Sizing degree measures the resistance of paper to water penetration, indicating how well your paper repels moisture. Wet strength refers to the paper's ability to maintain integrity and tensile strength when saturated, ensuring durability in wet conditions.
Table of Comparison
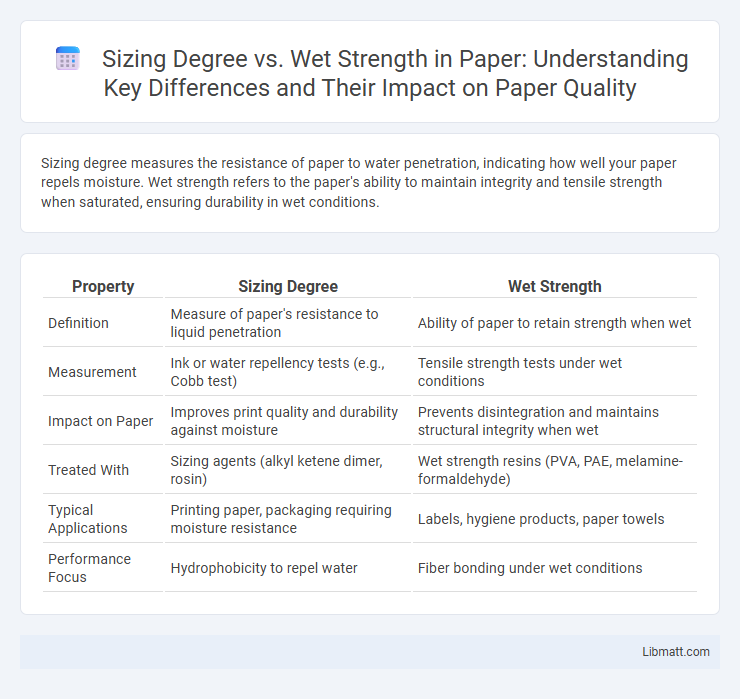
| Property | Sizing Degree | Wet Strength |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Measure of paper's resistance to liquid penetration | Ability of paper to retain strength when wet |
| Measurement | Ink or water repellency tests (e.g., Cobb test) | Tensile strength tests under wet conditions |
| Impact on Paper | Improves print quality and durability against moisture | Prevents disintegration and maintains structural integrity when wet |
| Treated With | Sizing agents (alkyl ketene dimer, rosin) | Wet strength resins (PVA, PAE, melamine-formaldehyde) |
| Typical Applications | Printing paper, packaging requiring moisture resistance | Labels, hygiene products, paper towels |
| Performance Focus | Hydrophobicity to repel water | Fiber bonding under wet conditions |
Understanding Sizing Degree in Papermaking
Sizing degree in papermaking measures the paper's resistance to liquid penetration, directly influencing wet strength by controlling fiber interaction with water. Higher sizing degrees typically enhance wet strength by limiting water absorption and maintaining structural integrity under moisture exposure. Precise control of sizing agents, such as alkyl ketene dimer (AKD) or rosin, optimizes sizing degree to achieve desired wet strength levels for specific paper applications.
Defining Wet Strength: Key Concepts
Wet strength refers to the ability of paper or fabric to retain its mechanical integrity when exposed to moisture or water, a critical factor in applications like packaging and hygiene products. This property is enhanced by additives such as resins or polymers that form cross-links within the material structure, preventing fiber separation in wet conditions. The sizing degree impacts wet strength by controlling the absorption of water; higher sizing levels typically reduce water penetration, thereby improving the retention of strength when wet.
Importance of Sizing Degree for Paper Performance
Sizing degree critically influences the wet strength of paper by controlling its resistance to water penetration and maintaining structural integrity when exposed to moisture. A higher sizing degree enhances paper durability and prevents fiber swelling, ensuring consistent performance in applications requiring water resistance. Your choice of sizing degree directly impacts the usability and longevity of paper products in wet or humid environments.
Mechanisms Influencing Wet Strength
Sizing degree impacts wet strength by altering fiber surface chemistry and water resistance. Increased sizing enhances fiber hydrophobicity, reducing water penetration and maintaining fiber-fiber bonding under wet conditions. Chemical additives in sizing form covalent bonds that reinforce the paper matrix, directly contributing to improved wet strength.
Chemical Additives Affecting Sizing and Wet Strength
Chemical additives such as alkyl ketene dimer (AKD) and rosin are commonly used to enhance sizing in paper, improving water resistance by creating a hydrophobic barrier within the fibers. Wet strength resins, including polyamide-epichlorohydrin (PAE) and melamine-formaldehyde, form covalent bonds that reinforce fiber networks, maintaining paper integrity under wet conditions. Your choice of additives must balance sizing efficiency with wet strength requirements to optimize paper performance in moisture-rich environments.
Sizing Degree versus Wet Strength: Core Differences
Sizing degree directly influences the paper's resistance to water penetration, while wet strength determines the paper's ability to maintain structural integrity when wet. Higher sizing degrees reduce liquid absorption by increasing hydrophobicity, whereas enhanced wet strength relies on chemical additives or fiber modifications to reinforce fiber bonding under moisture. The core difference lies in sizing's role in water repellency versus wet strength's focus on mechanical durability in wet conditions.
Factors Impacting Both Sizing and Wet Strength
The factors impacting both sizing degree and wet strength include the type and concentration of sizing agents, such as AKD or ASA, which affect the hydrophobicity and internal bonding of the paper fibers. pH level and drying temperature influence the curing process, directly altering the retention and reaction efficiency of sizing chemicals, thus modifying wet strength performance. You can optimize both properties by controlling fiber composition and refining processes to enhance the interaction between sizing agents and cellulose fibers.
Testing Methods for Sizing Degree and Wet Strength
Testing methods for sizing degree often include the Hercules Sizing Test (HST) and Cobb test, which measure water resistance and absorption rate of paper surfaces. Wet strength is typically evaluated using tensile strength testers under controlled wet conditions to assess the paper's durability when saturated. Both tests provide critical data for optimizing paper formulations to balance sizing effectiveness and mechanical performance in wet environments.
Industrial Applications: Sizing Degree vs Wet Strength
Sizing degree significantly influences wet strength in industrial applications, as higher sizing levels enhance fiber resistance to water, improving the durability of paper products under moist conditions. Your choice of sizing impacts the performance of items like packaging materials, where water resistance is critical to maintaining structural integrity. Optimizing sizing degree ensures a balance between wet strength and other mechanical properties, crucial for industries such as food packaging, hygiene products, and specialty papers.
Enhancing Paper Quality: Balancing Sizing and Wet Strength
Balancing sizing degree and wet strength is crucial for enhancing paper quality, as optimal sizing improves resistance to water penetration while maintaining sufficient wet strength prevents premature disintegration during handling or use. High sizing degrees increase hydrophobicity, reducing ink spread and improving print clarity, yet excessive sizing can compromise wet tensile strength, making paper brittle when wet. Your paper production process should carefully calibrate sizing agents to achieve the ideal balance, ensuring durability and functionality under both dry and wet conditions.
Sizing degree vs wet strength Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com