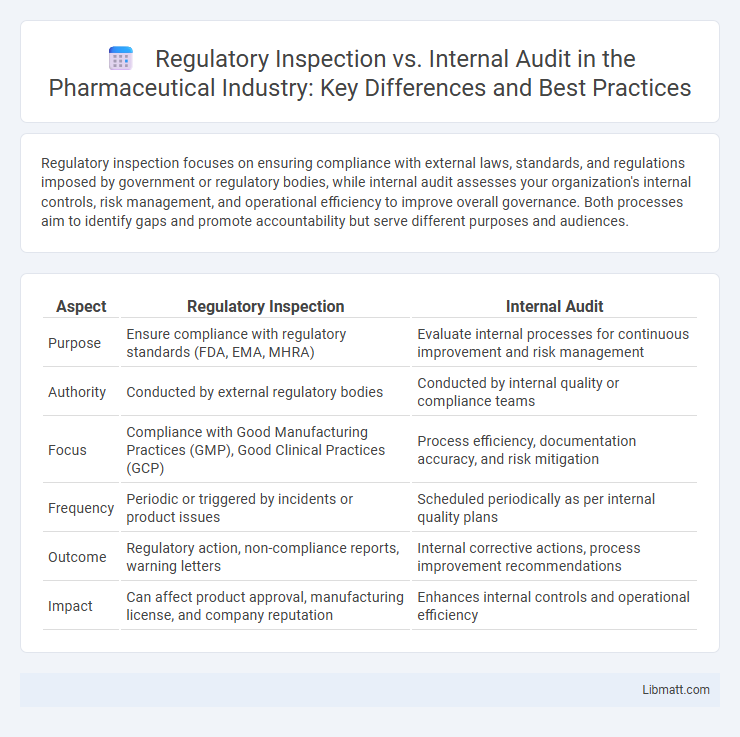
Regulatory inspection focuses on ensuring compliance with external laws, standards, and regulations imposed by government or regulatory bodies, while internal audit assesses your organization's internal controls, risk management, and operational efficiency to improve overall governance. Both processes aim to identify gaps and promote accountability but serve different purposes and audiences.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Regulatory Inspection | Internal Audit |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Ensure compliance with regulatory standards (FDA, EMA, MHRA) | Evaluate internal processes for continuous improvement and risk management |
| Authority | Conducted by external regulatory bodies | Conducted by internal quality or compliance teams |
| Focus | Compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), Good Clinical Practices (GCP) | Process efficiency, documentation accuracy, and risk mitigation |
| Frequency | Periodic or triggered by incidents or product issues | Scheduled periodically as per internal quality plans |
| Outcome | Regulatory action, non-compliance reports, warning letters | Internal corrective actions, process improvement recommendations |
| Impact | Can affect product approval, manufacturing license, and company reputation | Enhances internal controls and operational efficiency |
Introduction to Regulatory Inspections and Internal Audits
Regulatory inspections are formal evaluations conducted by government agencies to ensure compliance with laws, regulations, and industry standards within organizations. Internal audits are systematic, independent assessments carried out by company personnel to evaluate internal controls, risk management, and operational effectiveness. Both processes aim to improve organizational governance, but regulatory inspections emphasize external compliance, while internal audits focus on continuous internal improvement.
Defining Regulatory Inspection
Regulatory inspection is a formal evaluation conducted by government or authorized agencies to ensure compliance with laws, regulations, and standards within specific industries, such as pharmaceuticals, food safety, or environmental protection. These inspections assess adherence to mandatory requirements and often involve detailed documentation review, on-site facility examination, and interviews with personnel. Unlike internal audits, regulatory inspections carry legal authority and can result in enforcement actions or penalties if non-compliance is identified.
Understanding Internal Audit
Internal audit serves as a proactive risk management tool designed to evaluate and improve your organization's internal controls, governance, and operational efficiency. Unlike regulatory inspections conducted by external authorities to ensure compliance with legal standards, internal audits are performed by your own staff to identify potential issues before they escalate. This continuous self-assessment helps maintain preparedness for regulatory inspections and reinforces organizational accountability.
Key Differences Between Regulatory Inspection and Internal Audit
Regulatory inspections are conducted by external government agencies to ensure compliance with specific laws and regulations, whereas internal audits are performed by an organization's staff to evaluate internal controls and operational efficiency. Regulatory inspections often result in formal reports with potential penalties for non-compliance, while internal audits provide management with insights for continuous improvement without legal consequences. The scope of regulatory inspections is typically narrower and mandated by law, whereas internal audits cover broader organizational risks and strategic objectives.
Objectives of Regulatory Inspections
Regulatory inspections primarily aim to ensure compliance with laws, regulations, and standards set by governmental authorities, focusing on public safety, environmental protection, and consumer rights. These inspections verify that organizations meet mandatory requirements and take corrective actions when violations are identified, maintaining accountability and reducing risks. Unlike internal audits, regulatory inspections have the authority to impose penalties and enforce legal consequences for non-compliance.
Objectives of Internal Audits
Internal audits aim to evaluate and improve your organization's risk management, control, and governance processes, ensuring operational efficiency and compliance with internal policies. Unlike regulatory inspections that enforce external legal standards, internal audits focus on identifying gaps and recommending improvements proactively. This helps maintain continuous organizational performance and readiness for any external assessments.
Processes Involved in Regulatory Inspections
Regulatory inspections involve a thorough evaluation of compliance with laws, regulations, and industry standards through document reviews, on-site observations, and interviews with personnel. Inspectors assess operational processes, safety measures, and record-keeping practices to ensure your organization adheres to mandated requirements. These inspections often result in formal reports highlighting non-compliance issues and required corrective actions.
Processes Involved in Internal Audits
Internal audits involve systematic evaluations of an organization's processes, controls, and compliance with established standards to identify risks and improve operational efficiency. The process typically includes planning, risk assessment, conducting fieldwork through interviews and document reviews, and reporting findings to management. This approach ensures continuous improvement by addressing weaknesses before regulatory inspections identify non-compliance.
Compliance Implications: Regulatory Inspection vs. Internal Audit
Regulatory inspections enforce compliance with external laws and standards, often resulting in penalties for non-compliance, while internal audits focus on identifying and mitigating risks within your organization to improve adherence to policies. Regulatory inspections carry legal implications and may trigger corrective actions mandated by authorities, whereas internal audits support proactive compliance management and continuous improvement. Understanding these differences helps you prioritize resources effectively to maintain both regulatory compliance and operational excellence.
Best Practices for Managing Both Inspections and Audits
Effective management of regulatory inspections and internal audits requires establishing clear processes, maintaining comprehensive documentation, and ensuring ongoing staff training on compliance standards. You should implement a centralized system for tracking findings, corrective actions, and deadlines to facilitate transparency and accountability. Regular communication between audit and inspection teams helps align objectives, reduce redundancies, and improve overall compliance performance.
Regulatory inspection vs internal audit Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com