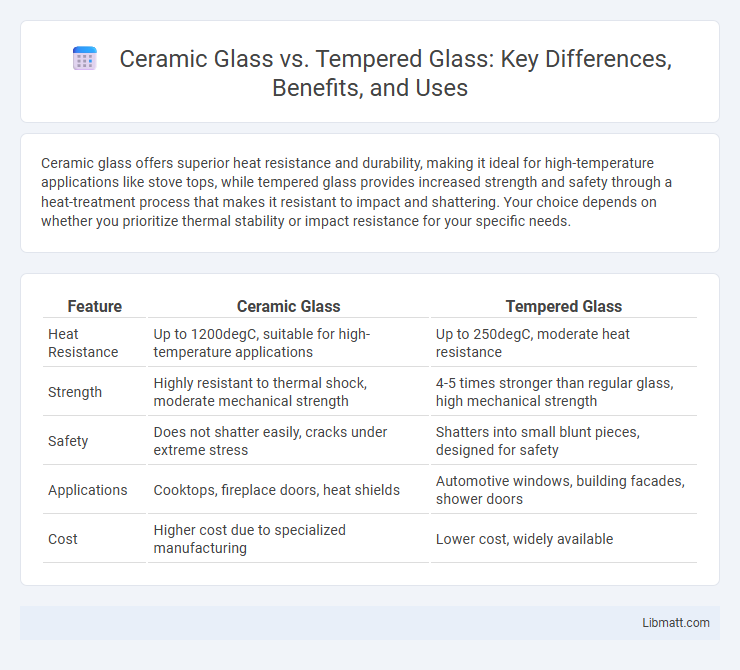
Ceramic glass offers superior heat resistance and durability, making it ideal for high-temperature applications like stove tops, while tempered glass provides increased strength and safety through a heat-treatment process that makes it resistant to impact and shattering. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize thermal stability or impact resistance for your specific needs.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ceramic Glass | Tempered Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Resistance | Up to 1200degC, suitable for high-temperature applications | Up to 250degC, moderate heat resistance |
| Strength | Highly resistant to thermal shock, moderate mechanical strength | 4-5 times stronger than regular glass, high mechanical strength |
| Safety | Does not shatter easily, cracks under extreme stress | Shatters into small blunt pieces, designed for safety |
| Applications | Cooktops, fireplace doors, heat shields | Automotive windows, building facades, shower doors |
| Cost | Higher cost due to specialized manufacturing | Lower cost, widely available |
Introduction to Ceramic Glass and Tempered Glass
Ceramic glass is a high-performance material made from glass-ceramic composites known for exceptional heat resistance and thermal shock durability, commonly used in cooktops and fireplace doors. Tempered glass undergoes a controlled thermal or chemical treatment process to enhance strength and safety by causing the glass to shatter into small, blunt pieces rather than sharp shards. Both materials serve distinct applications where durability and safety are critical, with ceramic glass excelling in extreme temperature environments and tempered glass providing enhanced impact resistance.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Ceramic glass is composed primarily of glass-ceramics containing crystalline structures formed through controlled crystallization during manufacturing, resulting in superior thermal resistance and structural stability. Tempered glass is made by rapidly cooling annealed glass surfaces through a process called tempering, which induces compressive stresses for increased strength and shatter resistance. The distinct manufacturing processes influence their physical properties, with ceramic glass suitable for high-heat applications and tempered glass designed for enhanced durability and safety.
Key Physical Properties Comparison
Ceramic glass offers exceptional thermal resistance and can withstand sudden temperature changes up to 750degC, making it ideal for stovetops and fireplaces, while tempered glass excels in impact resistance and safety, breaking into small non-sharp pieces upon fracture. Ceramic glass is less prone to scratching and chemical corrosion compared to tempered glass, which is more susceptible to surface damage but provides superior mechanical strength with a tensile strength around 120-300 MPa. Your choice depends on whether thermal durability or impact toughness is the priority for your application.
Heat Resistance and Thermal Shock
Ceramic glass offers superior heat resistance, enduring temperatures up to 1400degC, compared to tempered glass which typically withstands around 300degC. Ceramic glass's low thermal expansion provides exceptional resistance to thermal shock, making it ideal for applications with rapid temperature changes. Tempered glass, while stronger mechanically, is more prone to cracking under sudden temperature fluctuations due to its higher thermal expansion rate.
Strength and Durability Differences
Ceramic glass offers superior heat resistance and maintains structural integrity under extreme temperature fluctuations, making it highly durable in high-heat environments. Tempered glass is engineered through a heat-treatment process that increases its strength up to four times that of standard glass, providing excellent impact resistance but lower resistance to thermal stress compared to ceramic glass. Your choice between ceramic glass and tempered glass should consider whether strength under thermal stress or impact resistance is more critical for your application.
Safety Features and Breakage Patterns
Ceramic glass offers superior heat resistance and typically cracks into large, sharp shards upon breakage, posing higher injury risks compared to tempered glass. Tempered glass is engineered to shatter into small, blunt granules, significantly reducing the chance of cuts and enhancing overall safety in applications like automotive windows and kitchen appliances. Safety features of tempered glass include controlled breakage patterns and high impact resistance, whereas ceramic glass excels in thermal stability but lacks the safer fragmentation properties of tempered glass.
Applications in Home and Industry
Ceramic glass is widely used in high-temperature applications such as stove tops, fireplaces, and industrial furnace windows due to its excellent heat resistance and thermal shock stability. Tempered glass is commonly applied in safety-critical areas like automotive windows, shower doors, and architectural facades, offering superior strength and shatter resistance. Both materials serve crucial roles in home and industry, with ceramic glass favored for thermal durability and tempered glass preferred for impact safety and structural integrity.
Cost Comparison and Availability
Ceramic glass generally costs more than tempered glass due to its higher heat resistance and durability, making it a preferred choice for applications demanding thermal stability. Tempered glass is more widely available and budget-friendly, commonly used in automotive windows, furniture, and building facades. The cost difference and availability often influence selection based on project requirements and performance needs.
Maintenance and Longevity
Ceramic glass offers superior resistance to high temperatures, scratches, and stains, making it easier to maintain with simple cleaning methods and less frequent replacement. Tempered glass, while strong and durable, is more prone to chipping and requires careful handling to avoid damage, which can affect its longevity. Your choice between ceramic and tempered glass should consider the maintenance effort and how long you expect the surface to last under regular use.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Needs
Ceramic glass offers superior heat resistance and durability, making it ideal for ovens and stoves where high temperatures are common, while tempered glass provides enhanced safety through increased strength and shatter resistance, suitable for windows and doors. Your choice depends on the specific application requirements, such as exposure to heat or impact resistance. Evaluate the thermal tolerance and safety standards to select the glass that best supports your functional and safety needs.
Ceramic glass vs tempered glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com