Potency measures the strength or concentration of an active ingredient in a product, while purity refers to the absence of contaminants or impurities within that substance. Understanding the difference between potency and purity helps you evaluate the quality and effectiveness of pharmaceuticals or supplements accurately.
Table of Comparison
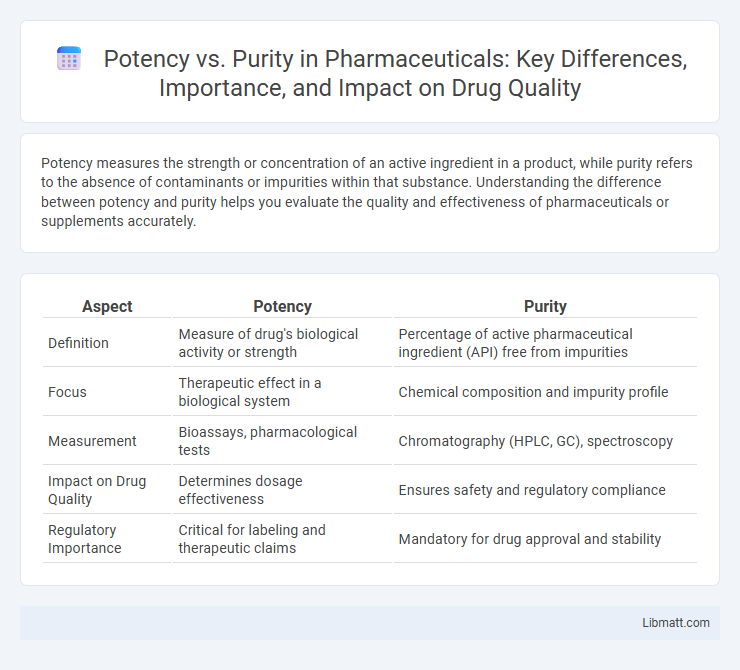
| Aspect | Potency | Purity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Measure of drug's biological activity or strength | Percentage of active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) free from impurities |
| Focus | Therapeutic effect in a biological system | Chemical composition and impurity profile |
| Measurement | Bioassays, pharmacological tests | Chromatography (HPLC, GC), spectroscopy |
| Impact on Drug Quality | Determines dosage effectiveness | Ensures safety and regulatory compliance |
| Regulatory Importance | Critical for labeling and therapeutic claims | Mandatory for drug approval and stability |
Understanding Potency and Purity: Key Definitions
Potency measures the concentration of active ingredients in a substance, indicating its strength and therapeutic effect, while purity refers to the absence of contaminants or impurities within the product. Accurate assessment of potency ensures dosage effectiveness, whereas high purity guarantees safety and quality, both critical for pharmaceuticals and chemical products. Distinguishing these parameters aids in optimizing formulations and regulatory compliance.
The Role of Potency in Product Effectiveness
Potency plays a crucial role in product effectiveness by determining the concentration of active ingredients available to produce the desired therapeutic outcome. Higher potency ensures that a smaller amount of product can deliver the intended effect, which is essential for consistency and reliability in treatment. Your choice of product should consider potency to achieve optimal results without unnecessarily increasing exposure to inactive substances.
Why Purity Matters in Chemical and Pharmaceutical Products
Purity in chemical and pharmaceutical products ensures the absence of impurities that could compromise safety, efficacy, and stability. High purity levels guarantee consistent potency, allowing your medications to deliver accurate therapeutic effects without harmful side effects. Regulatory standards prioritize purity to protect patient health and maintain product quality throughout manufacturing and storage.
Potency vs Purity: Similarities and Differences
Potency and purity are critical metrics in pharmaceutical and chemical analysis, where potency measures the active ingredient's strength or concentration in a formulation, while purity assesses the proportion of a substance free from impurities or contaminants. Both parameters directly impact drug efficacy and safety, yet potency relates to therapeutic effect, whereas purity ensures product quality and consistency. Understanding the distinction between potency and purity is essential for quality control, regulatory compliance, and accurate dosage determination in drug manufacturing.
How Potency and Purity Impact Consumer Safety
Potency and purity directly influence consumer safety by determining the effectiveness and risk level of a product, especially in pharmaceuticals and supplements. High potency ensures the desired therapeutic effect, while high purity minimizes harmful contaminants and adverse reactions. Your health depends on accurately labeled potency and purity to avoid overdosing or exposure to toxic substances.
Testing Methods for Measuring Potency
Testing methods for measuring potency include High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) and Gas Chromatography (GC), which provide precise quantification of active compounds. Mass Spectrometry (MS) coupled with chromatography enhances detection sensitivity and specificity, ensuring accurate potency assessment. You can rely on these advanced techniques to verify the strength of your products, distinguishing potency from purity effectively.
Techniques Used to Assess Purity
Techniques used to assess purity include High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC), Gas Chromatography (GC), and Mass Spectrometry (MS), which provide precise quantification of impurities in a substance. Spectroscopic methods such as Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) and Infrared Spectroscopy (IR) aid in identifying chemical structures and detecting adulterants. These analytical tools are essential for distinguishing purity from potency, ensuring accurate characterization of pharmaceutical compounds and supplements.
Regulatory Standards for Potency and Purity
Regulatory standards for potency and purity establish strict guidelines to ensure that pharmaceutical and supplement products contain the specified amount of active ingredients and are free from contaminants. Agencies such as the FDA and EMA require rigorous testing and validation to confirm that potency matches label claims and purity levels meet safety thresholds, protecting consumer health. Your trust in product quality depends on adherence to these established regulatory frameworks, which guarantee consistent efficacy and safety.
Common Misconceptions about Potency and Purity
Potency measures the strength or concentration of an active ingredient, while purity indicates the absence of contaminants or impurities. A common misconception is that high potency guarantees high purity, but a product can be potent yet contain unwanted substances. Understanding both factors is essential for accurate product evaluation and safety assurance.
Choosing Products: Balancing Potency and Purity for Best Results
Selecting products with a balanced combination of potency and purity ensures maximum efficacy while minimizing harmful contaminants. High potency guarantees the desired strength and effect, whereas superior purity reduces risks linked to additives or impurities. Consumers should seek third-party lab testing results that validate both the concentration of active ingredients and the absence of contaminants for optimal safety and performance.
Potency vs purity Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com