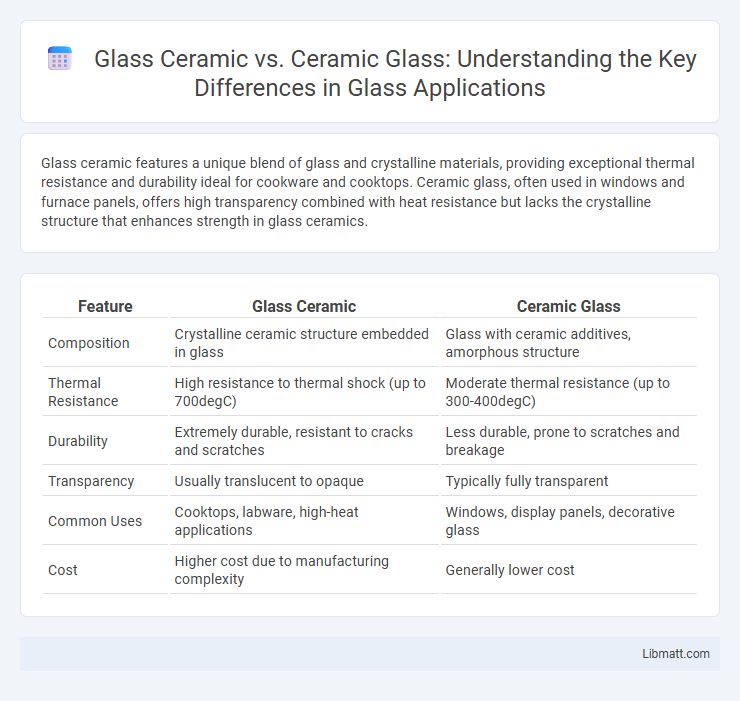
Glass ceramic features a unique blend of glass and crystalline materials, providing exceptional thermal resistance and durability ideal for cookware and cooktops. Ceramic glass, often used in windows and furnace panels, offers high transparency combined with heat resistance but lacks the crystalline structure that enhances strength in glass ceramics.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Glass Ceramic | Ceramic Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Crystalline ceramic structure embedded in glass | Glass with ceramic additives, amorphous structure |
| Thermal Resistance | High resistance to thermal shock (up to 700degC) | Moderate thermal resistance (up to 300-400degC) |
| Durability | Extremely durable, resistant to cracks and scratches | Less durable, prone to scratches and breakage |
| Transparency | Usually translucent to opaque | Typically fully transparent |
| Common Uses | Cooktops, labware, high-heat applications | Windows, display panels, decorative glass |
| Cost | Higher cost due to manufacturing complexity | Generally lower cost |
Introduction to Glass Ceramic and Ceramic Glass
Glass ceramic exhibits a unique microstructure combining crystalline and glassy phases, granting it exceptional thermal shock resistance and durability, making it ideal for cookware and stovetops. Ceramic glass, a transparent material primarily composed of aluminosilicate glass, offers high-temperature stability and optical clarity, commonly used in protective covers and optics. Understanding their distinct compositions and properties helps optimize applications where heat resistance and transparency are critical.
Defining Glass Ceramic: Composition and Properties
Glass ceramic is a material composed of a glassy matrix embedded with fine crystalline phases, offering exceptional thermal stability and mechanical strength. Its unique microstructure results from controlled crystallization during heat treatment, providing high resistance to thermal shock and enhanced durability compared to traditional ceramics. Glass ceramic's low thermal expansion and excellent chemical resistance make it ideal for applications in cooktops, aerospace, and electronics.
Understanding Ceramic Glass: Key Characteristics
Ceramic glass is a specialized material combining the thermal resistance of ceramics with the transparency of glass, enabling it to withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking. Its key characteristics include high thermal shock resistance, low thermal expansion, and excellent chemical durability, making it ideal for applications such as cooktops, fireplace doors, and protective screens. Unlike traditional glass ceramics, ceramic glass maintains optical clarity while providing exceptional mechanical strength and heat resistance.
Manufacturing Processes: Glass Ceramic vs Ceramic Glass
Glass ceramic is produced through controlled crystallization of certain glass compositions, involving heat treatment that transforms the glass into a partially crystalline material with enhanced thermal and mechanical properties. Ceramic glass, often known as borosilicate glass, is fabricated by melting raw materials like silica, boron oxide, and alkalis at high temperatures without undergoing crystallization, resulting in an amorphous, heat-resistant glass. Understanding these distinct manufacturing processes helps you choose the optimal material for applications requiring specific thermal resilience and structural stability.
Physical and Chemical Differences
Glass ceramic exhibits a crystalline microstructure formed through controlled crystallization, resulting in superior thermal shock resistance and enhanced mechanical strength compared to ceramic glass, which remains amorphous like standard glass but with improved heat resistance. Chemically, glass ceramic contains evenly distributed crystalline phases, providing low thermal expansion and high chemical durability, while ceramic glass is primarily silica-based with fewer crystalline inclusions, making it more prone to thermal stress but easier to shape. Your choice between these materials depends on application needs for durability and thermal stability, with glass ceramic ideal for demanding heat environments and ceramic glass suited for aesthetically versatile uses.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Glass ceramic offers superior thermal shock resistance due to its low thermal expansion coefficient, allowing it to withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking. Ceramic glass, while also resistant to heat, typically has a higher thermal expansion rate, making it less effective in extreme temperature fluctuations. For applications requiring consistent thermal stability and durability under high heat, glass ceramic is the preferred choice.
Applications in Industry and Everyday Use
Glass ceramic exhibits exceptional thermal shock resistance and mechanical strength, making it ideal for cookware, aerospace components, and electronics where durability under temperature fluctuations is critical. Ceramic glass, valued for its transparency and insulating properties, is commonly used in stovetop covers, fireplace doors, and protective lenses. Both materials serve crucial roles across industries, with glass ceramic preferred for structural applications and ceramic glass favored for visual and heat-resistant uses.
Durability and Longevity
Glass ceramic offers superior durability and longevity compared to ceramic glass due to its ability to withstand rapid temperature changes and mechanical stress without cracking. Your kitchen appliances and cookware made from glass ceramic maintain structural integrity over time, ensuring reliable performance even under heavy use. Ceramic glass, while heat resistant, tends to be more prone to thermal shock and wear, making glass ceramic the preferred choice for long-lasting, durable applications.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Material
Glass ceramic offers superior thermal shock resistance and durability, making it ideal for cookware and stovetops, but it tends to be more expensive and less impact-resistant compared to ceramic glass. Ceramic glass provides excellent heat resistance and aesthetic versatility at a lower cost, yet it is more prone to cracking under sudden temperature changes and requires careful handling. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize durability and performance or cost and design flexibility.
Choosing Between Glass Ceramic and Ceramic Glass
Choosing between glass ceramic and ceramic glass depends on their distinct properties and applications. Glass ceramic offers superior thermal resistance and durability, making it ideal for cookware and stovetops, while ceramic glass provides better clarity and aesthetic appeal, often used in architectural designs and fireplace panels. Understanding your specific needs ensures you select the material that balances performance and visual requirements effectively.
glass ceramic vs ceramic glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com