Sterile filling ensures that both the product and the container are free from contaminants by sterilizing each component before filling, while aseptic filling involves filling products into pre-sterilized containers in a sterile environment without necessarily sterilizing the final packaging together with the product. Understanding the differences between sterile and aseptic filling can help you choose the optimal method for maintaining product safety and extending shelf life.
Table of Comparison
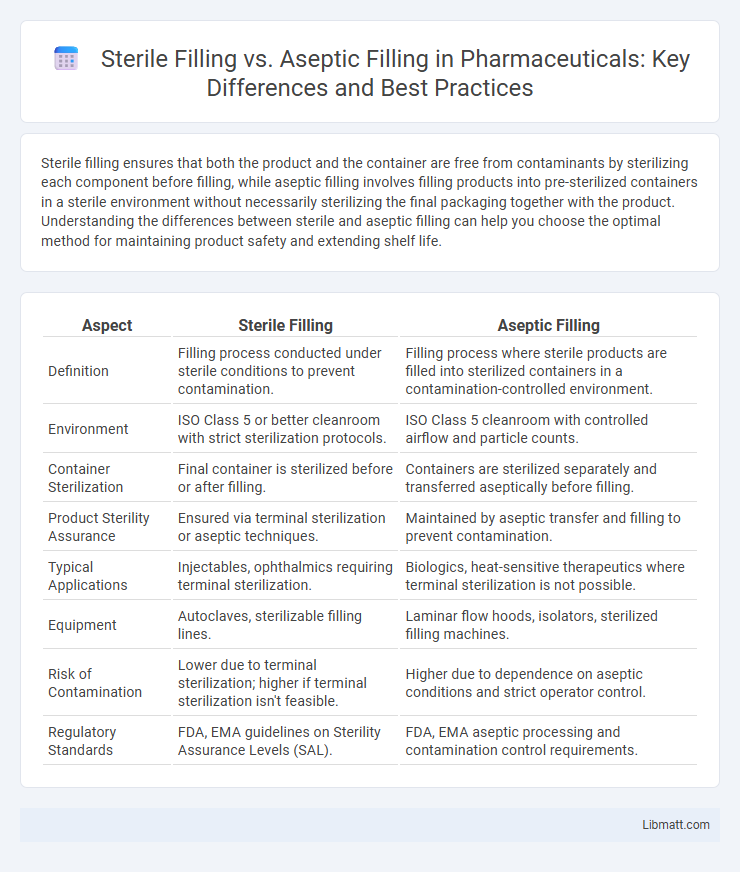
| Aspect | Sterile Filling | Aseptic Filling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Filling process conducted under sterile conditions to prevent contamination. | Filling process where sterile products are filled into sterilized containers in a contamination-controlled environment. |
| Environment | ISO Class 5 or better cleanroom with strict sterilization protocols. | ISO Class 5 cleanroom with controlled airflow and particle counts. |
| Container Sterilization | Final container is sterilized before or after filling. | Containers are sterilized separately and transferred aseptically before filling. |
| Product Sterility Assurance | Ensured via terminal sterilization or aseptic techniques. | Maintained by aseptic transfer and filling to prevent contamination. |
| Typical Applications | Injectables, ophthalmics requiring terminal sterilization. | Biologics, heat-sensitive therapeutics where terminal sterilization is not possible. |
| Equipment | Autoclaves, sterilizable filling lines. | Laminar flow hoods, isolators, sterilized filling machines. |
| Risk of Contamination | Lower due to terminal sterilization; higher if terminal sterilization isn't feasible. | Higher due to dependence on aseptic conditions and strict operator control. |
| Regulatory Standards | FDA, EMA guidelines on Sterility Assurance Levels (SAL). | FDA, EMA aseptic processing and contamination control requirements. |
Introduction to Sterile Filling and Aseptic Filling
Sterile filling involves packaging products in a sterile environment after they have undergone terminal sterilization to ensure microbial safety. Aseptic filling combines sterilized components, including the product, container, and closure, in a sterile environment without terminal sterilization, maintaining product sterility throughout the process. Both techniques are critical in pharmaceutical and biotechnology manufacturing for preserving product quality and preventing contamination.
Defining Sterile Filling
Sterile filling involves the process of transferring sterile products into sterilized containers within a controlled environment to prevent contamination. This method ensures that both the product and packaging maintain their sterility throughout the filling operation, critical for pharmaceuticals and medical devices. Your choice between sterile and aseptic filling depends on the required level of contamination control and regulatory compliance.
Understanding Aseptic Filling
Aseptic filling involves sterilizing both the product and the packaging separately before combining them in a sterile environment to prevent contamination. This process is critical for pharmaceuticals and food products requiring extended shelf life without preservatives. Sterile filling, by contrast, may involve sterilizing the product after filling, but aseptic filling maintains sterility throughout the entire packaging process.
Key Differences Between Sterile and Aseptic Filling
Sterile filling involves the use of pre-sterilized containers and environments to prevent contamination, whereas aseptic filling sterilizes both the product and packaging separately before filling in a sterile environment. Key differences include the timing and method of sterilization: sterile filling maintains sterility post-sterilization of components, while aseptic filling requires continuous sterile conditions throughout the process. Equipment complexity and cost tend to be higher in aseptic filling due to the need for more rigorous environmental controls and sterilization methods.
Advantages of Sterile Filling
Sterile filling offers advantages such as enhanced contamination control by maintaining a closed, sterile environment during the entire process, reducing the risk of microbial contamination. It ensures product stability and safety, which is critical for pharmaceuticals and sensitive medical products requiring strict sterility standards. Your manufacturing process benefits from consistent quality assurance and regulatory compliance when using sterile filling techniques.
Benefits of Aseptic Filling
Aseptic filling ensures that sterile products are packaged in a sterile environment, significantly reducing the risk of contamination and extending the shelf life without refrigeration. This process maintains product integrity and quality by using advanced sterilization methods for both the container and the product before filling. You benefit from enhanced safety and regulatory compliance, making aseptic filling ideal for pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and sensitive food products.
Common Applications in Pharmaceutical and Food Industries
Sterile filling is commonly used in pharmaceuticals for injectable drugs, vaccines, and ophthalmic solutions requiring strict contamination control, while aseptic filling is preferred for heat-sensitive products like biologics and certain nutritional supplements. In the food industry, sterile filling applies to dairy products and canned beverages, ensuring extended shelf life without preservatives, whereas aseptic filling often suits fruit juices and liquid egg products where maintaining flavor and nutritional value is critical. Understanding whether your product demands sterile or aseptic processes ensures compliance with industry standards and product safety.
Critical Equipment and Technology Used
Sterile filling depends on equipment such as autoclaves, sterilizing filters, and isolators to maintain sterility throughout the process, while aseptic filling relies on laminar airflow workstations, HEPA filters, and barrier systems to prevent contamination. Advanced technologies like blow-fill-seal machines and robotic arms enhance precision and minimize human contact in both methods. Your choice between sterile and aseptic filling should consider the specific equipment capabilities to ensure compliance with stringent regulatory standards and product safety.
Regulatory Requirements and Standards
Sterile filling mandates stringent compliance with FDA and EMA guidelines, enforcing ISO 14644 cleanroom classifications and USP <797> standards to prevent contamination during production. Aseptic filling requires adherence to Annex 1 of the EU GMP guidelines, emphasizing environmental monitoring, validated sterilization processes, and personnel training to maintain product sterility. Both filling methods demand rigorous validation, real-time monitoring, and documentation to ensure regulatory approval and product safety.
Choosing the Right Filling Method for Your Product
Sterile filling involves sterilizing both the product and container before filling, ensuring maximum contamination control for sensitive pharmaceuticals like injectables. Aseptic filling maintains sterility by filling sterilized products into sterilized containers in a sterile environment without terminal sterilization, suitable for heat-sensitive biologics. Your choice depends on product sensitivity, regulatory requirements, and production scale to ensure efficacy and safety.
Sterile Filling vs Aseptic Filling Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com