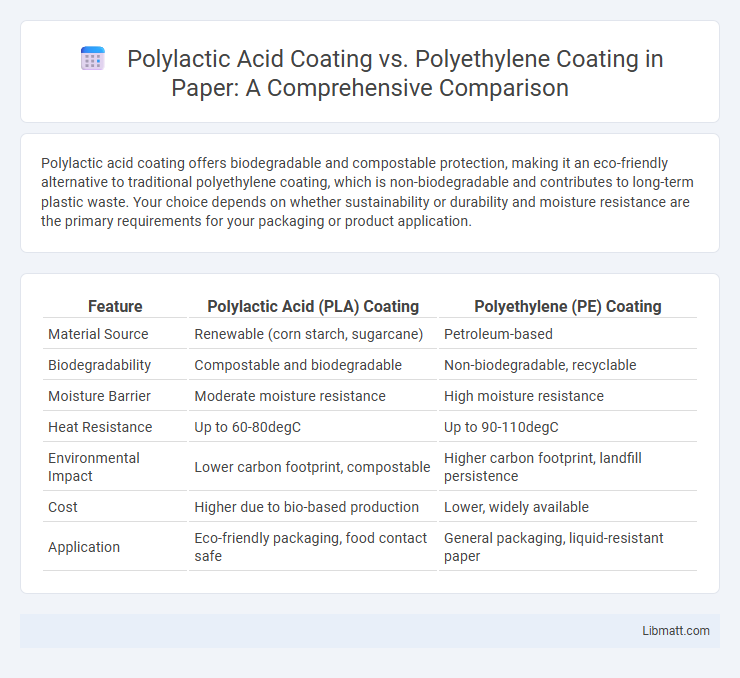
Polylactic acid coating offers biodegradable and compostable protection, making it an eco-friendly alternative to traditional polyethylene coating, which is non-biodegradable and contributes to long-term plastic waste. Your choice depends on whether sustainability or durability and moisture resistance are the primary requirements for your packaging or product application.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polylactic Acid (PLA) Coating | Polyethylene (PE) Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Renewable (corn starch, sugarcane) | Petroleum-based |
| Biodegradability | Compostable and biodegradable | Non-biodegradable, recyclable |
| Moisture Barrier | Moderate moisture resistance | High moisture resistance |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 60-80degC | Up to 90-110degC |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint, compostable | Higher carbon footprint, landfill persistence |
| Cost | Higher due to bio-based production | Lower, widely available |
| Application | Eco-friendly packaging, food contact safe | General packaging, liquid-resistant paper |
Introduction to Biodegradable and Conventional Coating Materials
Polylactic acid (PLA) coating is a biodegradable, eco-friendly alternative derived from renewable resources like corn starch, offering compostability and reduced environmental impact compared to conventional polyethylene (PE) coating, which is petroleum-based and non-biodegradable. PLA coatings provide excellent moisture barrier properties suitable for sustainable packaging, while PE coatings deliver durability and resistance but contribute to long-term plastic waste. Choosing the right coating depends on your product's sustainability goals and performance requirements, balancing environmental benefits with functional needs.
What is Polylactic Acid (PLA) Coating?
Polylactic Acid (PLA) coating is a biodegradable and bio-based polymer derived from renewable resources such as corn starch or sugarcane, offering an eco-friendly alternative to traditional petroleum-based coatings like polyethylene. PLA coatings provide excellent moisture barrier properties and are widely used in food packaging to enhance shelf life while reducing environmental impact due to their compostability. Compared to polyethylene coatings, PLA coatings decompose faster under industrial composting conditions, making them a preferred choice for sustainable packaging solutions.
What is Polyethylene (PE) Coating?
Polyethylene (PE) coating is a widely used plastic film applied to materials for enhanced moisture resistance and durability, commonly used in packaging and agriculture. This thermoplastic polymer provides a waterproof barrier, protecting products from contamination and extending shelf life. Compared to polylactic acid (PLA) coating, PE coatings often offer superior flexibility and chemical resistance but are less biodegradable and environmentally friendly.
Key Differences Between PLA and PE Coatings
Polylactic acid (PLA) coating is biodegradable and derived from renewable resources, making it an eco-friendly alternative to conventional polyethylene (PE) coatings, which are petroleum-based and non-biodegradable. PLA coatings offer excellent clarity and compostability but tend to have lower moisture barrier properties and heat resistance compared to PE coatings, which provide superior durability and water resistance. Your choice depends on the balance between environmental impact and functional performance required for the application.
Environmental Impact: PLA vs. PE Coatings
Polylactic acid (PLA) coatings offer a significant environmental advantage over polyethylene (PE) coatings due to their biodegradability and compostability, reducing plastic waste accumulation. PLA coatings are derived from renewable resources such as corn starch or sugarcane, which lowers the carbon footprint compared to petrochemical-based PE coatings. However, PE coatings exhibit superior durability and moisture resistance, making them less likely to degrade in landfills but contributing to long-term environmental persistence and microplastic pollution.
Performance and Durability Comparison
Polylactic acid (PLA) coatings offer excellent biodegradability and resistance to moisture, making them suitable for eco-friendly packaging but generally exhibit lower heat resistance and mechanical durability compared to polyethylene (PE) coatings. Polyethylene coatings provide superior durability, flexibility, and resistance to chemicals and abrasion, ensuring longer lifespan and better protection in industrial applications. Performance-wise, PE coatings outperform PLA in high-stress environments, while PLA coatings are preferred for sustainable, short-term use due to their compostable properties.
Applications and Industry Use Cases
Polylactic acid (PLA) coating is widely utilized in the food packaging industry due to its biodegradable and compostable properties, making it ideal for eco-friendly trays, cups, and disposable utensils. Polyethylene (PE) coating offers superior moisture barrier and durability, making it the preferred choice for liquid packaging, milk cartons, and flexible packaging in pharmaceuticals and consumer goods. Your choice between PLA and PE coatings should consider sustainability goals versus functional performance requirements in specific applications.
Cost Analysis: PLA vs. PE Coating
Polylactic acid (PLA) coating typically incurs higher production costs compared to polyethylene (PE) coating due to its bio-based raw materials and more complex manufacturing processes. PE coating benefits from established mass production with lower material and processing costs, making it more cost-effective for large-scale applications. However, PLA coatings may offer long-term economic advantages through biodegradability and regulatory incentives promoting sustainable packaging solutions.
Regulatory and Safety Considerations
Polylactic acid (PLA) coatings are derived from renewable resources and are generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by regulatory agencies such as the FDA, making them suitable for food packaging applications with biodegradable benefits. Polyethylene (PE) coatings, widely used for their excellent moisture and chemical resistance, comply with numerous safety standards but pose environmental concerns due to their non-biodegradable nature. Your choice between PLA and PE coatings should consider regulatory approvals specific to your industry and the long-term environmental impact of the materials.
Future Trends in Sustainable Coating Technologies
Polylactic acid (PLA) coatings are gaining traction as a sustainable alternative to polyethylene (PE) coatings due to their biodegradability and renewable sourcing from corn starch or sugarcane. Future trends emphasize the enhancement of PLA coatings' barrier properties and mechanical strength to rival PE's durability while maintaining compostability. Innovations in bio-based additives and nanotechnology aim to improve PLA coatings' performance, accelerating the shift toward eco-friendly packaging and reducing plastic pollution in various industries.
polylactic acid coating vs polyethylene coating Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com