Single packing offers convenience by packaging each item individually, making it easy for you to use or distribute one unit at a time. Multi-packaging combines multiple units into a single package, reducing overall packaging waste and often providing cost savings for bulk purchases.
Table of Comparison
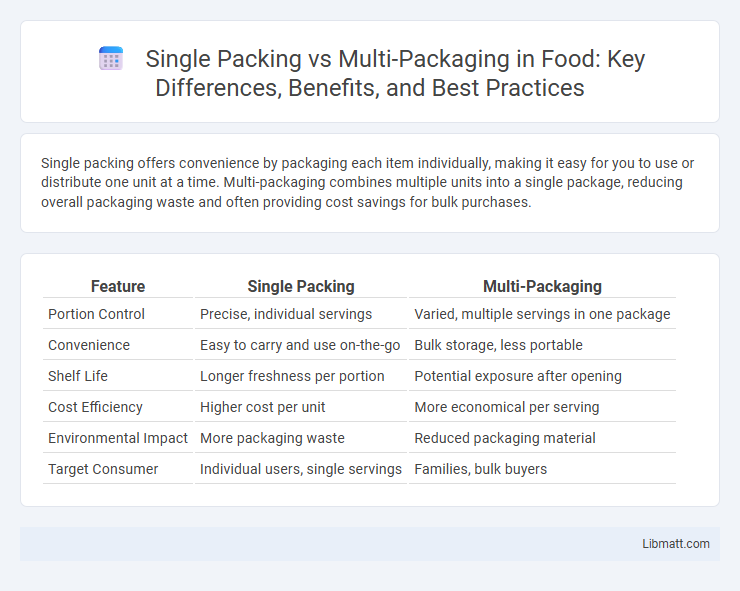
| Feature | Single Packing | Multi-Packaging |
|---|---|---|
| Portion Control | Precise, individual servings | Varied, multiple servings in one package |
| Convenience | Easy to carry and use on-the-go | Bulk storage, less portable |
| Shelf Life | Longer freshness per portion | Potential exposure after opening |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher cost per unit | More economical per serving |
| Environmental Impact | More packaging waste | Reduced packaging material |
| Target Consumer | Individual users, single servings | Families, bulk buyers |
Introduction to Single Packing and Multi-Packaging
Single packing involves packaging individual products separately, which enhances convenience, freshness, and easy distribution, especially for smaller quantities. Multi-packaging groups multiple single units into one larger package, optimizing shipping efficiency, reducing packaging waste, and promoting bulk purchasing benefits. Understanding these packaging methods helps you select the best option for your product handling and consumer needs.
Key Differences Between Single Packing and Multi-Packaging
Single packing involves packaging individual items separately, ensuring product protection and ease of handling, while multi-packaging groups several single units together for bulk sale or promotional purposes, enhancing convenience and value for customers. The choice between single packing and multi-packaging impacts inventory management, shipping efficiency, and consumer perception, with multi-packaging often reducing packaging waste and costs. Your decision should consider product type, target market, and sustainability goals to optimize packaging strategy effectively.
Pros and Cons of Single Packing
Single packing offers convenience and ease of use, allowing consumers to purchase precise quantities without waste, which enhances product freshness and reduces storage space. This packaging method often results in higher per-unit costs and increased environmental impact due to more packaging materials per item. However, single packing provides better portion control and simplifies inventory management for both retailers and consumers.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Multi-Packaging
Multi-packaging offers advantages such as cost savings through bulk purchasing, improved convenience for consumers, and reduced environmental impact due to less individual packaging waste. However, disadvantages include potential difficulties in storage, higher initial purchase costs, and increased risk of product spoilage or damage if one item within the pack deteriorates. Retailers may also face challenges in inventory management and shelf space allocation when dealing with multi-packaged goods.
Environmental Impact: Single vs Multi-Packaging
Single packaging generates more waste material per unit due to individual wrapping, leading to increased landfill contributions and higher resource consumption. Multi-packaging consolidates multiple items, reducing overall packaging material, transportation emissions, and carbon footprint. Efficient multi-pack solutions promote sustainability by minimizing plastic use and optimizing logistics for lower environmental impact.
Cost Comparison: Which is More Economical?
Single packing often incurs higher per-unit costs due to individual packaging materials and labor, making it less economical for large-scale distribution. Multi-packaging reduces overall expenses by sharing packaging resources across multiple units, optimizing shipping efficiency, and minimizing waste. Your choice should factor in order volume and storage considerations to determine which method delivers the best cost efficiency.
Consumer Preferences and Market Trends
Consumer preferences increasingly favor multi-packaging for its convenience, cost savings, and reduced environmental footprint, driving market trends toward bulk purchases and sustainable packaging solutions. Single packing remains popular for on-the-go consumption and portion control, appealing to consumers seeking freshness and ease of use. Market trends reveal a growing demand for eco-friendly materials in both packaging types, with brands innovating to balance consumer convenience and sustainability goals.
Suitability for Different Product Types
Single packing is ideal for perishable or high-value items that require individual protection and easy handling, while multi-packaging suits bulk or complementary products that benefit from combined storage and transport efficiency. Your choice hinges on the product's size, fragility, and consumer convenience preferences, as multi-packs excel in reducing material waste and boosting shelf presence for smaller items. Different product types demand distinct packaging strategies to optimize protection, cost-effectiveness, and customer appeal.
Packaging Efficiency and Convenience
Single packing offers higher packaging efficiency by minimizing material use and reducing waste per unit, making it ideal for products requiring individual handling. Multi-packaging enhances convenience for consumers by bundling multiple units, simplifying storage and transportation while often reducing overall packaging costs. Your choice depends on balancing the need for efficient resource use and the added convenience valued by your target market.
Choosing the Right Packaging Solution
Choosing the right packaging solution depends on factors like product type, shelf life, and consumer convenience. Single packing offers freshness and portion control, ideal for individual use or high-value items, while multi-packaging reduces costs and waste, catering to bulk buyers or families. Assess your product goals and target market to optimize Your packaging strategy for efficiency and sustainability.
single packing vs multi-packaging Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com