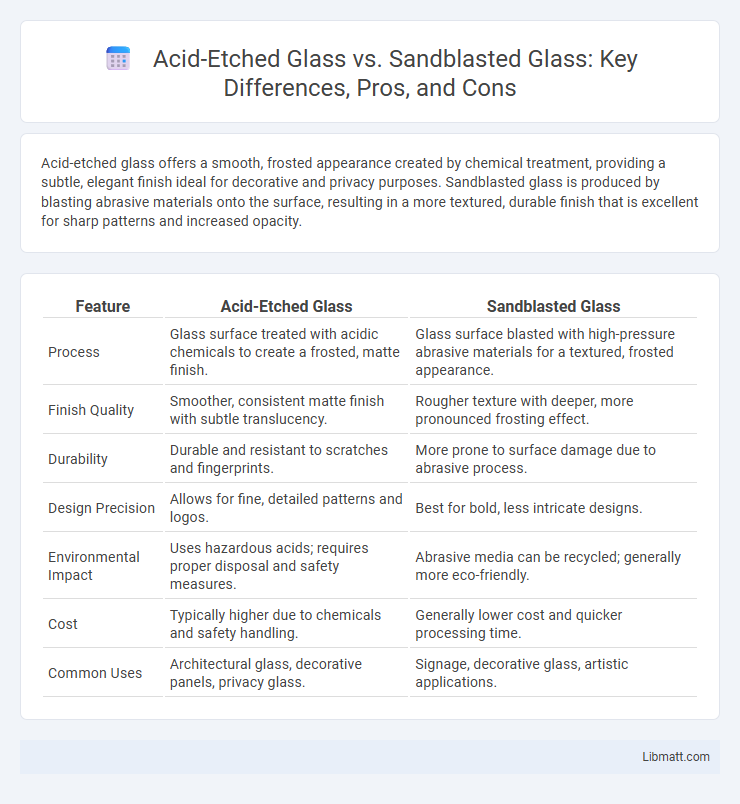
Acid-etched glass offers a smooth, frosted appearance created by chemical treatment, providing a subtle, elegant finish ideal for decorative and privacy purposes. Sandblasted glass is produced by blasting abrasive materials onto the surface, resulting in a more textured, durable finish that is excellent for sharp patterns and increased opacity.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Acid-Etched Glass | Sandblasted Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Glass surface treated with acidic chemicals to create a frosted, matte finish. | Glass surface blasted with high-pressure abrasive materials for a textured, frosted appearance. |
| Finish Quality | Smoother, consistent matte finish with subtle translucency. | Rougher texture with deeper, more pronounced frosting effect. |
| Durability | Durable and resistant to scratches and fingerprints. | More prone to surface damage due to abrasive process. |
| Design Precision | Allows for fine, detailed patterns and logos. | Best for bold, less intricate designs. |
| Environmental Impact | Uses hazardous acids; requires proper disposal and safety measures. | Abrasive media can be recycled; generally more eco-friendly. |
| Cost | Typically higher due to chemicals and safety handling. | Generally lower cost and quicker processing time. |
| Common Uses | Architectural glass, decorative panels, privacy glass. | Signage, decorative glass, artistic applications. |
Introduction to Acid-Etched and Sandblasted Glass
Acid-etched glass involves a chemical process using hydrofluoric acid to create a smooth, frosted surface that diffuses light uniformly, making it ideal for privacy and decorative applications. Sandblasted glass is produced by blasting abrasive materials like sand at high pressure onto the glass surface, resulting in a textured, matte finish with variable patterns and depth. Both techniques modify glass opacity without compromising structural integrity, widely used in architectural and interior design for aesthetic and functional purposes.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Acid-etched glass undergoes a chemical treatment using hydrofluoric acid to create a frosted, matte surface by selectively corroding the glass. Sandblasted glass is produced by propelling fine abrasive particles at high pressure onto the glass surface, physically abrading it to achieve a similar textured finish. Both processes enhance privacy and aesthetics, but acid etching offers finer detail with a smoother feel, while sandblasting allows for deeper patterns and more pronounced textures.
Surface Texture and Visual Appearance
Acid-etched glass features a smooth, frosted surface created through a chemical process that produces a uniform, matte finish, enhancing light diffusion without significant texture. Sandblasted glass has a slightly rougher surface with a more tactile feel, resulting from abrasive particles blasted onto the glass, which creates a varied, opaque appearance. The visual appearance of acid-etched glass tends to be softer and more subtle, while sandblasted glass offers a stronger, more pronounced texture and a distinctive, granular look.
Durability and Maintenance Requirements
Acid-etched glass offers a smooth, durable surface resistant to scratching and is easy to clean with mild detergents, making it ideal for low-maintenance applications. Sandblasted glass, while visually similar, tends to have a more textured surface that can trap dirt and require more frequent cleaning or specialized products to maintain clarity. Your choice depends on the balance between desired texture and the level of upkeep you are willing to commit to.
Privacy and Light Diffusion Capabilities
Acid-etched glass offers superior privacy by creating a uniformly frosted surface that obscures visibility while allowing ample natural light to diffuse evenly through the pane. Sandblasted glass provides customizable levels of privacy with varied patterns or textures, but its light diffusion is often less uniform, resulting in softer, more diffused illumination. Both treatments enhance privacy and brightness, yet acid-etched glass excels in consistent light diffusion, making it ideal for spaces requiring balanced illumination and seclusion.
Common Applications in Architecture and Design
Acid-etched glass is commonly used in interior partitions, bathroom windows, and decorative panels, offering a smooth, frosted appearance that enhances privacy while allowing light diffusion. Sandblasted glass is often selected for exterior facades, signage, and artistic installations due to its textured, slightly rough surface that provides durable matte finishes and intricate design possibilities. Your choice between the two can influence the aesthetic and functional qualities of architectural elements, balancing translucency, texture, and light transmission.
Cost Analysis and Budget Considerations
Acid-etched glass typically incurs higher costs due to the chemical process and specialized safety measures required, making it less budget-friendly compared to sandblasted glass. Sandblasted glass offers a more affordable option with quicker production times and lower labor expenses, appealing to projects with tighter budget constraints. Evaluating project scale and desired finish helps determine the most cost-effective choice between these two decorative glass treatments.
Environmental Impact and Safety Concerns
Acid-etched glass involves chemical use that can pose environmental hazards if not properly managed, whereas sandblasted glass uses abrasive materials that generate silica dust, raising health concerns. Proper ventilation and protective equipment are essential during sandblasting to minimize respiratory risks, while acid etching requires careful disposal to prevent chemical contamination. You should consider these environmental and safety factors when choosing between acid-etched and sandblasted glass for your project.
Customization and Design Flexibility
Acid-etched glass offers precise control over patterns and shades by using chemical etching techniques that allow for intricate, detailed designs with smooth finishes, ideal for personalized artwork or corporate logos. Sandblasted glass provides a more textured and frosted appearance through abrasive blasting, enabling varied depths and patterns but generally less subtlety in detail than acid-etching. Both methods support extensive customization, with acid-etching excelling in fine detail and sandblasting excelling in creating bold, tactile visual effects.
Choosing the Right Glass: Key Factors to Consider
When choosing between acid-etched glass and sandblasted glass, consider surface texture and design clarity, as acid-etched glass offers a smoother, more uniform finish while sandblasted glass provides a frosted, textured appearance with deeper relief. Durability and maintenance are crucial; acid-etched glass tends to be more resistant to wear and easier to clean, whereas sandblasted glass may accumulate dirt in its etched grooves. Your decision should align with the intended aesthetic, privacy needs, and maintenance preferences to ensure the best fit for your space.
acid-etched glass vs sandblasted glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com