Glass blocks and glass bricks are often used interchangeably, but glass blocks typically have a smoother texture and clearer appearance, making them ideal for modern architectural designs, while glass bricks tend to be more textured and decorative, providing enhanced privacy and aesthetic variety. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize transparency and sleekness or decorative patterns and light diffusion in your space.
Table of Comparison
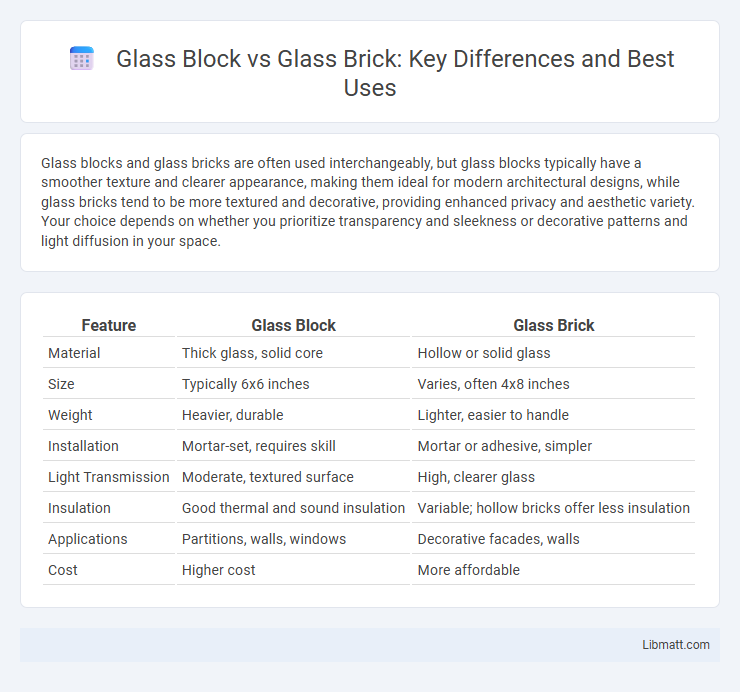
| Feature | Glass Block | Glass Brick |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Thick glass, solid core | Hollow or solid glass |
| Size | Typically 6x6 inches | Varies, often 4x8 inches |
| Weight | Heavier, durable | Lighter, easier to handle |
| Installation | Mortar-set, requires skill | Mortar or adhesive, simpler |
| Light Transmission | Moderate, textured surface | High, clearer glass |
| Insulation | Good thermal and sound insulation | Variable; hollow bricks offer less insulation |
| Applications | Partitions, walls, windows | Decorative facades, walls |
| Cost | Higher cost | More affordable |
Introduction to Glass Block and Glass Brick
Glass blocks and glass bricks are architectural elements made from thick, translucent glass designed to allow light while providing privacy and structural support. Glass blocks typically have a smooth or patterned surface and are used in walls and partitions, offering insulation and durability. Glass bricks refer to the same product and terms are often used interchangeably in construction and design contexts to describe these modular glass units.
Defining Glass Block and Glass Brick
Glass blocks are thick, hollow units typically used in architectural walls to allow light transmission while providing insulation and privacy, made from molded glass with a textured surface to diffuse light. Glass bricks are a subset of glass blocks primarily designed for decorative purposes, often featuring more refined shapes and patterns, and sometimes used in smaller installations like partitions or accents. Both serve to enhance natural lighting but differ in application and design detail, with glass blocks emphasizing structural function and glass bricks focusing on aesthetic appeal.
Key Material Differences
Glass blocks are typically made from thicker, molded glass with a hollow center, providing enhanced insulation and structural strength, while glass bricks are often thinner, solid pieces designed primarily for decorative applications. The manufacturing process of glass blocks involves sealing two glass panes with a hollow air pocket for thermal efficiency, whereas glass bricks may lack this feature, resulting in different light diffusion and heat retention properties. These material differences affect their suitability for construction, with glass blocks favored in walls requiring durability and insulation, and glass bricks chosen for ornamental use and design flexibility.
Design and Aesthetic Variations
Glass blocks and glass bricks both enhance interior and exterior design with their unique texture and light diffusion properties, but glass blocks offer a broader range of sizes, patterns, and finishes, enabling more intricate architectural customization. Glass bricks tend to have uniform shapes and smoother surfaces, ideal for minimalist and modern aesthetics, while glass blocks can incorporate frosted, patterned, or colored glass options that add depth and visual interest. The choice between glass block and glass brick significantly influences the visual impact and ambiance, making glass blocks preferable for projects seeking artistic versatility.
Structural Strength and Durability
Glass blocks offer superior structural strength and durability compared to glass bricks due to their thicker walls and reinforced construction. Your project benefits from enhanced impact resistance and load-bearing capacity when using glass blocks, making them ideal for both exterior and interior installations. Glass bricks, while aesthetically pleasing, generally provide less robustness and are more prone to damage under heavy use or environmental stress.
Insulation and Energy Efficiency
Glass blocks provide superior insulation and enhanced energy efficiency due to their thicker walls and airtight seals, effectively reducing heat transfer and minimizing energy loss. Glass bricks, often thinner and less dense, typically offer lower thermal performance but may be more cost-effective for decorative applications. Choosing glass blocks can significantly improve Your building's insulation, leading to lower heating and cooling costs.
Installation Process Comparison
Glass block and glass brick installations differ primarily in complexity and technique; glass blocks require precise mortar application and alignment to ensure stability and water resistance, while glass bricks often come with interlocking edges or are mounted with adhesives, simplifying the process. Glass blocks demand skilled labor for cutting and fitting, making the installation more time-consuming and labor-intensive compared to the generally easier and faster glass brick installation, which can be suitable for DIY projects. Your choice between the two should consider the available installation expertise and the structural requirements of your project.
Common Applications and Uses
Glass block and glass brick are widely used in architectural and interior design for natural light diffusion and privacy. Glass blocks are commonly installed in exterior walls, shower enclosures, and office partitions due to their strength and insulation properties. Glass bricks are often favored for decorative features, such as garden walls, stairway accents, and room dividers, combining aesthetic appeal with functional light transmission.
Cost Factors and Budget Considerations
Glass block and glass brick vary in cost due to differences in manufacturing processes and design complexity, with glass blocks generally priced higher because of their thicker, more durable construction. Budget considerations should include installation expenses, as glass bricks often require more labor-intensive fitting and specialized mortar, increasing overall costs compared to the relatively straightforward installation of glass blocks. Your choice should balance initial material expenses with long-term maintenance and energy efficiency benefits provided by each option.
Which Is Best: Glass Block or Glass Brick?
Glass block and glass brick both offer unique advantages for architectural and design purposes, but glass block is typically favored for structural applications due to its thicker walls and greater durability. Glass bricks tend to be lighter and more decorative, making them ideal for interior partitions and artistic installations. Choosing between glass block and glass brick depends on the specific project requirements, including strength, insulation properties, and aesthetic preferences.
glass block vs glass brick Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com