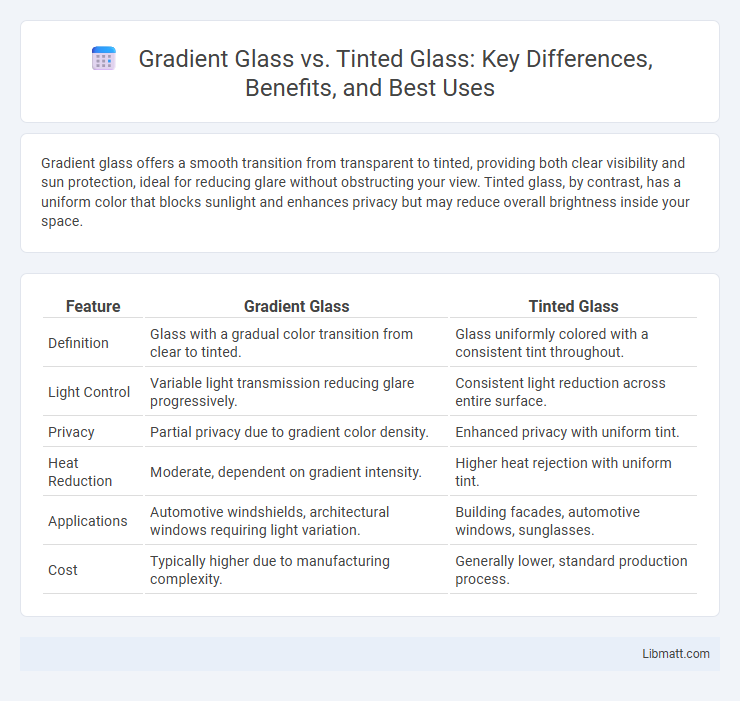
Gradient glass offers a smooth transition from transparent to tinted, providing both clear visibility and sun protection, ideal for reducing glare without obstructing your view. Tinted glass, by contrast, has a uniform color that blocks sunlight and enhances privacy but may reduce overall brightness inside your space.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Gradient Glass | Tinted Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Glass with a gradual color transition from clear to tinted. | Glass uniformly colored with a consistent tint throughout. |
| Light Control | Variable light transmission reducing glare progressively. | Consistent light reduction across entire surface. |
| Privacy | Partial privacy due to gradient color density. | Enhanced privacy with uniform tint. |
| Heat Reduction | Moderate, dependent on gradient intensity. | Higher heat rejection with uniform tint. |
| Applications | Automotive windshields, architectural windows requiring light variation. | Building facades, automotive windows, sunglasses. |
| Cost | Typically higher due to manufacturing complexity. | Generally lower, standard production process. |
Introduction to Gradient Glass and Tinted Glass
Gradient glass features a smooth transition from transparent to colored or shaded areas, offering both aesthetic appeal and functional benefits such as glare reduction. Tinted glass uniformly absorbs or reflects sunlight to lower heat and ultraviolet (UV) penetration, enhancing energy efficiency and privacy. Your choice between gradient and tinted glass depends on the desired balance of style, light control, and thermal performance for your space.
Understanding Gradient Glass: Features and Design
Gradient glass features a smooth transition from transparent to colored, offering both aesthetic appeal and functional benefits like light control and privacy. Its design allows natural light to filter softly while reducing glare and UV exposure, enhancing comfort in interiors or automotive applications. You can choose gradient glass for stylish, energy-efficient solutions that balance visibility with shading.
What is Tinted Glass? Key Characteristics
Tinted glass is specially treated with color pigments or metal oxides to reduce glare and limit solar heat transmission, enhancing energy efficiency and comfort. Key characteristics include varied color options, improved UV protection, and increased privacy without compromising visibility. Your choice of tinted glass can significantly impact your building's cooling costs and interior lighting quality.
Visual Appeal: Gradient vs Tinted Glass Aesthetics
Gradient glass offers a smooth transition of color that enhances architectural design by creating dynamic visual effects and depth, while tinted glass provides a uniform shade that reduces glare and adds a sleek, consistent look to windows and facades. The subtle color shifts in gradient glass allow for customizable aesthetics that can highlight interior spaces and complement varying light conditions, whereas tinted glass emphasizes functionality with a minimalist style. Both options improve energy efficiency, but gradient glass excels in delivering artistic appeal through its seamless blending of tones.
Light Control and Privacy Comparison
Gradient glass offers superior light control by allowing natural light to enter through the clear sections while gradually reducing glare and heat with its tinted gradient, ideal for spaces needing balanced illumination without harsh sunlight. Tinted glass provides consistent privacy and light reduction across the entire surface, effectively blocking visibility and reducing brightness but can significantly darken interiors. Choosing between gradient and tinted glass depends on the desired blend of daylight access and privacy levels, with gradient glass favoring adjustable light diffusion and tinted glass prioritizing uniform shading and concealment.
Energy Efficiency: Gradient Glass vs Tinted Glass
Gradient glass enhances energy efficiency by allowing varying light transmission, reducing heat gain while maximizing natural daylight. Tinted glass uniformly limits sunlight, which can lower cooling costs but may reduce interior brightness. Your choice depends on balancing energy savings with desired daylight levels for optimal comfort and utility.
UV Protection Capabilities
Gradient glass offers partial UV protection by incorporating a gradual tint that reduces sunlight exposure primarily in the upper section of the glass, effectively shielding against harmful UV rays while maintaining visibility. Tinted glass provides consistent UV protection across the entire surface by embedding UV-absorbing materials, resulting in more effective defense against UV radiation. For enhanced UV protection, tinted glass is generally preferred due to its uniform filtering properties throughout the glass panel.
Durability and Maintenance Differences
Gradient glass features a gradual transition from clear to shaded, which helps reduce visible dirt and minor scratches, enhancing its durability over time. Tinted glass offers uniform shading that can better withstand UV damage, decreasing fading and structural degradation, but may show smudges more prominently. Maintenance for gradient glass generally requires gentler cleaning to preserve the gradient effect, while tinted glass demands routine checks for coating wear to maintain its protective qualities.
Applications in Architecture and Interior Design
Gradient glass enhances architectural and interior designs by offering dynamic light control and aesthetic versatility, making it ideal for modern facades, partitions, and skylights. Tinted glass, known for its ability to reduce glare and improve energy efficiency, is commonly used in windows, curtain walls, and sunrooms to create comfortable indoor environments. Your choice between gradient and tinted glass depends on the desired balance between visual appeal and functional performance in specific architectural applications.
Cost Considerations and Value for Investment
Gradient glass typically costs more than tinted glass due to its complex manufacturing process, offering customized light diffusion and aesthetic appeal that enhances property value. Tinted glass, while more affordable and effective in reducing glare and heat, may not provide the same premium look or energy savings as gradient glass. Your investment in gradient glass can yield higher long-term value through improved energy efficiency and design versatility compared to the lower initial cost but limited benefits of tinted glass.
Gradient glass vs tinted glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com