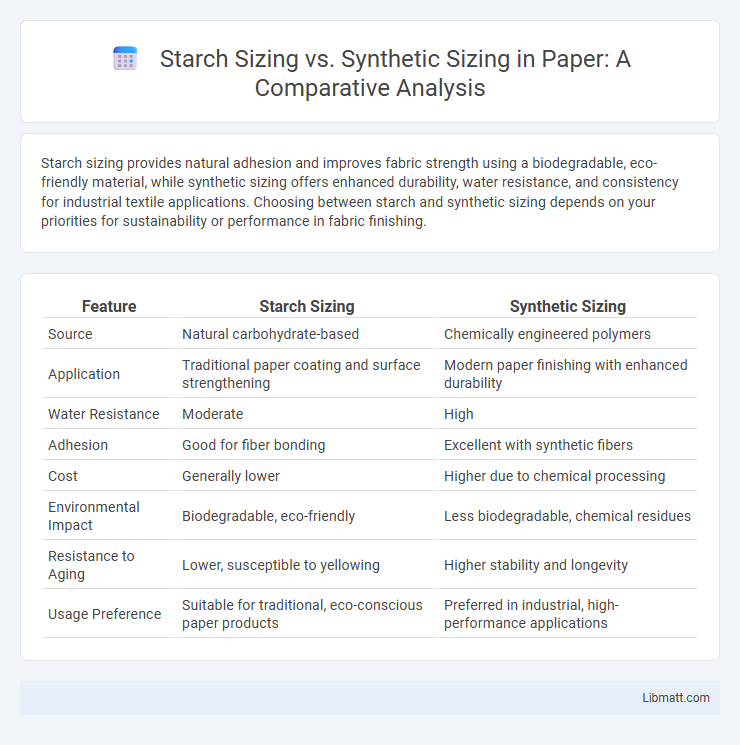
Starch sizing provides natural adhesion and improves fabric strength using a biodegradable, eco-friendly material, while synthetic sizing offers enhanced durability, water resistance, and consistency for industrial textile applications. Choosing between starch and synthetic sizing depends on your priorities for sustainability or performance in fabric finishing.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Starch Sizing | Synthetic Sizing |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural carbohydrate-based | Chemically engineered polymers |
| Application | Traditional paper coating and surface strengthening | Modern paper finishing with enhanced durability |
| Water Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Adhesion | Good for fiber bonding | Excellent with synthetic fibers |
| Cost | Generally lower | Higher due to chemical processing |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, eco-friendly | Less biodegradable, chemical residues |
| Resistance to Aging | Lower, susceptible to yellowing | Higher stability and longevity |
| Usage Preference | Suitable for traditional, eco-conscious paper products | Preferred in industrial, high-performance applications |
Introduction to Sizing in Textile Manufacturing
Sizing in textile manufacturing enhances yarn strength and reduces breakage during weaving, with starch sizing and synthetic sizing being two primary methods. Starch sizing uses natural polysaccharides that provide excellent adhesion and film formation but can increase moisture retention. Synthetic sizing agents, typically based on polyvinyl alcohol or acrylates, offer superior washability, uniform coating, and improved performance in high-speed weaving processes.
Overview of Starch Sizing
Starch sizing is a traditional method used in the textile and paper industries to enhance fabric strength and surface smoothness by applying a natural carbohydrate-based adhesive. It improves warp thread abrasion resistance and reduces yarn hairiness, leading to improved fabric quality during weaving and printing processes. Compared to synthetic sizing agents, starch offers biodegradability and ease of removal but may have lower moisture resistance and durability.
Overview of Synthetic Sizing
Synthetic sizing, primarily composed of polymers such as polyurethane, polyvinyl acetate, or acrylics, offers superior water resistance and durability compared to traditional starch sizing. This modern alternative enhances the fabric's strength, smoothness, and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for industrial textile applications. Your choice of synthetic sizing can significantly improve production efficiency and fabric performance in demanding environments.
Composition and Properties of Starch Sizes
Starch sizing is derived from natural polysaccharides like corn, potato, or wheat starch, consisting primarily of amylose and amylopectin, which provide excellent film-forming, adhesive, and moisture-absorbing properties. Synthetic sizing, made from chemical polymers such as polyvinyl acetate or acrylics, offers superior water resistance, uniformity, and faster drying times compared to natural starch. Your choice between starch sizing and synthetic sizing depends on the desired balance of biodegradability, strength, and performance in specific industrial or textile applications.
Composition and Properties of Synthetic Sizes
Synthetic sizes are typically composed of polymeric materials such as polyvinyl acetate, acrylics, and styrene-based compounds, offering superior water resistance and adhesion compared to natural starch sizes. Their molecular structure allows for enhanced film formation, durability, and flexibility, making them ideal for modern paper and textile applications. You benefit from improved performance in coating, binding, and surface strength due to these advanced properties.
Performance Comparison: Starch vs Synthetic Sizing
Starch sizing provides excellent adhesion and film-forming properties, enhancing fabric strength and smoothness, but it is susceptible to microbial degradation and lower wear resistance. Synthetic sizing, often based on polyvinyl alcohol or acrylates, offers superior durability, chemical stability, and resistance to high-temperature processing, resulting in improved fabric performance during weaving and finishing. In industrial applications, synthetic sizing generally outperforms starch in terms of abrasion resistance and moisture tolerance, making it the preferred choice for heavy-duty textiles.
Environmental Impact: Natural vs Chemical Sizing Agents
Natural starch sizing agents, derived from renewable plant sources such as corn and potato, offer biodegradability and lower toxicity, resulting in reduced environmental pollution and easier wastewater treatment. Synthetic sizing agents, composed of petrochemical-based polymers, often exhibit persistence in ecosystems, contributing to water contamination and increased ecological risks due to their slower degradation rates. Choosing starch sizing minimizes carbon footprint and supports sustainable textile processing by leveraging biodegradable, eco-friendly materials over chemically intensive synthetic alternatives.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Starch sizing typically incurs lower upfront material costs due to its natural availability and biodegradability, making it economically favorable for small to medium-scale operations prioritizing sustainability. Synthetic sizing, while generally more expensive initially, offers enhanced performance and durability that can reduce long-term expenses related to fabric strength and processing efficiency. Economic considerations must also factor in the environmental compliance costs and potential savings from reduced waste when choosing between starch and synthetic sizing agents.
Application Methods and Compatibility with Fabrics
Starch sizing is typically applied through dipping or padding and is most compatible with natural fibers like cotton and linen due to its biodegradable and heat-resistant properties. Synthetic sizing, often applied via spraying or foam technology, provides superior adhesion and is compatible with both natural and synthetic fabrics, enhancing fabric strength and abrasion resistance. Both sizing methods require precise control of concentration and application technique to ensure optimal fabric hand feel and performance during weaving or finishing processes.
Future Trends in Textile Sizing Technologies
Future trends in textile sizing technologies reveal a shift from traditional starch sizing to innovative synthetic sizing agents that offer enhanced sustainability and performance. Synthetic sizing materials deliver superior adhesion, flexibility, and resistance to water and chemicals, which significantly improves fabric processing efficiency and product durability. Your choice between starch and synthetic sizing will increasingly depend on environmental impact considerations and the demand for high-performance textiles in advanced applications.
Starch sizing vs synthetic sizing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com