Fire-resistant glass is designed to withstand fire and heat for a specified period, maintaining structural integrity and preventing flames from spreading, while fire-protective glass primarily focuses on limiting heat transfer and blocking radiant heat to protect people and property on the non-fire side. Choosing the right fire-resistant or fire-protective glass enhances Your building's safety by effectively managing fire hazards according to specific safety requirements.
Table of Comparison
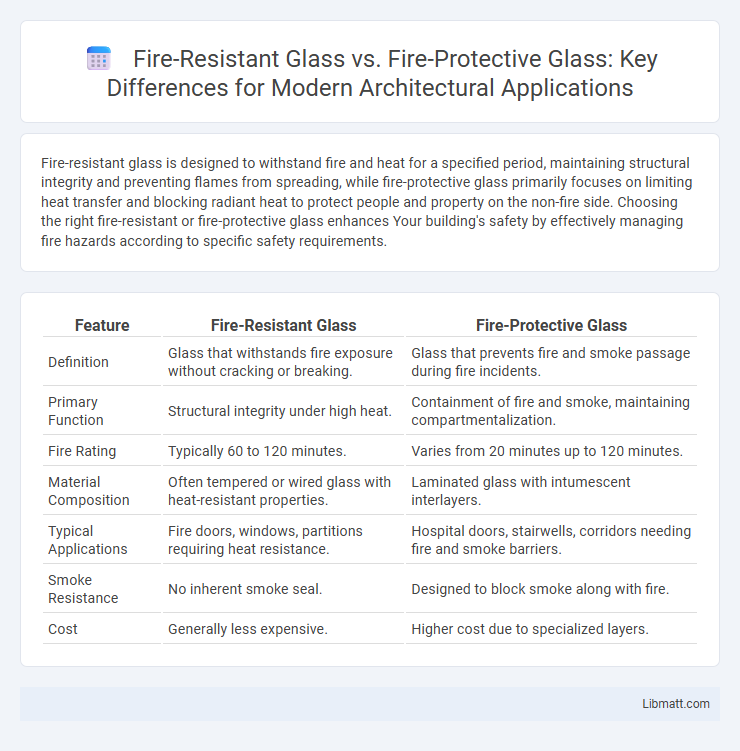
| Feature | Fire-Resistant Glass | Fire-Protective Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Glass that withstands fire exposure without cracking or breaking. | Glass that prevents fire and smoke passage during fire incidents. |
| Primary Function | Structural integrity under high heat. | Containment of fire and smoke, maintaining compartmentalization. |
| Fire Rating | Typically 60 to 120 minutes. | Varies from 20 minutes up to 120 minutes. |
| Material Composition | Often tempered or wired glass with heat-resistant properties. | Laminated glass with intumescent interlayers. |
| Typical Applications | Fire doors, windows, partitions requiring heat resistance. | Hospital doors, stairwells, corridors needing fire and smoke barriers. |
| Smoke Resistance | No inherent smoke seal. | Designed to block smoke along with fire. |
| Cost | Generally less expensive. | Higher cost due to specialized layers. |
Introduction to Fire-Resistant and Fire-Protective Glass
Fire-resistant glass is designed to withstand high temperatures and prevent the passage of flames and smoke during a fire, providing critical time for evacuation and firefighting. Fire-protective glass, while similar, primarily focuses on slowing heat transfer and offering visibility, making it suitable for areas where containment without blocking sightlines is essential. Choosing the right glass for Your building depends on the specific fire safety requirements and regulatory standards.
Defining Fire-Resistant Glass
Fire-resistant glass is engineered to withstand high temperatures and prevent the spread of flames and smoke during a fire, providing critical time for evacuation and reducing property damage. Unlike fire-protective glass, fire-resistant glass is tested to specific standards such as ASTM E119 or EN 13501-2, ensuring it maintains structural integrity under fire exposure. Understanding the precise role of fire-resistant glass in your safety planning can significantly enhance the fire protection strategy in buildings.
What is Fire-Protective Glass?
Fire-protective glass is a specially engineered glazing material designed to prevent the passage of flames, smoke, and heat during a fire, ensuring both containment and safety. It typically consists of multiple layers, including intumescent interlayers that expand under heat to block fire transmission while allowing some visibility. Your choice of fire-protective glass can enhance building safety by meeting stringent fire-resistance standards without compromising design aesthetics.
Key Differences Between Fire-Resistant and Fire-Protective Glass
Fire-resistant glass is designed to withstand high temperatures and prevent the passage of flames and smoke for a specified period, often meeting stringent fire-resistance ratings. Fire-protective glass primarily focuses on limiting heat transfer and maintaining structural integrity under fire conditions but may not block flames completely. Understanding these distinctions helps you select the appropriate glass type for compliance with building codes and safety standards in fire-prone environments.
Performance Standards and Certifications
Fire-resistant glass is tested and certified to withstand fire and prevent heat transfer for a specific duration, complying with standards such as ASTM E119 or EN 1363-1. Fire-protective glass meets fire safety requirements but generally provides lower heat insulation and may adhere to standards like BS 476. Choosing the right glass for Your project depends on the needed fire performance rating and relevant certifications to ensure safety and compliance.
Applications in Building Design and Architecture
Fire-resistant glass is ideal for applications requiring extended fire containment, such as stairwells, fire doors, and elevator shafts, where preventing flame and smoke passage protects occupants and property. Fire-protective glass suits areas needing shorter fire exposure resistance, like interior partitions and office windows, offering safety without compromising natural light or visibility. Architects and designers select these materials based on fire rating, transparency, and building codes to optimize safety and aesthetic value in commercial and residential structures.
Advantages of Fire-Resistant Glass
Fire-resistant glass offers superior containment of fire and smoke, providing crucial additional time for evacuation and emergency response compared to fire-protective glass. Its ability to withstand high temperatures and maintain structural integrity prevents the spread of flames and reduces property damage. This durability enhances building safety, meeting stringent fire codes and insurance requirements for commercial and residential applications.
Benefits of Fire-Protective Glass
Fire-protective glass offers superior safety by not only withstanding high temperatures but also preventing the spread of flames and smoke, making it crucial in emergency evacuation routes. Your building's structural integrity is maintained longer during a fire, reducing damage and allowing more time for occupants to escape. This glass type enhances compliance with fire safety regulations while improving overall resilience in fire-prone environments.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Fire Glass
When choosing between fire-resistant glass and fire-protective glass, consider factors such as the glass's fire rating, thermal insulation properties, and impact resistance to ensure compliance with building codes and safety standards. Your decision should also account for the duration of fire exposure the glass can withstand, the specific application environment, and the integration with surrounding fire safety systems. Evaluating visibility requirements, maintenance needs, and cost-effectiveness will further help tailor the choice to your project's safety and design goals.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Solution for Safety
Fire-resistant glass provides a crucial barrier that withstands high temperatures and prevents fire from spreading, making it ideal for areas requiring containment. Fire-protective glass focuses on maintaining structural integrity while limiting heat transfer, ensuring your safety through both insulation and visibility. Your choice depends on specific safety requirements, building codes, and the level of fire resistance needed to protect lives and property effectively.
fire-resistant glass vs fire-protective glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com