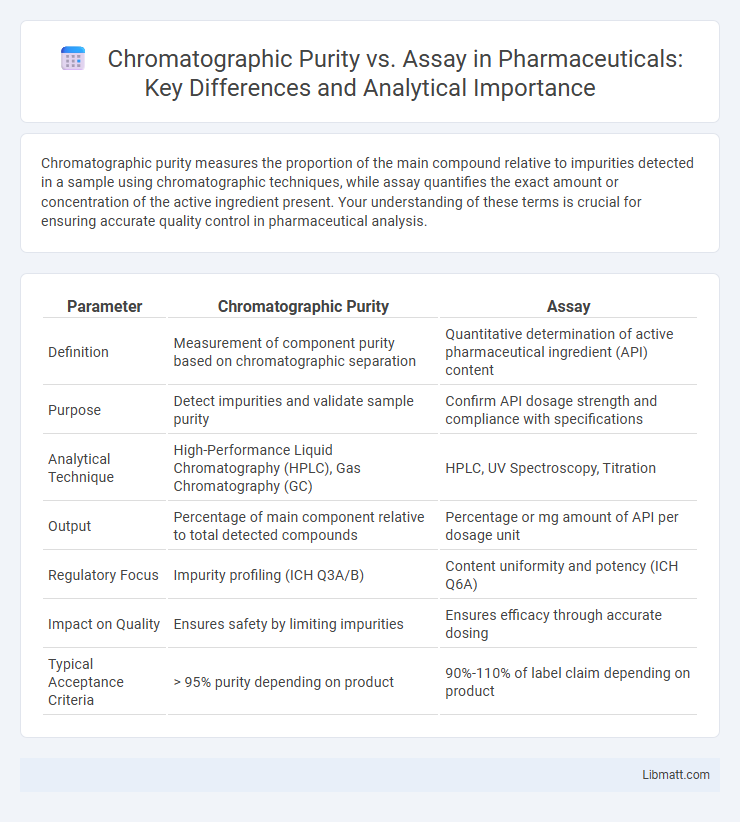
Chromatographic purity measures the proportion of the main compound relative to impurities detected in a sample using chromatographic techniques, while assay quantifies the exact amount or concentration of the active ingredient present. Your understanding of these terms is crucial for ensuring accurate quality control in pharmaceutical analysis.
Table of Comparison
| Parameter | Chromatographic Purity | Assay |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Measurement of component purity based on chromatographic separation | Quantitative determination of active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) content |
| Purpose | Detect impurities and validate sample purity | Confirm API dosage strength and compliance with specifications |
| Analytical Technique | High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC), Gas Chromatography (GC) | HPLC, UV Spectroscopy, Titration |
| Output | Percentage of main component relative to total detected compounds | Percentage or mg amount of API per dosage unit |
| Regulatory Focus | Impurity profiling (ICH Q3A/B) | Content uniformity and potency (ICH Q6A) |
| Impact on Quality | Ensures safety by limiting impurities | Ensures efficacy through accurate dosing |
| Typical Acceptance Criteria | > 95% purity depending on product | 90%-110% of label claim depending on product |
Introduction to Chromatographic Purity and Assay
Chromatographic purity measures the proportion of the main compound relative to impurities in a sample, ensuring accurate identification and quantification through techniques like HPLC or GC. Assay determines the exact concentration or potency of the active ingredient within a pharmaceutical product, crucial for dosage accuracy and regulatory compliance. Understanding the distinction between chromatographic purity and assay allows you to ensure both the quality and efficacy of your pharmaceutical formulations.
Understanding Chromatographic Purity
Chromatographic purity measures the proportion of a desired compound free from impurities detected through chromatographic techniques, providing a clear profile of sample composition. Unlike assay, which quantifies the total amount of the active ingredient present, chromatographic purity ensures the absence or minimal presence of contaminants affecting product quality. Understanding chromatographic purity helps you accurately assess sample integrity and pharmaceutical efficacy.
What is Assay in Analytical Chemistry?
Assay in analytical chemistry refers to the quantitative measurement of the specific active component or compound in a sample, indicating its concentration or potency. Chromatographic purity, on the other hand, measures the proportion of the desired compound compared to impurities in a mixture. Your understanding of assay is crucial for accurately determining the strength and quality of pharmaceutical substances or chemical products.
Key Differences Between Chromatographic Purity and Assay
Chromatographic purity measures the relative proportion of the main compound compared to impurities using techniques like HPLC, focusing on impurity profiles and separation efficiency. Assay quantifies the exact amount or concentration of the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in a sample, providing content accuracy critical for dosage determination. Your pharmaceutical analysis requires understanding both to ensure product safety and regulatory compliance.
Importance of Chromatographic Purity in Pharmaceuticals
Chromatographic purity is crucial in pharmaceuticals as it ensures the absence of impurities that can affect drug safety and efficacy, directly impacting patient health outcomes. High chromatographic purity indicates precise separation of active pharmaceutical ingredients from contaminants, supporting regulatory compliance and quality control. This parameter complements assay results by confirming not just the quantity but the quality and integrity of the drug substance.
Role of Assay in Quality Control
Assay plays a crucial role in quality control by quantifying the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) to ensure the correct dosage strength in drug products. It provides precise measurement of the drug concentration, confirming compliance with regulatory specifications and batch-to-batch consistency. Chromatographic purity complements assay by identifying impurities, but assay remains essential for verifying the potency and effectiveness of the pharmaceutical formulation.
Methods for Determining Chromatographic Purity
Chromatographic purity is determined using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and gas chromatography (GC), which separate and quantify impurities within a sample. Methods such as gradient elution, UV detection, and mass spectrometry coupling enhance the accuracy of identifying minor contaminants. Your choice between chromatographic purity and assay depends on whether the goal is to measure the percentage of the desired compound or to evaluate overall sample cleanliness.
Techniques Used for Assay Analysis
Techniques used for assay analysis commonly include High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC), Gas Chromatography (GC), and UV-Visible Spectrophotometry, providing quantitative measurement of active pharmaceutical ingredients. Chromatographic methods like HPLC offer high specificity and sensitivity for separating and quantifying compounds in complex mixtures. These techniques ensure accurate determination of assay values, essential for verifying drug potency and compliance with pharmacopeial standards.
Challenges in Separating Purity and Assay Results
Chromatographic purity and assay results pose challenges due to overlapping impurities and active ingredients that can complicate clear differentiation during analysis. Variations in method sensitivity and selectivity often affect accurate quantification, making it difficult to separate the contribution of impurities from the target compound. Precise calibration and method validation are critical to resolve these issues and ensure reliable purity and assay measurements in pharmaceutical quality control.
Conclusion: Ensuring Quality through Purity and Assay Testing
Chromatographic purity and assay testing are critical for ensuring pharmaceutical quality by verifying the identity and concentration of active ingredients while detecting impurities. High chromatographic purity confirms the absence of contaminants, directly impacting drug safety and efficacy. Combining chromatographic purity with accurate assay results guarantees comprehensive quality control for reliable therapeutic outcomes.
Chromatographic purity vs assay Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com