Laminated glass consists of two or more layers of glass bonded with an interlayer, providing enhanced safety and basic sound reduction. Acoustic glass is specially designed with multiple layers and interlayers that significantly improve noise insulation, making it ideal for creating a quieter environment in your home or office.
Table of Comparison
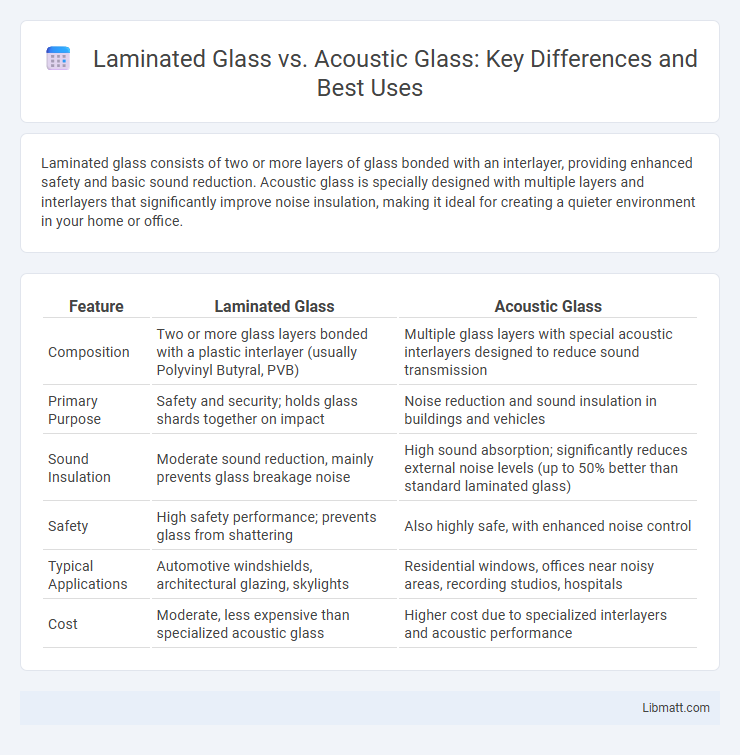
| Feature | Laminated Glass | Acoustic Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Two or more glass layers bonded with a plastic interlayer (usually Polyvinyl Butyral, PVB) | Multiple glass layers with special acoustic interlayers designed to reduce sound transmission |
| Primary Purpose | Safety and security; holds glass shards together on impact | Noise reduction and sound insulation in buildings and vehicles |
| Sound Insulation | Moderate sound reduction, mainly prevents glass breakage noise | High sound absorption; significantly reduces external noise levels (up to 50% better than standard laminated glass) |
| Safety | High safety performance; prevents glass from shattering | Also highly safe, with enhanced noise control |
| Typical Applications | Automotive windshields, architectural glazing, skylights | Residential windows, offices near noisy areas, recording studios, hospitals |
| Cost | Moderate, less expensive than specialized acoustic glass | Higher cost due to specialized interlayers and acoustic performance |
Introduction to Laminated Glass and Acoustic Glass
Laminated glass consists of two or more layers of glass bonded with an interlayer, providing enhanced safety, UV protection, and impact resistance. Acoustic glass is specifically designed to reduce noise transmission, featuring additional interlayers or specialized materials that improve sound insulation performance. Your choice between laminated and acoustic glass depends on whether safety, noise reduction, or a combination of both is the primary concern for your space.
Composition and Structure Comparison
Laminated glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded by an interlayer, typically polyvinyl butyral (PVB), providing structural integrity and safety by holding shards together upon impact. Acoustic glass features a specialized acoustic interlayer, such as a viscoelastic polymer, designed to dampen sound vibrations and enhance noise reduction performance. The key compositional difference lies in the interlayer's material and thickness, with acoustic glass using thicker or multiple acoustic layers to optimize sound insulation compared to standard laminated glass.
Sound Insulation Performance
Laminated glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded with an interlayer, offering moderate sound insulation by reducing noise transmission. Acoustic glass, specifically designed with thicker layers and specialized interlayers, provides superior soundproofing performance by effectively dampening sound vibrations across a wider frequency range. Your choice of acoustic glass can significantly enhance noise reduction in environments requiring high-quality sound insulation.
Safety and Security Features
Laminated glass consists of two or more layers bonded with an interlayer, providing superior impact resistance and preventing shattering, which enhances safety by holding the glass together upon breakage. Acoustic glass incorporates specialized interlayers designed to reduce noise transmission while also maintaining security by offering robust resistance against forced entry. Both types improve safety and security, with laminated glass excelling in impact protection and acoustic glass balancing sound insulation with durable construction.
Energy Efficiency and UV Protection
Laminated glass offers superior UV protection by incorporating a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) layer that blocks up to 99% of harmful ultraviolet rays, reducing interior fading and skin damage. Acoustic glass, designed primarily for sound insulation, generally includes multiple glass layers with acoustic interlayers but may provide less effective UV shielding compared to laminated glass. Both types contribute to energy efficiency by enhancing thermal insulation, yet laminated glass's UV-blocking properties make it more effective in reducing cooling costs and protecting interior furnishings.
Applications in Residential and Commercial Buildings
Laminated glass offers enhanced safety and UV protection, making it ideal for residential windows, skylights, and commercial storefronts where security and durability are priorities. Acoustic glass specializes in noise reduction, providing superior sound insulation for apartments, office partitions, and conference rooms to create quieter, more comfortable environments. Choosing the right glass improves your building's performance by balancing safety, aesthetics, and acoustic comfort based on specific application needs.
Durability and Maintenance Requirements
Laminated glass features a robust interlayer that holds shards in place upon impact, offering enhanced durability and resistance to breakage compared to acoustic glass. Acoustic glass incorporates specialized layers for sound insulation but may require more frequent inspection and maintenance to preserve its noise-reduction properties. Regular cleaning and occasional resealing help maintain the structural integrity and performance of both glass types.
Cost Considerations
Laminated glass generally offers a more cost-effective solution compared to acoustic glass due to its simpler manufacturing process and widespread availability. Acoustic glass incorporates multiple layers and specialized interlayers that enhance soundproofing but increase production expenses and retail price. Selecting between laminated and acoustic glass depends on budget constraints and the required level of noise reduction for specific applications.
Installation Process and Compatibility
Laminated glass involves bonding layers of glass with a plastic interlayer, making its installation similar to standard glass but requiring precise handling to avoid damage to the interlayer. Acoustic glass combines laminated glass with specialized soundproofing materials, demanding careful installation to maintain its noise reduction properties and compatibility with soundproof framing systems. You should ensure both types are compatible with your existing window frames and consult professionals skilled in handling their specific installation requirements for optimal performance.
Which Glass Type Should You Choose?
Choosing between laminated glass and acoustic glass depends on your specific needs for safety and sound insulation. Laminated glass offers superior impact resistance and security by holding shattered pieces together, making it ideal for windows where protection is a priority. Acoustic glass is designed to reduce noise pollution effectively, making it the better option if your primary concern is soundproofing your home or workspace.
laminated glass vs acoustic glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com