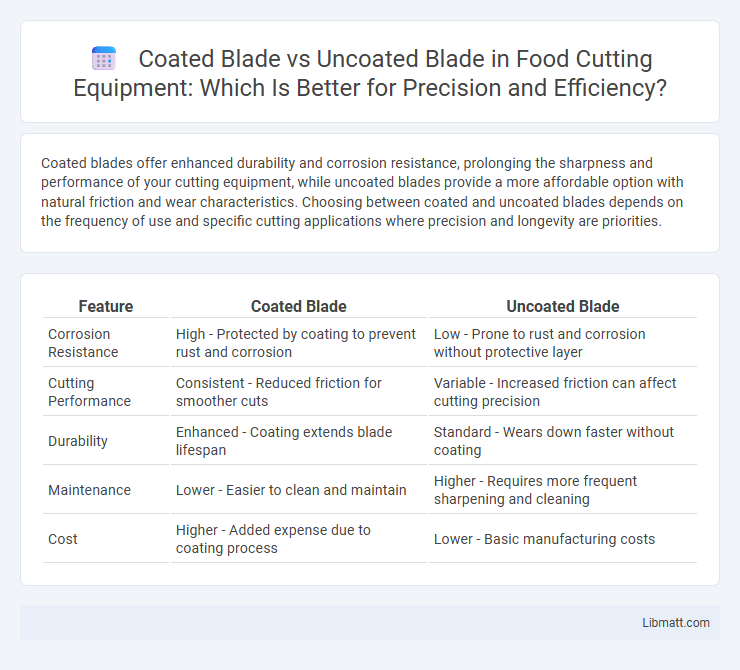
Coated blades offer enhanced durability and corrosion resistance, prolonging the sharpness and performance of your cutting equipment, while uncoated blades provide a more affordable option with natural friction and wear characteristics. Choosing between coated and uncoated blades depends on the frequency of use and specific cutting applications where precision and longevity are priorities.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Coated Blade | Uncoated Blade |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | High - Protected by coating to prevent rust and corrosion | Low - Prone to rust and corrosion without protective layer |
| Cutting Performance | Consistent - Reduced friction for smoother cuts | Variable - Increased friction can affect cutting precision |
| Durability | Enhanced - Coating extends blade lifespan | Standard - Wears down faster without coating |
| Maintenance | Lower - Easier to clean and maintain | Higher - Requires more frequent sharpening and cleaning |
| Cost | Higher - Added expense due to coating process | Lower - Basic manufacturing costs |
Introduction to Coated vs Uncoated Blades
Coated blades feature a thin layer of material such as titanium, chromium, or diamond-like carbon that enhances durability, reduces friction, and improves corrosion resistance compared to uncoated blades. Uncoated blades rely solely on the base metal, often resulting in faster wear and the need for more frequent replacements in demanding cutting applications. Choosing the right blade depends on your cutting requirements, with coated blades offering extended tool life and better performance for high-precision or abrasive materials.
Key Differences Between Coated and Uncoated Blades
Coated blades feature a thin layer of materials such as titanium nitride or diamond-like carbon, enhancing durability, reducing friction, and improving corrosion resistance compared to uncoated blades. Uncoated blades generally offer sharper initial cutting edges but may dull faster and require more frequent maintenance. Choosing a coated blade can extend the lifespan and maintain cutting performance, benefiting your productivity in demanding applications.
Material Composition and Manufacturing
Coated blades in cutting equipment typically feature a base metal, such as high-carbon steel or stainless steel, enhanced with a thin layer of materials like titanium nitride or diamond-like carbon to increase hardness and reduce friction. Uncoated blades consist solely of the base metal, relying on the raw material's intrinsic properties for durability and sharpness. Your choice between coated and uncoated blades should consider how the manufacturing process and material composition affect performance, wear resistance, and maintenance frequency.
Performance and Efficiency Comparison
Coated blades offer enhanced cutting performance by reducing friction, increasing durability, and maintaining sharpness longer than uncoated blades, which often dull more quickly and require frequent replacements. The coating materials, such as titanium nitride or diamond-like carbon, improve efficiency by enabling smoother cuts, reducing heat buildup, and minimizing material adhesion. Uncoated blades may perform adequately for basic tasks but generally lack the longevity and cutting precision that coated blades provide in demanding industrial applications.
Durability and Lifespan Analysis
Coated blades in cutting equipment typically exhibit enhanced durability due to protective layers such as titanium nitride, which reduce friction and resistance to wear. This coating extends the blade's lifespan by minimizing corrosion and maintaining sharpness longer compared to uncoated blades. Uncoated blades, while often more cost-effective initially, experience faster dulling and require more frequent replacement under heavy or abrasive cutting conditions.
Cost Implications and Budget Considerations
Coated blades typically carry a higher upfront cost due to advanced materials and protective layers, which enhance durability and reduce blade replacement frequency. Uncoated blades are more budget-friendly initially but may lead to increased expenses over time because of faster wear and more frequent replacements. Assessing your cutting workload and maintenance budget can help you determine if the initial investment in coated blades aligns with your long-term cost-efficiency goals.
Applications and Industry Suitability
Coated blades offer enhanced wear resistance and reduced friction, making them ideal for high-precision cutting in industries such as aerospace, electronics, and automotive manufacturing. Uncoated blades are preferred for general-purpose cutting tasks where cost efficiency and material versatility are prioritized, like in woodworking, packaging, and textile production. Selecting between coated and uncoated blades depends on factors like cutting speed, material hardness, and desired blade longevity specific to industry applications.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Coated blades in cutting equipment require less frequent sharpening and resist corrosion, reducing overall maintenance time and effort. Uncoated blades typically demand regular sharpening and cleaning to prevent rust and maintain cutting performance. Proper care for coated blades extends their lifespan by protecting the cutting edge from wear, while uncoated blades need consistent upkeep to avoid premature dulling and degradation.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Coated blades typically have a longer lifespan due to enhanced durability, reducing the frequency of replacement and minimizing waste compared to uncoated blades. Uncoated blades, though often cheaper initially, may require more frequent disposal, increasing environmental impact through higher resource consumption and landfill contribution. Choosing a high-quality coated blade aligns with sustainable practices by lowering overall material usage and supporting waste reduction initiatives in your cutting operations.
Choosing the Right Blade for Your Needs
Choosing between coated and uncoated blades depends on the material and cutting frequency; coated blades offer enhanced durability and corrosion resistance for heavy-duty or abrasive materials, extending blade life. Uncoated blades provide sharper initial cuts and are cost-effective for softer materials or occasional use. Evaluating cutting speed, precision requirements, and maintenance frequency ensures selection of the optimal blade for efficiency and performance.
coated blade vs uncoated blade (in cutting equipment) Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com