Barrier coating forms a protective layer on the surface of materials to prevent moisture, oxygen, or contaminants from penetrating, enhancing shelf life and product quality. Extrusion coating involves applying a molten polymer layer onto substrates through a coating die, creating a strong, uniform bond ideal for packaging and waterproofing applications.
Table of Comparison
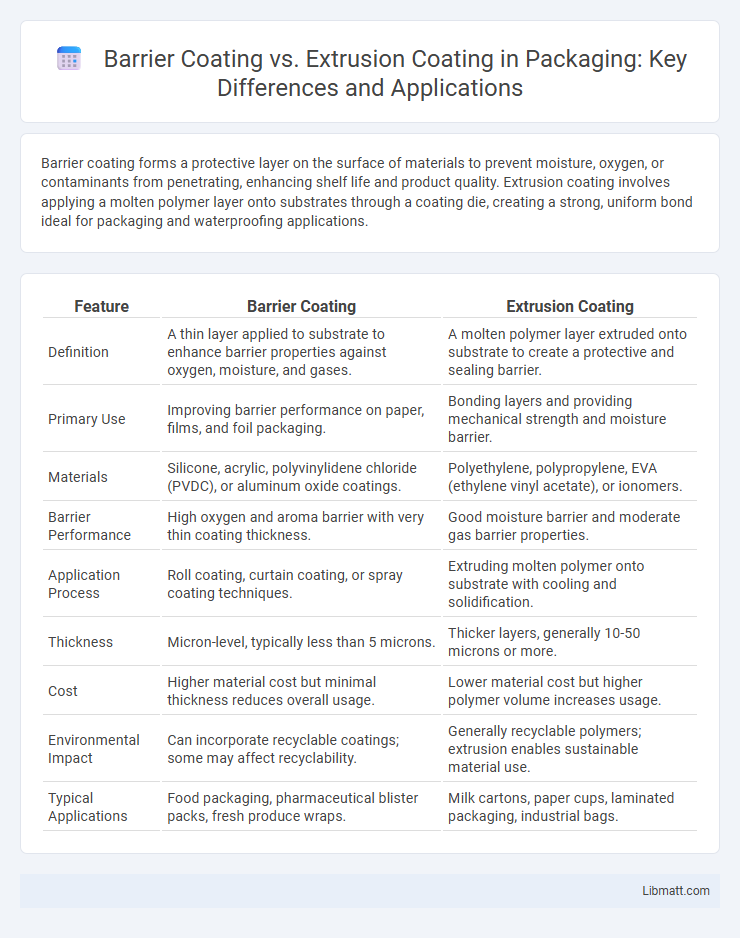
| Feature | Barrier Coating | Extrusion Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A thin layer applied to substrate to enhance barrier properties against oxygen, moisture, and gases. | A molten polymer layer extruded onto substrate to create a protective and sealing barrier. |
| Primary Use | Improving barrier performance on paper, films, and foil packaging. | Bonding layers and providing mechanical strength and moisture barrier. |
| Materials | Silicone, acrylic, polyvinylidene chloride (PVDC), or aluminum oxide coatings. | Polyethylene, polypropylene, EVA (ethylene vinyl acetate), or ionomers. |
| Barrier Performance | High oxygen and aroma barrier with very thin coating thickness. | Good moisture barrier and moderate gas barrier properties. |
| Application Process | Roll coating, curtain coating, or spray coating techniques. | Extruding molten polymer onto substrate with cooling and solidification. |
| Thickness | Micron-level, typically less than 5 microns. | Thicker layers, generally 10-50 microns or more. |
| Cost | Higher material cost but minimal thickness reduces overall usage. | Lower material cost but higher polymer volume increases usage. |
| Environmental Impact | Can incorporate recyclable coatings; some may affect recyclability. | Generally recyclable polymers; extrusion enables sustainable material use. |
| Typical Applications | Food packaging, pharmaceutical blister packs, fresh produce wraps. | Milk cartons, paper cups, laminated packaging, industrial bags. |
Introduction to Barrier Coating and Extrusion Coating
Barrier coating involves applying a thin layer of material to substrates like paper or plastic films to enhance moisture, gas, or aroma resistance, crucial for food packaging preservation. Extrusion coating uses molten polymers such as polyethylene to create a continuous, protective film over substrates, providing mechanical strength and moisture resistance. Both techniques play vital roles in packaging technologies, with barrier coating emphasizing functional protection and extrusion coating focusing on physical durability.
Defining Barrier Coating: Key Features
Barrier coating enhances packaging materials by applying thin layers of polymers or inorganic substances that provide superior protection against moisture, oxygen, and contaminants. This coating improves shelf life and product integrity without significantly increasing packaging weight or compromising recyclability. Unlike extrusion coating, which melts and bonds a plastic resin to substrates, barrier coatings specifically target permeability control for sensitive products like food and pharmaceuticals.
Understanding Extrusion Coating Technology
Extrusion coating technology involves applying a molten polymer layer onto a substrate, creating a uniform, durable barrier that enhances moisture and gas resistance. Unlike barrier coating, which uses thin chemical layers for protection, extrusion coating forms a thicker, more robust film ideal for flexible packaging applications. You benefit from improved product shelf life and packaging strength through precise control of extrusion coating parameters.
Materials Used in Barrier vs Extrusion Coating
Barrier coatings primarily utilize materials such as polyvinylidene chloride (PVDC), polyethylene terephthalate (PET), and ethylene vinyl alcohol (EVOH) to provide superior moisture, oxygen, and aroma resistance. Extrusion coatings commonly employ thermoplastics like polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), and ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA), which offer strong adhesion and durability but less effective barrier properties. The choice of materials directly affects the performance in food packaging applications where barrier coatings excel in preserving freshness, while extrusion coatings enhance mechanical strength and sealability.
Performance Comparison: Barrier Properties
Barrier coating offers superior protection against oxygen, moisture, and contaminants due to its multi-layer formulation, enhancing shelf life for sensitive products. Extrusion coating provides a strong, durable seal ideal for mechanical resistance but may have lower resistance to gas permeability compared to barrier coatings. Your choice depends on the required barrier properties for preserving product integrity under specific environmental conditions.
Cost Implications of Each Coating Method
Barrier coating typically involves higher material and application costs due to specialized polymers designed to enhance product protection, resulting in increased overall expenses. Extrusion coating offers a cost-effective alternative by applying a molten polymer layer directly onto substrates, reducing production time and waste. Your choice between these methods depends on balancing budget constraints with desired barrier performance and product longevity.
Application Areas: Barrier vs Extrusion Coating
Barrier coating is commonly used in food packaging, pharmaceuticals, and electronics to provide enhanced protection against moisture, oxygen, and contaminants, ensuring product stability and extended shelf life. Extrusion coating finds application in flexible packaging, paperboard lamination, and industrial uses, offering strong adhesion and improved mechanical properties for products like liquid packaging cartons and hygiene products. Your choice between barrier and extrusion coating depends on the specific protection requirements and substrate compatibility of your application area.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Barrier coating typically uses fewer chemical solvents and can be more environmentally friendly by reducing energy consumption during application compared to extrusion coating. Extrusion coating involves melting polymers at high temperatures, resulting in higher energy use and increased carbon emissions. Choosing barrier coatings may improve Your packaging's sustainability by lowering its overall ecological footprint.
Recent Innovations in Coating Technologies
Recent innovations in barrier coating technologies have enhanced moisture and oxygen resistance by incorporating nanomaterials and bio-based polymers, significantly extending food shelf life. Extrusion coating advancements now enable ultrathin films with superior adhesion and heat sealability, improving packaging durability and recyclability. Your choice between barrier and extrusion coatings should consider these technological improvements to optimize product protection and sustainability.
Choosing the Right Coating: Factors to Consider
Selecting between barrier coating and extrusion coating depends on factors such as the type of substrate, desired moisture and oxygen resistance, and cost-effectiveness. Barrier coatings excel in creating thin, uniform layers that enhance shelf life by preventing gas and moisture permeation, ideal for flexible packaging materials. Extrusion coatings provide robust mechanical strength and heat-sealability, making them suitable for products requiring durability and strong adhesion to substrates like paperboard.
Barrier coating vs extrusion coating Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com