Blending seamlessly combines multiple elements to create a smooth, unified result, while mixing involves combining components without necessarily achieving a uniform texture. Your choice between blending and mixing depends on the desired consistency and final outcome of your project or recipe.
Table of Comparison
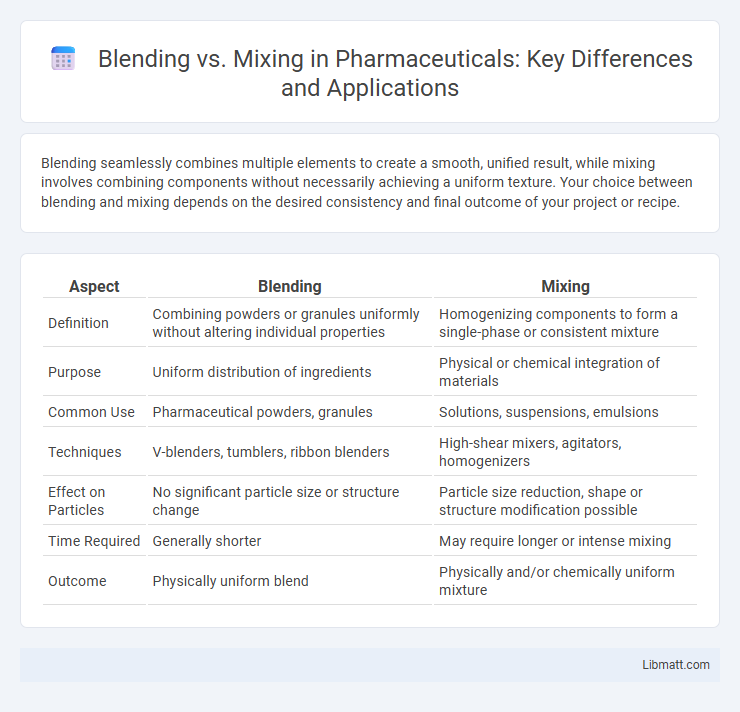
| Aspect | Blending | Mixing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combining powders or granules uniformly without altering individual properties | Homogenizing components to form a single-phase or consistent mixture |
| Purpose | Uniform distribution of ingredients | Physical or chemical integration of materials |
| Common Use | Pharmaceutical powders, granules | Solutions, suspensions, emulsions |
| Techniques | V-blenders, tumblers, ribbon blenders | High-shear mixers, agitators, homogenizers |
| Effect on Particles | No significant particle size or structure change | Particle size reduction, shape or structure modification possible |
| Time Required | Generally shorter | May require longer or intense mixing |
| Outcome | Physically uniform blend | Physically and/or chemically uniform mixture |
Understanding Blending and Mixing
Blending involves smoothly combining multiple elements to create a unified and seamless result, often used in design and art to achieve harmony. Mixing refers to the process of physically or digitally combining different components, retaining some distinct individual characteristics within the final product. Understanding the differences between blending and mixing helps optimize creative workflows and achieve desired aesthetic or functional outcomes.
Key Differences Between Blending and Mixing
Blending involves combining ingredients uniformly to create a smooth, homogeneous texture, often used in food preparation or cosmetics to achieve consistency. Mixing refers to the process of stirring or folding components together, which may not result in a uniform texture and is commonly applied in baking or industrial applications. Understanding these key differences helps you select the appropriate technique for your desired outcome, ensuring optimal texture and quality.
Common Applications of Blending
Blending is commonly used in industries like food production, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics to create uniform mixtures of ingredients with specific textures and flavors. Your product benefits from blending when combining powders, liquids, or solids to achieve consistency and quality without altering the individual properties of each component. This process ensures homogeneous distribution, critical for taste, efficacy, and appearance in finished goods.
Popular Uses for Mixing
Mixing is widely used in the culinary industry for combining ingredients to create uniform textures and balanced flavors in recipes such as sauces, doughs, and beverages. In music production, mixing involves adjusting and combining multiple audio tracks to achieve a harmonious and polished sound. The cosmetics industry also relies on mixing to blend pigments and chemicals into consistent products like foundations and creams.
Equipment Comparison: Blenders vs Mixers
Blenders typically feature a high-speed motor with sharp blades designed for pulverizing fruits, vegetables, and liquids, making them ideal for smoothies, soups, and purees. Mixers generally come with beaters or whisks powered by a lower-speed motor optimized for combining dry ingredients or whipping creams and eggs, best suited for baking tasks. While blenders excel in creating smooth textures with liquids, mixers offer precise control for thicker mixtures and dough preparation.
Texture and Consistency Outcomes
Blending creates a smooth and uniform texture by thoroughly combining ingredients into a cohesive mixture, often resulting in creamy or liquid consistency ideal for sauces, smoothies, and purees. Mixing, on the other hand, gently combines components, maintaining some texture and distinct elements, which is suitable for batters, doughs, and salads where varied consistency enhances the final dish. Your choice between blending and mixing directly impacts the texture outcome, influencing the mouthfeel and presentation of your culinary creations.
Nutritional Impact: Blending vs Mixing
Blending breaks down whole fruits and vegetables into a smooth consistency, preserving most of the fiber and nutrients while allowing for easier digestion and nutrient absorption. Mixing, on the other hand, simply combines ingredients without altering their physical structure, which retains the original texture but may result in less nutrient bioavailability compared to blending. Your choice between blending and mixing can influence the nutritional impact, with blending often enhancing nutrient absorption and overall dietary benefits.
Speed and Efficiency Considerations
Blending typically offers faster processing speeds due to its use of high-speed blades that rapidly break down ingredients, making it highly efficient for creating smooth textures in a short time. Mixing, by contrast, relies on slower, more controlled movements designed to combine ingredients gently without over-processing, resulting in longer processing times but greater precision. The choice between blending and mixing depends on the desired consistency and the balance between speed and texture control in food preparation.
Best Practices for Blending and Mixing
Best practices for blending emphasize achieving a harmonious integration of flavors or components, maintaining balance and consistency throughout the process. Mixing techniques focus on thoroughly combining ingredients to ensure uniformity in texture and composition, preventing separation or inconsistencies. Understanding the specific properties of each ingredient helps you optimize both blending and mixing for superior quality results.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Needs
Blending combines ingredients to create a uniform texture, ideal for smoothies and sauces where smooth consistency matters most. Mixing involves incorporating components without fully homogenizing them, perfect for recipes like salads or batters that require distinct textures. Understanding these differences helps you select the right technique based on your recipe's desired outcome and texture preferences.
Blending vs Mixing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com