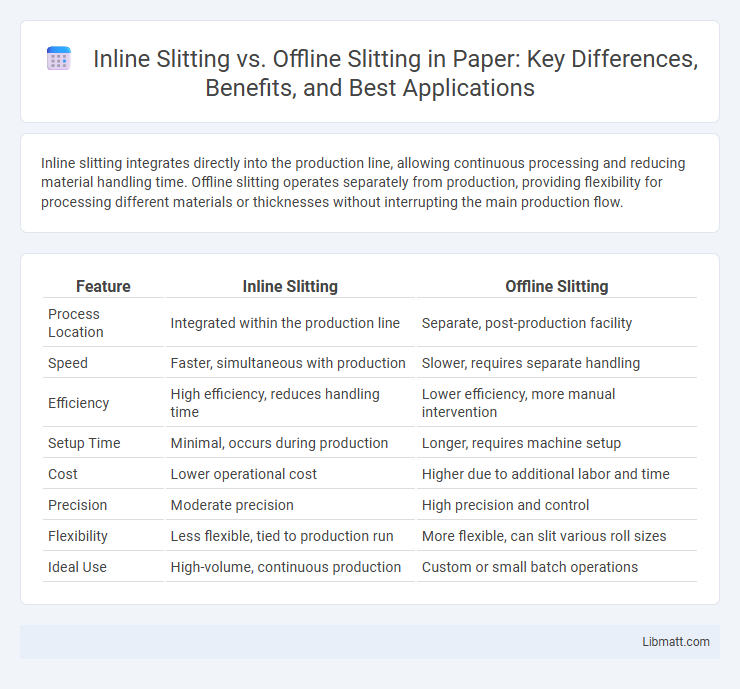
Inline slitting integrates directly into the production line, allowing continuous processing and reducing material handling time. Offline slitting operates separately from production, providing flexibility for processing different materials or thicknesses without interrupting the main production flow.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Inline Slitting | Offline Slitting |
|---|---|---|
| Process Location | Integrated within the production line | Separate, post-production facility |
| Speed | Faster, simultaneous with production | Slower, requires separate handling |
| Efficiency | High efficiency, reduces handling time | Lower efficiency, more manual intervention |
| Setup Time | Minimal, occurs during production | Longer, requires machine setup |
| Cost | Lower operational cost | Higher due to additional labor and time |
| Precision | Moderate precision | High precision and control |
| Flexibility | Less flexible, tied to production run | More flexible, can slit various roll sizes |
| Ideal Use | High-volume, continuous production | Custom or small batch operations |
Introduction to Slitting Processes
Inline slitting integrates the cutting process directly into the production line, streamlining workflow and reducing handling time for your materials. Offline slitting, performed separately from production, allows for greater control and flexibility in cutting specifications but may increase turnaround time. Understanding these differences helps optimize efficiency and quality based on your specific operational needs.
What is Inline Slitting?
Inline slitting is a process where the material is cut into narrower strips during the main production workflow, directly on the production line. This method enhances efficiency by reducing handling time and minimizing material waste compared to offline slitting, which occurs after the primary production. Your manufacturing operations benefit from faster turnaround and improved precision with inline slitting technology.
What is Offline Slitting?
Offline slitting is a process where large rolls of material are unwound and slit into narrower rolls separately from the primary production line. This method allows for greater flexibility in adjusting slit widths and accommodating varying production schedules without halting the main manufacturing process. Offline slitting is commonly used in industries such as paper, film, and metal to prepare material for specific applications or downstream processes.
Key Differences Between Inline and Offline Slitting
Inline slitting integrates directly into the production line, allowing for real-time cutting of materials without interrupting the manufacturing process, which enhances efficiency and reduces handling time. Offline slitting operates as a separate process, where materials are cut after production, offering greater flexibility for customization and quality control but requiring additional handling and time. Your choice between inline and offline slitting depends on factors such as production speed, precision requirements, and workflow optimization.
Advantages of Inline Slitting
Inline slitting offers significant advantages by integrating the slitting process directly into the production line, which reduces material handling and minimizes waste. This method enhances efficiency and productivity by enabling real-time quality control and faster turnaround times for converting operations. Your manufacturing workflow benefits from lower labor costs and a streamlined process, making inline slitting ideal for high-volume or just-in-time production environments.
Advantages of Offline Slitting
Offline slitting offers the advantage of greater flexibility in handling various materials and thicknesses without disrupting the main production line, ensuring minimal downtime. It enables precise customization and maintenance of slitting equipment independently, which enhances product quality and reduces operational risks. Your manufacturing process benefits from higher throughput and consistent slit quality due to dedicated slitting systems optimized for specific tasks.
Applications for Inline Slitting
Inline slitting is ideal for high-speed production lines in packaging, printing, and converting industries where continuous processing enhances efficiency. It is commonly applied in manufacturing flexible packaging films, labels, tapes, and laminates, allowing simultaneous printing, coating, and slitting without stopping the line. This method reduces material handling and downtime, improving productivity in sectors requiring precise and consistent slit widths.
Applications for Offline Slitting
Offline slitting is widely used in industries requiring high precision and flexibility, such as packaging, converting, and label manufacturing. It allows for detailed customization and handling of various materials like films, foils, and paper in smaller production runs or specialized orders. This method supports frequent changeovers and complex slitting patterns that are essential for diverse product specifications.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Slitting Method
Choosing between inline slitting and offline slitting depends on production speed, material type, and budget constraints. Inline slitting offers higher efficiency by integrating directly into the production line, ideal for large-scale continuous runs, while offline slitting provides greater flexibility and precision for shorter or varied job requirements. Evaluating your specific volume, quality demands, and equipment investment will ensure the optimal slitting method for your operation.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Slitting Process
Selecting the right slitting process depends on production volume, precision requirements, and workflow efficiency. Inline slitting integrates directly into the production line for faster turnaround and reduced handling, making it ideal for high-volume, continuous runs. Offline slitting offers greater flexibility and precision control, suitable for shorter runs or specialized materials requiring careful handling.
Inline slitting vs offline slitting Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com