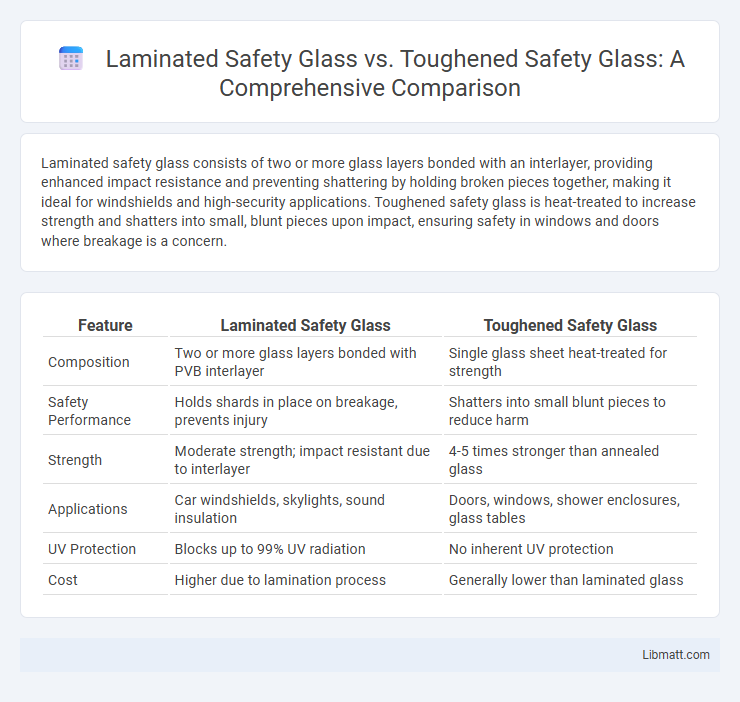
Laminated safety glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded with an interlayer, providing enhanced impact resistance and preventing shattering by holding broken pieces together, making it ideal for windshields and high-security applications. Toughened safety glass is heat-treated to increase strength and shatters into small, blunt pieces upon impact, ensuring safety in windows and doors where breakage is a concern.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Laminated Safety Glass | Toughened Safety Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Two or more glass layers bonded with PVB interlayer | Single glass sheet heat-treated for strength |
| Safety Performance | Holds shards in place on breakage, prevents injury | Shatters into small blunt pieces to reduce harm |
| Strength | Moderate strength; impact resistant due to interlayer | 4-5 times stronger than annealed glass |
| Applications | Car windshields, skylights, sound insulation | Doors, windows, shower enclosures, glass tables |
| UV Protection | Blocks up to 99% UV radiation | No inherent UV protection |
| Cost | Higher due to lamination process | Generally lower than laminated glass |
Introduction to Safety Glass Types
Laminated safety glass consists of two or more layers of glass bonded with an interlayer, offering high impact resistance and preventing shards from dispersing upon breakage. Toughened safety glass undergoes chemical or thermal treatment to increase strength, shattering into small, less harmful granules when broken. Both types enhance safety but serve different applications based on durability and impact absorption characteristics.
What is Laminated Safety Glass?
Laminated safety glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded together with an interlayer, usually polyvinyl butyral (PVB), which holds the layers in place upon impact to prevent shattering. This structure enhances safety by reducing the risk of injury from sharp glass fragments and provides superior sound insulation and UV protection. Commonly used in automotive windshields and building facades, laminated glass offers improved strength and durability compared to regular glass.
What is Toughened (Tempered) Safety Glass?
Toughened (tempered) safety glass is a type of treated glass designed to withstand higher impact and thermal stress compared to standard glass, increasing your overall safety in various applications. This glass undergoes a controlled heating and rapid cooling process, which enhances its strength and causes it to shatter into small, blunt pieces rather than sharp shards if broken. It is commonly used in automotive windows, shower screens, and architectural elements where durability and safety are crucial.
Manufacturing Process Comparison
Laminated safety glass is manufactured by bonding two or more glass layers with an interlayer, usually made of polyvinyl butyral (PVB), under heat and pressure, resulting in a glass that holds together when shattered. Toughened safety glass, also known as tempered glass, undergoes a rapid cooling process after being heated to around 620degC, which creates compressive stresses on the surface and tensile stresses inside, enhancing its strength and ensuring it breaks into small, blunt pieces. Your choice depends on the required safety performance and specific application, as laminated glass offers superior impact resistance and acoustic properties, while toughened glass excels in structural strength and thermal resistance.
Key Strength Differences
Laminated safety glass consists of two or more layers of glass bonded with an interlayer, providing enhanced impact resistance and preventing shattering by holding fragments together, making it ideal for security and noise reduction. Toughened safety glass, also known as tempered glass, is heat-treated to increase its strength, offering superior resistance to thermal stress and breakage, and it shatters into small blunt pieces for safety. The primary strength difference lies in laminated glass's ability to maintain integrity upon impact, while toughened glass excels in strength and thermal resistance but breaks completely under extreme force.
Safety and Breakage Behavior
Laminated safety glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded with an interlayer that holds shards together upon impact, preventing injury and maintaining structural integrity. Toughened safety glass, also known as tempered glass, is heat-treated to increase strength and shatters into small granular pieces to reduce harm but does not remain intact after breakage. The choice between laminated and toughened safety glass depends on the required level of safety retention and specific breakage behavior in different applications such as automotive, architectural, and security glazing.
Applications and Uses in Construction
Laminated safety glass is widely used in construction for applications requiring enhanced security and noise reduction, such as facades, skylights, and balustrades, due to its ability to hold shards together when broken. Toughened safety glass is preferred for areas that demand high strength and resistance to impact, including windows, doors, and partitions, as it shatters into small, blunt pieces to reduce injury risk. Both types contribute to building safety standards but are chosen based on specific structural and safety requirements in architectural design.
Sound and UV Performance
Laminated safety glass offers superior sound insulation due to its interlayer that absorbs acoustic energy, significantly reducing noise transmission compared to toughened safety glass. It also provides enhanced UV protection by blocking up to 99% of harmful ultraviolet rays, thus protecting interiors from fading and damage. Toughened safety glass excels in strength and thermal resistance but lacks the same level of sound dampening and UV filtering properties as laminated glass.
Cost Considerations
Laminated safety glass typically costs more than toughened safety glass due to its multi-layer construction, incorporating a plastic interlayer that enhances impact resistance and sound insulation. Toughened safety glass is generally less expensive, providing strength through a heat treatment process, making it a cost-effective choice for applications requiring high durability and shatter resistance. Budget decisions should weigh the higher upfront cost of laminated glass against its superior safety features and potential for reduced repair or replacement expenses.
Choosing the Right Safety Glass for Your Needs
Laminated safety glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded with an interlayer, providing superior impact resistance and preventing shattering into sharp pieces, making it ideal for applications requiring enhanced security and sound insulation. Toughened safety glass undergoes thermal tempering processes, resulting in higher strength and a safer break into small granular fragments, suitable for areas with high thermal stress or pedestrian safety concerns. Your choice between laminated and toughened safety glass depends on factors like impact resistance, safety requirements, acoustic insulation, and application environment.
Laminated safety glass vs toughened safety glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com