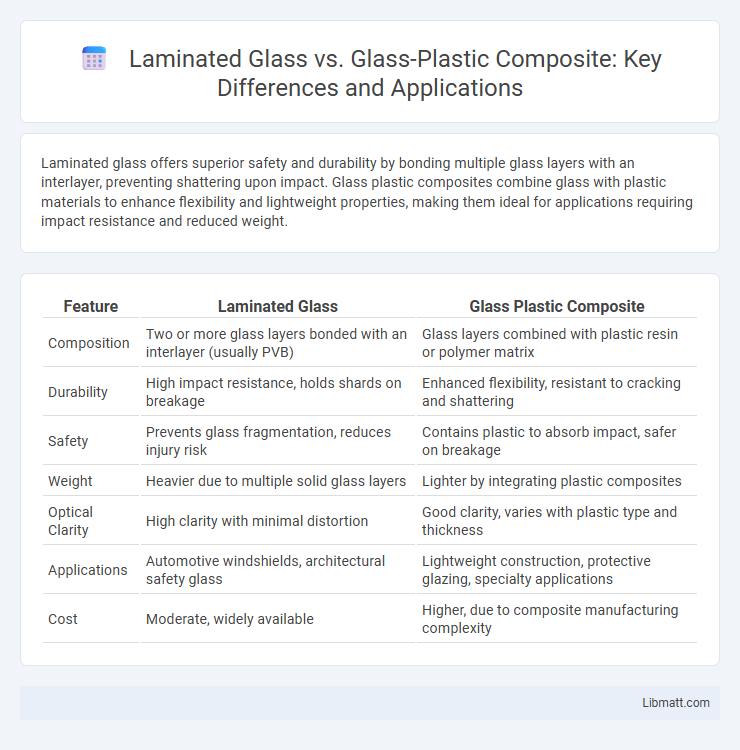
Laminated glass offers superior safety and durability by bonding multiple glass layers with an interlayer, preventing shattering upon impact. Glass plastic composites combine glass with plastic materials to enhance flexibility and lightweight properties, making them ideal for applications requiring impact resistance and reduced weight.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Laminated Glass | Glass Plastic Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Two or more glass layers bonded with an interlayer (usually PVB) | Glass layers combined with plastic resin or polymer matrix |
| Durability | High impact resistance, holds shards on breakage | Enhanced flexibility, resistant to cracking and shattering |
| Safety | Prevents glass fragmentation, reduces injury risk | Contains plastic to absorb impact, safer on breakage |
| Weight | Heavier due to multiple solid glass layers | Lighter by integrating plastic composites |
| Optical Clarity | High clarity with minimal distortion | Good clarity, varies with plastic type and thickness |
| Applications | Automotive windshields, architectural safety glass | Lightweight construction, protective glazing, specialty applications |
| Cost | Moderate, widely available | Higher, due to composite manufacturing complexity |
Definition and Composition: Laminated Glass vs Glass Plastic Composite
Laminated glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded with an interlayer, typically polyvinyl butyral (PVB), enhancing safety and sound insulation. Glass plastic composite combines glass fibers embedded in a polymer matrix, offering high strength-to-weight ratio and impact resistance. The primary difference lies in laminated glass's focus on layered glass and interlayer adhesion, while glass plastic composite integrates glass fibers within plastic for structural applications.
Manufacturing Process Comparison
Laminated glass is produced by bonding two or more glass layers with an interlayer of polyvinyl butyral (PVB) through heat and pressure, creating a durable and impact-resistant structure. Glass-plastic composites involve embedding glass fibers within a plastic resin matrix via processes like injection molding or lay-up methods, resulting in a lightweight yet strong material. The manufacturing of laminated glass centers on lamination and curing techniques, while glass-plastic composites rely on resin curing and fiber reinforcement for structural integrity.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Differences
Laminated glass features a layer of polyvinyl butyral (PVB) bonded between two glass sheets, providing enhanced mechanical strength and impact resistance compared to standard glass plastic composites that often use acrylic or polycarbonate layers. The interlayer in laminated glass absorbs and distributes forces more effectively, reducing the risk of shattering and increasing durability in safety applications. Your choice between laminated glass and glass plastic composites should consider that laminated glass offers superior long-term performance in structural integrity and resistance to environmental stressors.
Safety and Impact Resistance
Laminated glass offers superior safety by holding shards together upon impact, reducing injury risk compared to glass plastic composites, which may delaminate under stress. The polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer in laminated glass enhances impact resistance, making it ideal for automotive windshields and security applications. Your choice between laminated glass and glass plastic composite should prioritize impact resistance needs and safety requirements for optimal protection.
Acoustic and Thermal Insulation Performance
Laminated glass offers superior acoustic insulation by effectively reducing sound transmission through its interlayer, making it ideal for noise-sensitive environments. Its thermal insulation performance is enhanced by the interlayer's ability to limit heat transfer, contributing to better energy efficiency compared to standard glass. Glass plastic composites provide enhanced impact resistance but generally exhibit lower acoustic and thermal insulation values due to the plastic layer's differing thermal conductivity and sound dampening properties.
Weight and Thickness Considerations
Laminated glass typically offers greater thickness and weight due to multiple glass layers bonded with interlayers, enhancing safety and sound insulation. Glass plastic composites, combining glass with lightweight polymers, reduce overall weight significantly while maintaining strength and flexibility. Your choice between the two should consider the balance between structural requirements and the need for lightweight materials in specific applications.
UV and Weather Resistance Properties
Laminated glass offers superior UV protection and excellent weather resistance due to its interlayer that blocks harmful ultraviolet rays and prevents glass shattering. Glass plastic composites provide enhanced flexibility and impact resistance but may degrade faster under prolonged UV exposure without proper additives. You should choose laminated glass for long-term durability and consistent protection against weathering and UV damage.
Cost Analysis and Economic Factors
Laminated glass typically incurs higher upfront costs due to its complex manufacturing process involving multiple glass layers and interlayers for enhanced safety and durability. Glass plastic composites offer a cost-effective alternative, leveraging lighter materials and simpler production methods that reduce material and transportation expenses. Long-term economic factors favor laminated glass in applications requiring impact resistance and longevity, while glass plastic composites benefit projects prioritizing budget and ease of installation.
Application Areas and Industry Usage
Laminated glass is widely used in automotive windshields, architectural glazing, and safety barriers due to its superior impact resistance and shatterproof properties. Glass plastic composites find applications in aerospace, electronics, and lightweight structural components, where flexibility and weight reduction are critical. Your choice between these materials should consider the specific industry requirements and the desired balance between durability and weight.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Laminated glass offers enhanced sustainability through its durability and recyclability, reducing the need for frequent replacements and minimizing waste. Glass plastic composites, while lightweight and corrosion-resistant, often pose recycling challenges due to the combination of materials, leading to environmental concerns in disposal processes. Your choice of laminated glass supports eco-friendly building practices by promoting longer lifespan and easier material recovery.
laminated glass vs glass plastic composite Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com