Manual filling requires you to enter data or complete forms by hand, which can be time-consuming and prone to errors. Automatic filling uses software to quickly populate fields with saved information, increasing efficiency and reducing mistakes in your workflow.
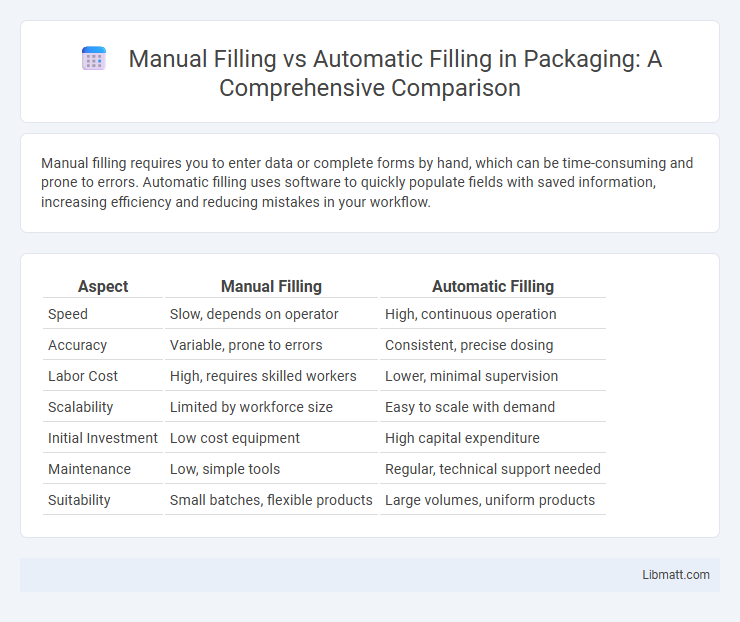
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Manual Filling | Automatic Filling |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Slow, depends on operator | High, continuous operation |
| Accuracy | Variable, prone to errors | Consistent, precise dosing |
| Labor Cost | High, requires skilled workers | Lower, minimal supervision |
| Scalability | Limited by workforce size | Easy to scale with demand |
| Initial Investment | Low cost equipment | High capital expenditure |
| Maintenance | Low, simple tools | Regular, technical support needed |
| Suitability | Small batches, flexible products | Large volumes, uniform products |
Introduction to Filling Methods
Manual filling involves human operators physically placing products or materials into containers, allowing for flexibility and control in small-scale or customized production. Automatic filling uses machinery to dispense precise volumes or weights at high speed, ensuring consistent output and efficiency in large-scale manufacturing. Choosing between these methods depends on production volume, accuracy requirements, and cost considerations.
Overview of Manual Filling
Manual filling involves inputting data or materials by hand, requiring direct human intervention and attention to detail. This method is commonly used in small-scale or customized production processes where precision is essential, despite being time-consuming and labor-intensive. Manual filling offers flexibility for handling varied product sizes and types, but it typically results in slower throughput compared to automated systems.
Overview of Automatic Filling
Automatic filling utilizes advanced machinery and sensors to dispense precise quantities of liquids or materials into containers, significantly enhancing production speed and accuracy. This technology reduces human error and contamination risks by maintaining consistent filling volumes and hygiene standards during packaging processes. Industries such as pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, and cosmetics widely implement automatic filling to boost efficiency and ensure quality control.
Key Differences Between Manual and Automatic Filling
Manual filling requires human intervention to operate machinery and manage product placement, resulting in slower processing speeds and higher labor costs. Automatic filling utilizes advanced sensors and programmable machines, enhancing accuracy, efficiency, and consistency in high-volume production environments. Your choice impacts operational productivity, error rates, and overall scalability.
Efficiency Comparison: Speed and Output
Automatic filling significantly outperforms manual filling in speed, often completing tasks in a fraction of the time by utilizing advanced machinery and automation technologies. Manual filling relies on human labor, which increases the risk of inconsistencies and slower output rates, limiting overall efficiency in high-volume production environments. Optimizing your operations with automatic filling systems can dramatically boost throughput and reduce labor costs.
Accuracy and Consistency in Filling
Automatic filling systems deliver superior accuracy and consistency compared to manual filling by minimizing human errors and ensuring uniform product volumes. These systems utilize precise sensors and calibrated mechanisms to maintain consistent fill levels, which reduces product waste and enhances quality control. Manual filling often results in variable fill amounts due to operator fatigue and inconsistencies, compromising product standardization and customer satisfaction.
Labor and Cost Considerations
Manual filling requires significant labor investment, leading to higher operational costs due to increased workforce hours and potential for human error. Automatic filling systems reduce labor demands and improve efficiency, resulting in lower long-term expenses despite higher initial equipment investment. The cost-benefit balance favors automation in high-volume production environments where labor savings and consistency are critical.
Suitability for Different Productions Scales
Manual filling is best suited for small-scale or custom production runs where flexibility and precision are crucial, while automatic filling excels in large-scale manufacturing with high-speed, consistent output requirements. Your choice depends on production volume, product type, and budget constraints, as manual processes allow for detailed control and customization. Automation reduces labor costs and minimizes human error, making it ideal for mass production environments.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Manual filling requires frequent maintenance checks to ensure valves and seals function correctly, with troubleshooting often relying on visual inspections and manual adjustments. Automatic filling systems incorporate sensors and automated controls that facilitate real-time diagnostics and streamlined maintenance schedules, reducing downtime. Your choice affects maintenance complexity and troubleshooting efficiency, with automation offering proactive system alerts to preempt issues.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Filling Method
Manual filling offers precision and control for small-scale or customized tasks, while automatic filling ensures speed and consistency in high-volume production. Your decision should balance accuracy needs, production scale, and cost efficiency, with automation favored for large batches and manual methods suitable for detailed, variable fills. Selecting the right filling method optimizes workflow, reduces waste, and enhances overall productivity.
Manual filling vs automatic filling Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com