Neutral papermaking uses alkaline pH conditions to enhance paper longevity and strength by preventing acid degradation, while acid papermaking involves acidic conditions that can lead to faster paper deterioration. Your choice between neutral and acid papermaking impacts the durability and archival quality of the final product.
Table of Comparison
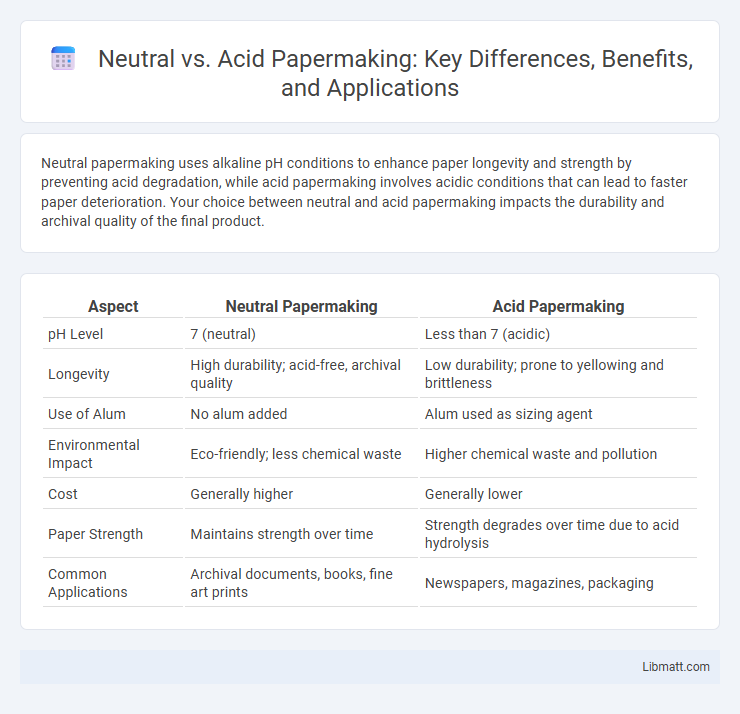
| Aspect | Neutral Papermaking | Acid Papermaking |
|---|---|---|
| pH Level | 7 (neutral) | Less than 7 (acidic) |
| Longevity | High durability; acid-free, archival quality | Low durability; prone to yellowing and brittleness |
| Use of Alum | No alum added | Alum used as sizing agent |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly; less chemical waste | Higher chemical waste and pollution |
| Cost | Generally higher | Generally lower |
| Paper Strength | Maintains strength over time | Strength degrades over time due to acid hydrolysis |
| Common Applications | Archival documents, books, fine art prints | Newspapers, magazines, packaging |
Introduction to Papermaking Processes
Neutral papermaking uses a pH around 7 during pulp processing, preserving fibers and enhancing longevity, whereas acid papermaking employs acidic conditions with a pH below 5, leading to faster fiber degradation over time. Neutral processes minimize chemical reactions that cause yellowing and brittleness, making it preferred for archival and high-quality paper products. Acid papermaking, historically common for mass-market paper, offers faster production but compromises durability and archival stability.
Overview of Acid Papermaking
Acid papermaking involves using acidic sizing agents like alum and rosin to enhance water resistance and printability, common in historical paper production. This process results in faster drying times but causes long-term deterioration due to acid-induced cellulose breakdown, leading to yellowing and brittleness. Your choice of acid papermaking impacts paper longevity and archival quality, making it less suitable for preservation purposes.
Fundamentals of Neutral Papermaking
Neutral papermaking relies on using alkaline substances such as calcium carbonate as a buffering agent to maintain a pH around 7 during production, resulting in enhanced paper durability and longer lifespan. Unlike acidic papermaking, which uses alum and sulfuric acid creating a pH below 7, neutral papermaking prevents acid hydrolysis, reducing cellulose degradation and yellowing over time. Understanding these fundamentals ensures your paper products achieve superior archival quality and environmental sustainability.
Key Differences Between Acid and Neutral Papermaking
Neutral papermaking uses alkaline sizing agents, producing paper with higher longevity and resistance to yellowing, while acid papermaking relies on acidic sizing that can cause paper to become brittle and degrade over time. The pH level during the papermaking process is the primary differentiator, affecting the paper's durability, archival quality, and environmental impact. Your choice between neutral and acid papermaking should consider the intended lifespan and preservation requirements of the final product.
Impact on Paper Longevity and Durability
Neutral papermaking, utilizing a pH level around 7, significantly enhances paper longevity by preventing acid hydrolysis that degrades cellulose fibers over time. Acid papermaking, with a pH below 7, accelerates paper brittleness and yellowing due to acidic compounds breaking down cellulose chains. Archival and conservation-quality papers favor neutral papermaking for superior durability, resistance to aging, and preservation of printed materials.
Environmental Considerations and Sustainability
Neutral papermaking, which uses a pH around 7, significantly reduces the release of acidic waste into the environment, enhancing sustainability by minimizing soil and water acidification. Acid papermaking, operating at a lower pH, often involves chlorine-based bleaching chemicals that contribute to toxic effluent and long-term environmental harm. Transitioning to neutral papermaking supports eco-friendly practices by enabling recycling processes that preserve fiber quality and reduce the demand for virgin pulp, promoting resource conservation.
Effects on Printing and Ink Performance
Neutral papermaking enhances printing quality by providing a stable pH environment that reduces paper degradation and maintains ink adhesion over time. Acid papermaking, characterized by low pH levels, can cause paper to become brittle, leading to ink cracking and color fading during printing processes. Your choice between neutral and acid papermaking directly impacts ink performance, durability, and overall print clarity.
Cost Implications in Acid vs Neutral Papermaking
Neutral papermaking typically reduces long-term costs due to enhanced paper durability and resistance to yellowing, minimizing the need for frequent replacements. Acid papermaking often entails lower initial production expenses but incurs higher archival and maintenance costs as acid-induced deterioration accelerates paper decay. Choosing neutral papermaking aligns with your goals for cost efficiency over the paper's lifespan.
Industry Trends and Adoption Rates
Neutral papermaking is increasingly favored in the paper industry due to its environmental benefits and compatibility with recycled fibers, contributing to a steady rise in adoption rates. Acid papermaking, once predominant, faces decline as manufacturers shift toward sustainable practices and longer-lasting paper products resistant to yellowing and degradation. Industry trends indicate a growing preference for neutral pH processes, driven by regulations and consumer demand for eco-friendly and archival-quality papers.
Future Outlook for Papermaking Technologies
Neutral papermaking, utilizing pH-neutral or slightly alkaline conditions, is increasingly favored due to its enhanced durability and compatibility with recycled fibers, while acid papermaking faces decline because acidic conditions degrade paper over time. Innovations in enzymatic treatments and nanotechnology are advancing neutral papermaking, improving strength and printability without compromising environmental sustainability. Industry trends emphasize eco-friendly additives and energy-efficient processes, positioning neutral papermaking as the foundation for future sustainable paper production technologies.
Neutral vs acid papermaking Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com