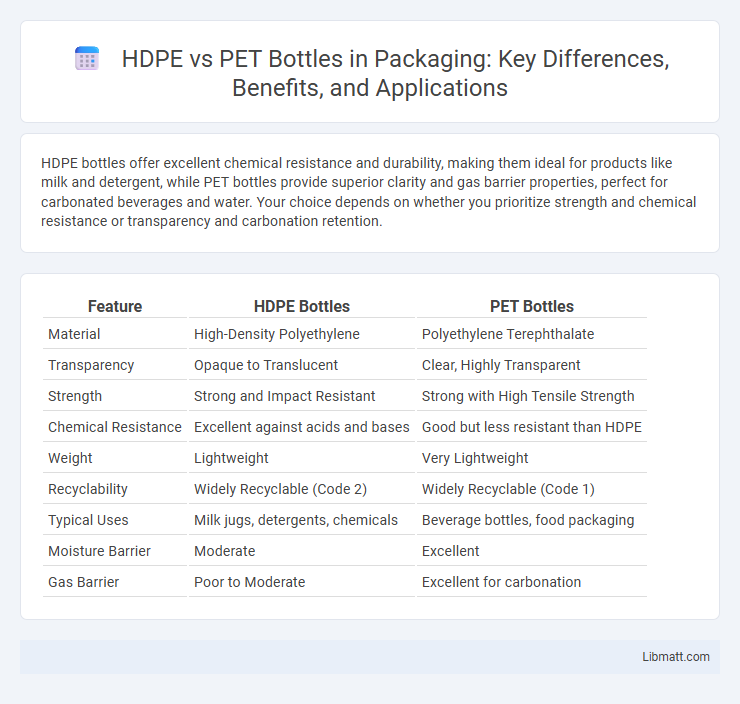
HDPE bottles offer excellent chemical resistance and durability, making them ideal for products like milk and detergent, while PET bottles provide superior clarity and gas barrier properties, perfect for carbonated beverages and water. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize strength and chemical resistance or transparency and carbonation retention.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | HDPE Bottles | PET Bottles |
|---|---|---|
| Material | High-Density Polyethylene | Polyethylene Terephthalate |
| Transparency | Opaque to Translucent | Clear, Highly Transparent |
| Strength | Strong and Impact Resistant | Strong with High Tensile Strength |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent against acids and bases | Good but less resistant than HDPE |
| Weight | Lightweight | Very Lightweight |
| Recyclability | Widely Recyclable (Code 2) | Widely Recyclable (Code 1) |
| Typical Uses | Milk jugs, detergents, chemicals | Beverage bottles, food packaging |
| Moisture Barrier | Moderate | Excellent |
| Gas Barrier | Poor to Moderate | Excellent for carbonation |
Introduction to HDPE and PET Bottles
HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) bottles are known for their durability, chemical resistance, and lightweight properties, making them ideal for packaging household products and chemicals. PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) bottles offer excellent clarity, strength, and are widely used for beverages and food packaging due to their superior barrier properties. Understanding the distinct benefits of HDPE versus PET bottles helps you select the right material based on your product's storage needs and sustainability goals.
Chemical Composition and Structure
HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) bottles consist of long-chain hydrocarbons with a linear structure, providing high tensile strength and resistance to chemicals and moisture. PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) bottles are composed of repeating ester units derived from terephthalic acid and ethylene glycol, resulting in a thermoplastic polyester with excellent clarity and gas barrier properties. The chemical structure of HDPE grants it rigidity and chemical resistance, while PET's aromatic ester bonds offer enhanced strength and recyclability.
Manufacturing Processes
HDPE bottles are produced using blow molding techniques, primarily extrusion blow molding, which shapes the molten plastic into durable, flexible containers suitable for a variety of products. PET bottles undergo injection stretch blow molding, a process that involves injecting molten PET into a mold, then stretching and blowing it to create strong, clear containers ideal for beverages and food packaging. Understanding the differences in these manufacturing processes can help you choose the best bottle type for your packaging needs based on strength, clarity, and production efficiency.
Physical Properties Comparison
HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) bottles exhibit higher impact resistance and greater flexibility compared to PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) bottles, which offer superior clarity and higher tensile strength. PET bottles demonstrate better gas barrier properties, making them ideal for carbonation retention, whereas HDPE's moisture barrier is more effective for non-carbonated liquids. The melting point of HDPE ranges around 130degC, lower than PET's approximately 250degC, influencing their respective processing and recycling methods.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
HDPE bottles have a lower environmental impact due to their higher recyclability rate and ability to be recycled multiple times into products like piping and plastic lumber. PET bottles, while widely recycled into fibers for clothing and carpeting, often face challenges with contamination and degradation in quality after recycling. Both materials contribute to reducing landfill waste, but HDPE's robustness and recyclability make it a more sustainable choice in packaging applications.
Safety and Food Compatibility
HDPE bottles offer excellent chemical resistance and are widely recognized as safe for food and beverage storage, meeting FDA and EU regulatory standards for food contact materials. PET bottles provide high clarity and strong barrier properties against moisture and gases, ensuring freshness while being approved for direct food contact by global health authorities. Both materials are BPA-free and widely used in the food industry, but HDPE is preferred for opaque or heavy-duty applications, whereas PET is chosen for its transparency and lightweight characteristics.
Common Uses and Applications
HDPE bottles are widely used for milk containers, detergent bottles, and shampoo packaging due to their durability and resistance to chemicals. PET bottles are commonly found in beverage containers such as water, soda, and juice bottles because of their clarity and strong barrier properties. Your choice depends on the specific application requirements, especially regarding chemical resistance and transparency.
Cost Considerations
HDPE bottles generally offer lower production costs compared to PET bottles due to cheaper raw materials and simpler manufacturing processes. Your choice of PET bottles entails higher expenses but benefits from superior clarity and strength, which can justify the cost in premium product packaging. Evaluating volume requirements and desired bottle properties will help determine the most cost-effective option for your packaging needs.
Pros and Cons of HDPE vs PET Bottles
HDPE bottles offer superior chemical resistance and are more impact-resistant, making them ideal for household and industrial products, but they have lower clarity compared to PET bottles. PET bottles provide excellent transparency and are lightweight with high tensile strength, perfect for beverages and food packaging, though they are less resistant to heat and can be more prone to gas permeability. Your choice between HDPE and PET bottles depends on the specific needs of durability, appearance, and product compatibility.
Choosing the Right Bottle Material
HDPE bottles offer excellent chemical resistance, making them ideal for household cleaners and milk packaging, while PET bottles provide superior clarity and gas barrier properties, commonly used for beverages and food products. Selecting the right bottle material depends on factors like product compatibility, required shelf life, and sustainability goals, with PET being widely recycled and HDPE offering high durability. Consider environmental impact and regulatory compliance to optimize packaging performance and consumer safety.
HDPE vs PET bottles Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com