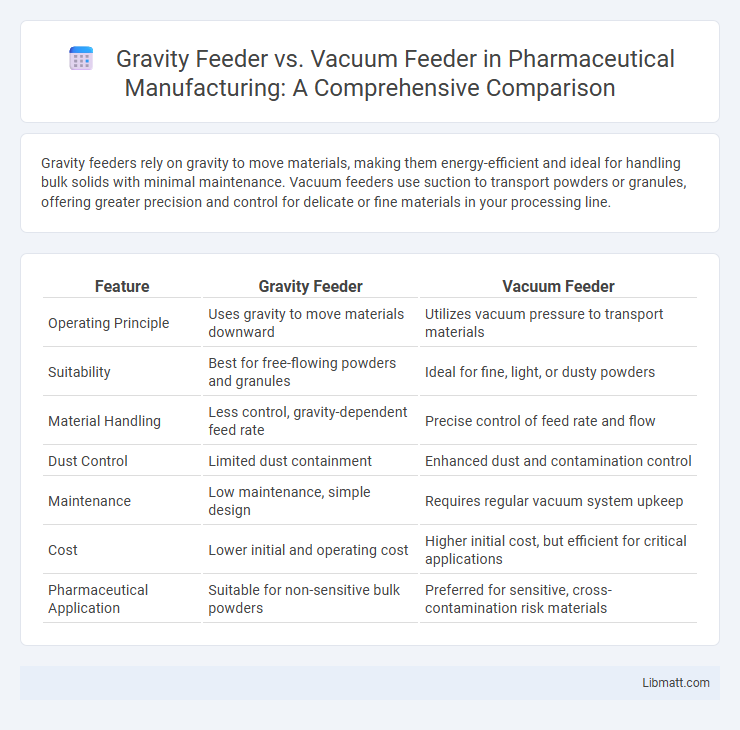
Gravity feeders rely on gravity to move materials, making them energy-efficient and ideal for handling bulk solids with minimal maintenance. Vacuum feeders use suction to transport powders or granules, offering greater precision and control for delicate or fine materials in your processing line.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Gravity Feeder | Vacuum Feeder |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Principle | Uses gravity to move materials downward | Utilizes vacuum pressure to transport materials |
| Suitability | Best for free-flowing powders and granules | Ideal for fine, light, or dusty powders |
| Material Handling | Less control, gravity-dependent feed rate | Precise control of feed rate and flow |
| Dust Control | Limited dust containment | Enhanced dust and contamination control |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, simple design | Requires regular vacuum system upkeep |
| Cost | Lower initial and operating cost | Higher initial cost, but efficient for critical applications |
| Pharmaceutical Application | Suitable for non-sensitive bulk powders | Preferred for sensitive, cross-contamination risk materials |
Introduction to Gravity Feeders and Vacuum Feeders
Gravity feeders use the natural force of gravity to move materials from one point to another, relying on inclined surfaces or chutes to guide the flow. Vacuum feeders use suction to lift and transport materials in sealed systems, providing precise control over the transfer process and reducing contamination risks. Your choice between these systems depends on the material type, desired handling speed, and application environment.
How Gravity Feeders Work
Gravity feeders operate by utilizing the natural force of gravity to move materials from a higher point to a lower collection area, ensuring a continuous and controlled flow without the need for external power sources. These systems typically consist of a hopper or funnel where bulk materials are loaded, allowing them to slide down smooth surfaces or chutes into the feeding mechanism or processing equipment. Their simple design minimizes mechanical complexity and energy consumption, making gravity feeders ideal for handling granular or free-flowing substances efficiently.
How Vacuum Feeders Operate
Vacuum feeders operate by creating negative pressure to draw materials from a supply container through a sealed system, ensuring efficient and controlled material transfer. These feeders utilize vacuum pumps to generate suction, enabling precise feeding of powders, granules, and other bulk solids without spillage or exposure to air. Compared to gravity feeders, vacuum feeders provide enhanced accuracy and contamination control, particularly in automated pharmaceutical and food processing applications.
Key Differences Between Gravity and Vacuum Feeders
Gravity feeders rely on the natural force of gravity to move materials from one point to another, making them ideal for handling free-flowing powders and granules with minimal energy consumption. Vacuum feeders use suction to transport materials, providing precise control and handling of fine powders, sticky substances, or materials that tend to clump, ensuring consistent feed rates. Your choice between a gravity feeder and a vacuum feeder depends on the specific material properties and application requirements, with gravity feeders offering simplicity and cost-effectiveness while vacuum feeders deliver accuracy and versatility.
Advantages of Gravity Feeders
Gravity feeders offer energy-efficient operation by utilizing natural force to move materials, reducing the need for external power sources. They provide consistent and gentle material handling, minimizing damage to delicate products during the feeding process. Your production line can benefit from simpler maintenance and lower operational costs due to their straightforward design and fewer mechanical components.
Benefits of Vacuum Feeders
Vacuum feeders offer precise and consistent material handling by using suction to transfer powders, granules, and other bulk materials without contamination, making them ideal for pharmaceutical and food industries. Their closed system design reduces dust emissions and product loss, enhancing hygiene and minimizing environmental impact. Compared to gravity feeders, vacuum feeders provide greater flexibility in material transfer over longer distances and elevated heights, improving operational efficiency.
Applications: When to Use Gravity vs Vacuum Feeders
Gravity feeders are ideal for applications involving small to medium-sized parts that require gentle handling, such as in packaging or assembly lines where parts can flow naturally by gravity. Vacuum feeders excel in scenarios demanding precise placement and control of lightweight or irregularly shaped items, commonly used in electronics or pharmaceutical industries. Your choice depends on the part characteristics and process requirements, with gravity feeders offering simplicity and cost-efficiency while vacuum feeders provide accuracy and versatility.
Maintenance and Durability Considerations
Gravity feeders require minimal maintenance due to their simple mechanical design and lack of moving parts, resulting in less downtime and lower long-term costs. Vacuum feeders, while offering precise material handling, involve more complex components such as vacuum pumps and seals that demand regular inspection and replacement to ensure durability. Your choice between these feeders should factor in the ease of upkeep and the specific application's wear and tear to optimize operational efficiency.
Cost Comparison of Gravity and Vacuum Feeders
Gravity feeders generally incur lower upfront and maintenance costs compared to vacuum feeders, making them a more budget-friendly option for simple material handling applications. Vacuum feeders, while more expensive initially due to their complex suction-based mechanisms, offer better precision and reduced material wastage, potentially lowering long-term operational expenses. The choice between gravity and vacuum feeders depends on the specific application requirements, balancing cost efficiency with performance needs.
Choosing the Right Feeder for Your Needs
Selecting the right feeder depends on material type, flow characteristics, and application requirements. Gravity feeders are ideal for free-flowing, lightweight granules, leveraging gravity for simple, cost-effective dispensing, while vacuum feeders excel in precisely handling fine powders or irregular shapes by using suction for controlled delivery. Evaluating factors like material sensitivity, feed rate consistency, and equipment compatibility ensures optimal performance and minimal downtime.
Gravity Feeder vs Vacuum Feeder Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com