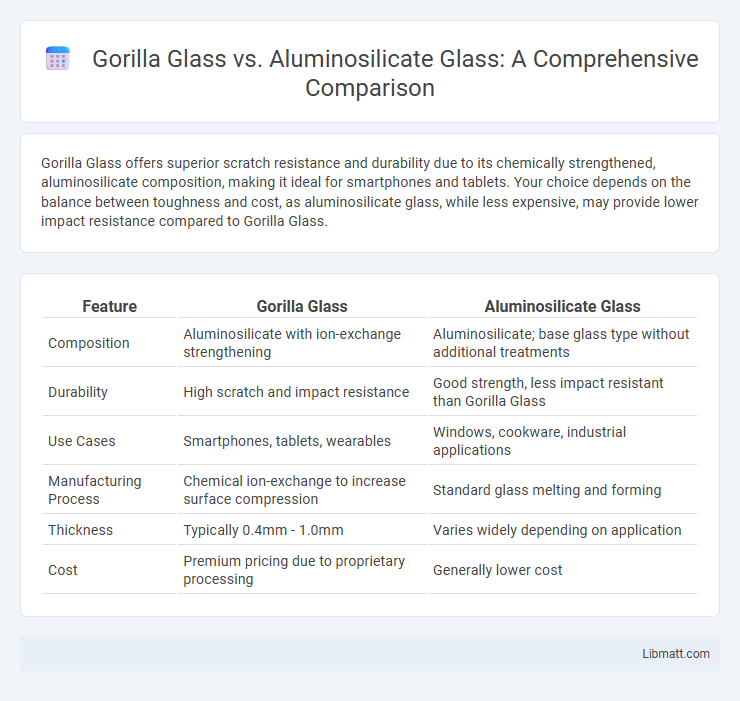
Gorilla Glass offers superior scratch resistance and durability due to its chemically strengthened, aluminosilicate composition, making it ideal for smartphones and tablets. Your choice depends on the balance between toughness and cost, as aluminosilicate glass, while less expensive, may provide lower impact resistance compared to Gorilla Glass.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Gorilla Glass | Aluminosilicate Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Aluminosilicate with ion-exchange strengthening | Aluminosilicate; base glass type without additional treatments |
| Durability | High scratch and impact resistance | Good strength, less impact resistant than Gorilla Glass |
| Use Cases | Smartphones, tablets, wearables | Windows, cookware, industrial applications |
| Manufacturing Process | Chemical ion-exchange to increase surface compression | Standard glass melting and forming |
| Thickness | Typically 0.4mm - 1.0mm | Varies widely depending on application |
| Cost | Premium pricing due to proprietary processing | Generally lower cost |
Introduction to Gorilla Glass and Aluminosilicate Glass
Gorilla Glass is a chemically strengthened alkali-aluminosilicate glass developed by Corning, widely used in smartphones and tablets for its high scratch resistance and durability. Aluminosilicate glass is a category of glass composed primarily of aluminum oxide and silicon dioxide, offering enhanced mechanical strength and thermal stability, commonly found in protective covers and industrial applications. Both materials leverage chemical composition and heat treatments to achieve superior toughness compared to standard soda-lime glass.
Composition and Manufacturing Differences
Gorilla Glass is an alkali-aluminosilicate sheet glass chemically strengthened through an ion-exchange process that replaces smaller sodium ions with larger potassium ions, resulting in increased surface compression and enhanced scratch resistance. Aluminosilicate glass, while also containing aluminum oxide and silicon dioxide, is often manufactured using different tempering methods such as heat treatment for improved toughness without the specific ion-exchange treatment characteristic of Gorilla Glass. The distinct chemical composition ratios and manufacturing techniques give Gorilla Glass superior strength-to-weight ratio and durability, making it highly suited for portable electronic devices compared to conventional aluminosilicate glasses.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Gorilla Glass offers superior strength and scratch resistance due to its chemically strengthened aluminosilicate composition, making it highly durable against daily wear and impact. Aluminosilicate glass also provides excellent durability but typically lacks the same level of thinness and toughness achieved by Gorilla Glass through advanced ion-exchange processes. Your choice between these materials depends on the required balance of strength, weight, and cost for specific applications like smartphones or rugged devices.
Scratch Resistance: Which Performs Better?
Gorilla Glass exhibits superior scratch resistance compared to aluminosilicate glass due to its chemically strengthened surface achieved through ion exchange processes. The high-density atomic structure of Gorilla Glass provides enhanced durability against abrasive materials, making it a preferred choice for smartphones and tablets. Aluminosilicate glass offers moderate scratch resistance but generally falls short in maintaining surface integrity under frequent contact with rough objects.
Impact and Drop Resistance
Gorilla Glass features chemically strengthened aluminosilicate composition with an ion-exchange process that enhances its atomic structure, resulting in superior impact and drop resistance compared to standard aluminosilicate glass. Your devices benefit from Gorilla Glass's ability to withstand high-impact forces and reduce the risk of cracking or shattering during accidental drops. While both materials offer durability, Gorilla Glass is specifically engineered to deliver exceptional protection in smartphones, tablets, and other portable electronics.
Clarity and Optical Properties
Gorilla Glass offers superior clarity with enhanced light transmission and reduced haze, providing sharper visuals and vibrant colors for your device screens. Aluminosilicate glass also delivers high optical quality with good transparency and resistance to yellowing over time, but typically falls short of the ultra-clear performance found in Gorilla Glass. Choosing Gorilla Glass ensures optimal visual experience, especially for high-resolution displays where clarity and color accuracy are critical.
Thickness and Weight Considerations
Gorilla Glass typically offers a thinner profile compared to aluminosilicate glass, contributing to lighter device components without sacrificing durability. Aluminosilicate glass generally requires increased thickness to achieve similar strength, resulting in a marginally heavier overall weight. Manufacturers often prefer Gorilla Glass for slim, lightweight designs in smartphones and tablets due to its optimized balance of thickness and weight.
Cost and Availability
Gorilla Glass, produced by Corning, generally commands a higher price due to its advanced chemical strengthening process and superior scratch resistance, making it prevalent in premium smartphones and tablets. Aluminosilicate glass, while offering good strength and durability, is more cost-effective and widely available for use in budget to mid-range electronic devices and other applications like automotive windows. The cost disparity stems from Gorilla Glass's proprietary manufacturing techniques, whereas aluminosilicate glass benefits from more established and scalable production methods, impacting overall availability in the market.
Typical Applications in Consumer Electronics
Gorilla Glass is extensively used in smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices due to its high scratch resistance and durability. Aluminosilicate glass is commonly applied in rugged electronics and vehicle displays where enhanced impact resistance is critical. Both materials offer lightweight protection, but Gorilla Glass dominates the mainstream consumer electronics market for touchscreens and device covers.
Future Trends and Innovations
Gorilla Glass continues to lead innovations with enhanced scratch resistance, improved toughness, and advancements in ultra-thin, flexible designs ideal for foldable devices. Aluminosilicate glass remains crucial for cost-effective, durable applications, with emerging treatments improving its chemical strengthening and thermal stability. Your choice between these materials will hinge on balancing cutting-edge protection and budget-friendly durability in future consumer electronics.
Gorilla glass vs aluminosilicate glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com