Bleached pulp undergoes chemical treatment to remove lignin, resulting in a brighter, whiter appearance ideal for high-quality paper products, while unbleached pulp retains its natural color and fibers, providing increased strength and environmental benefits by reducing chemical usage. Your choice between the two depends on whether you prioritize aesthetic appeal or ecological sustainability in your paper applications.
Table of Comparison
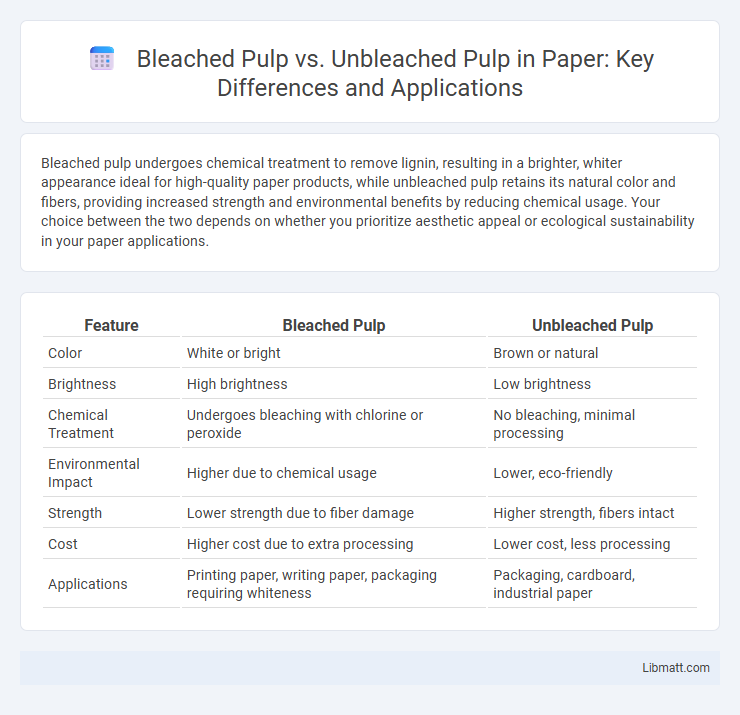
| Feature | Bleached Pulp | Unbleached Pulp |
|---|---|---|
| Color | White or bright | Brown or natural |
| Brightness | High brightness | Low brightness |
| Chemical Treatment | Undergoes bleaching with chlorine or peroxide | No bleaching, minimal processing |
| Environmental Impact | Higher due to chemical usage | Lower, eco-friendly |
| Strength | Lower strength due to fiber damage | Higher strength, fibers intact |
| Cost | Higher cost due to extra processing | Lower cost, less processing |
| Applications | Printing paper, writing paper, packaging requiring whiteness | Packaging, cardboard, industrial paper |
Introduction to Pulp Types
Bleached pulp undergoes chemical treatments to remove lignin and impurities, resulting in a brighter, whiter appearance ideal for high-quality paper products requiring smooth texture and aesthetic appeal. Unbleached pulp retains more lignin, offering increased strength and durability, making it suitable for packaging materials and industrial applications where color brightness is less critical. The choice between bleached and unbleached pulp depends on the specific requirements for strength, appearance, and environmental considerations in paper manufacturing.
What is Bleached Pulp?
Bleached pulp is chemically treated wood pulp that has undergone a whitening process to remove lignin, resulting in a higher brightness and purity level compared to unbleached pulp. This treatment enhances the pulp's strength, softness, and suitability for producing high-quality paper products such as printing paper, tissue, and packaging materials. Your choice of bleached pulp ensures a cleaner appearance and improved performance in applications requiring a pristine, white finish.
What is Unbleached Pulp?
Unbleached pulp is a type of wood pulp that retains its natural brown color and is not subjected to chemical bleaching processes, preserving lignin and other natural components of the wood fibers. It offers higher strength and reduced chemical use compared to bleached pulp, making it a preferred choice for products such as cardboard, paper bags, and packaging materials where whiteness is not critical. The environmental impact of unbleached pulp is generally lower, as it avoids the pollutants and energy consumption associated with bleaching agents like chlorine or chlorine dioxide.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Bleached pulp undergoes chemical treatments such as chlorine dioxide or hydrogen peroxide to remove lignin and achieve a bright, white appearance, enhancing paper quality and purity. Unbleached pulp retains its natural brown color as it skips these bleaching stages, resulting in a stronger fiber structure but a darker product. Your choice between bleached and unbleached pulp impacts manufacturing costs, environmental footprint, and the intended use of the final paper product.
Environmental Impact Analysis
Bleached pulp undergoes chemical treatments that release chlorine compounds and other pollutants, contributing to significant water pollution and ecosystem damage. Unbleached pulp production reduces chemical usage, resulting in lower emissions of harmful byproducts and less environmental contamination. Choosing unbleached pulp supports sustainable forestry practices and decreases the carbon footprint of paper manufacturing.
Chemical Usage in Production
Bleached pulp production involves the use of chlorine-based compounds, oxygen, or hydrogen peroxide to remove lignin and achieve a white appearance, which increases chemical consumption and environmental impact. Unbleached pulp retains most of its natural lignin, requiring fewer chemicals and resulting in lower chemical oxygen demand (COD) and less hazardous waste. The chemical savings in unbleached pulp production make it more sustainable, but it results in darker pulp suitable for packaging and other applications where whiteness is not critical.
Strength and Quality Differences
Bleached pulp exhibits higher brightness and purity due to the removal of lignin, which enhances the overall appearance but can slightly reduce fiber strength compared to unbleached pulp. Unbleached pulp retains lignin, contributing to greater tensile strength, durability, and resistance to processing stresses, making it ideal for packaging and industrial uses. The choice between bleached and unbleached pulp depends on the required balance of aesthetic quality versus mechanical strength.
Common Applications and Uses
Bleached pulp is widely used in the production of high-quality paper products such as printing paper, writing paper, and sanitary products due to its bright, white appearance and smooth texture. Unbleached pulp, favored for its strength and natural color, is commonly found in packaging materials, cardboard, and paper bags where durability is essential. Both types serve crucial roles in the paper industry, with bleached pulp preferred for aesthetics and unbleached pulp for toughness and environmental benefits.
Cost Considerations
Bleached pulp typically incurs higher production costs due to additional chemical processing and energy consumption, increasing the expense of raw materials and manufacturing. Unbleached pulp offers cost savings by eliminating bleaching stages, resulting in lower operational expenses and reduced chemical usage. These cost differences significantly impact pricing strategies and procurement decisions in industries like paper manufacturing and packaging.
Sustainability and Future Trends
Bleached pulp undergoes chemical treatments that increase brightness but raise environmental concerns due to high water and energy use, while unbleached pulp retains natural fibers, offering a more sustainable option with lower ecological impact. Future trends emphasize developing eco-friendly bleaching technologies and increasing the use of unbleached pulp in packaging and textiles to reduce carbon footprints and enhance recyclability. Your choice of pulp can significantly influence sustainability goals by balancing product quality with environmental responsibility.
Bleached pulp vs unbleached pulp Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com