
Definitions: What is Seaming?
Seaming is the process of joining two or more pieces of fabric, metal, or other materials along a line by sewing, welding, or fastening to create a continuous piece. It is commonly used in manufacturing industries such as textiles, roofing, and metalworking to ensure structural integrity and durability. Your choice of seaming method impacts the strength and flexibility of the final product, making it essential to select the appropriate technique for the material and application.
Definitions: What is Sealing?
Sealing is the process of applying a protective barrier to prevent the passage of air, water, or contaminants through gaps or joints in materials, ensuring durability and efficiency. This technique is commonly used in construction, automotive, and packaging industries to maintain structural integrity and enhance energy conservation. Your choice of sealing materials and methods directly impacts the performance and longevity of the sealed surface.
Key Differences Between Seaming and Sealing
Seaming involves joining two or more pieces of material together with stitches, adhesives, or mechanical fasteners to create a continuous surface, commonly used in fabric, metal, or plastic applications. Sealing refers to applying a substance or method to close gaps, preventing the passage of fluids, air, or contaminants, ensuring protection and durability. Understanding these key differences helps you choose the right technique for structural integrity or environmental protection in your projects.
Types of Seaming Techniques
Seaming techniques include heat sealing, ultrasonic seaming, and double seaming, each designed for specific materials and applications. Heat sealing uses thermal energy to fuse materials, commonly applied in packaging and textiles, while ultrasonic seaming employs high-frequency vibrations to bond synthetic fabrics without thread. Double seaming involves mechanically folding and compressing metal or plastic layers for airtight closures, ideal for cans and containers.
Types of Sealing Methods
Sealing methods include adhesive sealing, solvent sealing, heat sealing, and mechanical sealing, each chosen based on material compatibility and application requirements. Adhesive sealing uses bonding agents for flexible and strong seals, while solvent sealing relies on chemical solvents to soften surfaces and create a fusion. Heat sealing melts thermoplastic materials to form airtight seals, and mechanical sealing employs physical force or components such as gaskets and O-rings to prevent leaks.
Applications of Seaming in Various Industries
Seaming is widely utilized in industries such as automotive, apparel, and packaging to join materials securely and efficiently. In automotive manufacturing, seaming ensures the structural integrity of metal panels, while in apparel, it provides both durability and aesthetic appeal to garments. Your products benefit from precise seaming techniques that enhance performance, longevity, and overall quality across these diverse applications.
Applications of Sealing in Different Fields
Sealing is vital across various industries, including automotive manufacturing where it prevents fluid leaks and enhances vehicle durability, and in electronics for protecting components from dust and moisture intrusion. In construction, sealing is used to ensure airtight and watertight building envelopes, improving energy efficiency and structural integrity. The food packaging sector relies on sealing technology to extend shelf life by preventing contamination and preserving product freshness.
Advantages and Disadvantages: Seaming vs Sealing
Seaming offers strong mechanical strength and durability, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications but can be labor-intensive and less flexible. Sealing provides excellent protection against moisture and air infiltration with easier application, yet it may lack the structural integrity offered by seaming. Your choice depends on the balance between durability requirements and environmental resistance for optimal performance.
Choosing the Right Method: Seaming or Sealing?
Choosing between seaming and sealing depends on your project's material type and the required durability. Seaming involves joining materials edge-to-edge through stitching or welding, providing strong mechanical bonds ideal for fabrics and roofing membranes. Sealing, using adhesives or tapes, creates waterproof and airtight barriers suited for preventing leaks in containers and enclosures.
Seaming vs Sealing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com