Wired glass offers enhanced fire resistance by embedding a metal mesh within the glass to prevent shattering during high temperatures, making it ideal for safety in fire-rated doors and windows. Tempered glass provides superior strength and shatter resistance by undergoing a heat treatment process, which causes it to break into small, blunt pieces for safer impact protection in everyday use.
Table of Comparison
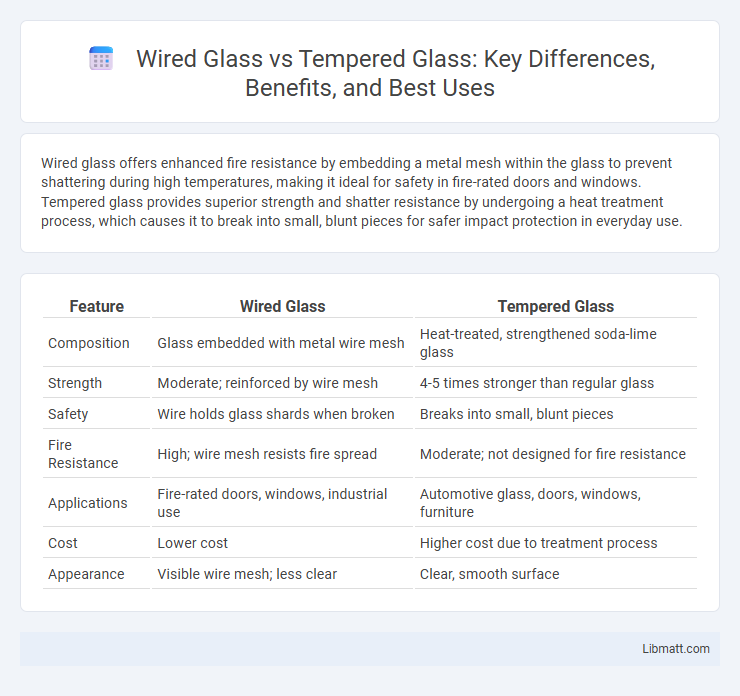
| Feature | Wired Glass | Tempered Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Glass embedded with metal wire mesh | Heat-treated, strengthened soda-lime glass |
| Strength | Moderate; reinforced by wire mesh | 4-5 times stronger than regular glass |
| Safety | Wire holds glass shards when broken | Breaks into small, blunt pieces |
| Fire Resistance | High; wire mesh resists fire spread | Moderate; not designed for fire resistance |
| Applications | Fire-rated doors, windows, industrial use | Automotive glass, doors, windows, furniture |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost due to treatment process |
| Appearance | Visible wire mesh; less clear | Clear, smooth surface |
Introduction: Wired Glass vs Tempered Glass
Wired glass features embedded metal mesh that enhances fire resistance and prevents shattering, making it ideal for fire-rated doors and partitions. Tempered glass undergoes a heat treatment process that significantly increases its strength and causes it to break into small, blunt pieces, ensuring safety in impact-prone areas like windows and shower enclosures. Choosing between wired glass and tempered glass depends on your specific needs for fire protection versus impact resistance.
What Is Wired Glass?
Wired glass is a type of safety glass that incorporates a mesh of thin steel wires embedded within the glass to prevent shattering upon impact. This design enhances fire resistance by maintaining the integrity of the glass during high temperatures, making it suitable for fire-rated windows and doors. While wired glass provides additional security and fire protection, it is generally less resistant to impact compared to tempered glass, which is heat-treated to increase strength and safety.
What Is Tempered Glass?
Tempered glass is a type of safety glass processed by controlled thermal or chemical treatments to increase its strength compared to standard glass. It is designed to shatter into small, blunt pieces rather than sharp shards, reducing injury risks upon breakage. Your choice of tempered glass ensures enhanced durability and safety, making it ideal for applications such as windows, doors, and automotive glass.
Key Differences Between Wired and Tempered Glass
Wired glass contains a mesh of metal wires embedded within the glass, enhancing fire resistance and preventing shattering, whereas tempered glass undergoes thermal tempering to increase strength and break into small, blunt pieces for safety. Wired glass typically offers superior fire protection and transparency retention during flames but has lower impact resistance compared to tempered glass, which is designed for high-impact durability and safety glazing. Choosing between wired and tempered glass depends on prioritizing fire resistance or mechanical strength in applications such as windows, doors, and partitions.
Strength and Impact Resistance Comparison
Tempered glass offers superior strength and impact resistance compared to wired glass, making it less prone to shattering under high stress. Wired glass incorporates a metal mesh that holds fragments together upon breakage, but it is more brittle and less resistant to direct impacts. When prioritizing safety and durability, especially for your applications requiring robust protection, tempered glass is generally the more reliable option.
Fire Safety and Code Compliance
Wired glass offers enhanced fire safety by maintaining integrity and limiting flame spread during fires, making it compliant with many fire-rated building codes. Tempered glass, while stronger and more resistant to impact, may not meet fire safety standards as it can shatter under extreme heat. Building codes often require wired glass for fire-rated assemblies in commercial and institutional settings due to its proven performance in containing fire and smoke.
Applications and Common Uses
Wired glass is commonly used in fire-rated doors and windows due to its enhanced fire resistance and ability to contain flames, making it ideal for schools, hospitals, and industrial buildings. Tempered glass is favored for applications requiring high impact resistance and safety, such as automotive windows, shower doors, and glass doors in homes and commercial spaces. Your choice between wired glass and tempered glass should depend on whether fire protection or strength and safety against shattering is the primary concern.
Cost and Installation Considerations
Wired glass generally costs less than tempered glass, making it a budget-friendly option for projects requiring fire resistance and security. Installation of wired glass is typically simpler due to its rigidity and weight, reducing labor time and costs compared to tempered glass, which requires specialized cutting and handling techniques. Your choice depends on balancing initial expenses with long-term benefits such as durability and safety compliance.
Safety Concerns and Performance
Wired glass offers enhanced fire resistance and maintains structural integrity during high-temperature exposure but poses greater risk of shattering into sharp, hazardous fragments upon impact. Tempered glass provides superior impact resistance and breaks into small, blunt granules, significantly reducing injury risk and improving overall safety in everyday use. For high-traffic or safety-critical environments, tempered glass outperforms wired glass in impact resistance and safe breakage while wired glass remains preferred for fire-rated applications.
Which Glass Type Is Better for Your Project?
Tempered glass offers superior strength and safety compared to wired glass, making it ideal for projects requiring impact resistance and compliance with modern building codes. Wired glass provides fire resistance and prevents glass from shattering upon breakage but is generally weaker and less resistant to impacts. Selecting between wired and tempered glass depends on prioritizing either fire safety standards or enhanced durability and safety features for your specific project needs.
wired glass vs tempered glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com