USP water meets stringent purity standards for pharmaceutical use, ensuring minimal contaminants and suitability for injection or formulation. EP water, adhering to the European Pharmacopoeia, guarantees compliance with European regulatory requirements for quality and safety, providing reliable hydration for medicinal processes.
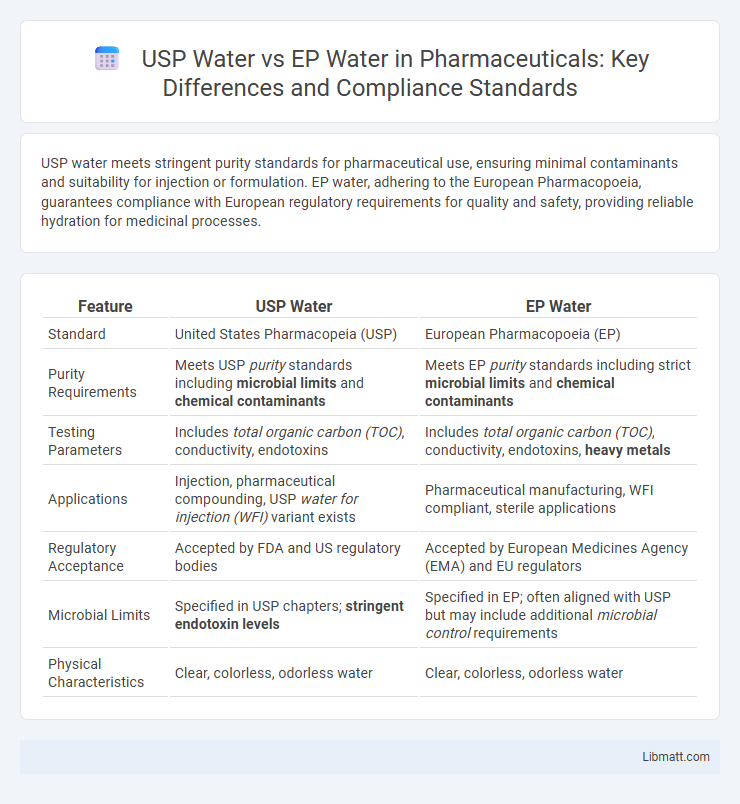
Table of Comparison
| Feature | USP Water | EP Water |
|---|---|---|
| Standard | United States Pharmacopeia (USP) | European Pharmacopoeia (EP) |
| Purity Requirements | Meets USP purity standards including microbial limits and chemical contaminants | Meets EP purity standards including strict microbial limits and chemical contaminants |
| Testing Parameters | Includes total organic carbon (TOC), conductivity, endotoxins | Includes total organic carbon (TOC), conductivity, endotoxins, heavy metals |
| Applications | Injection, pharmaceutical compounding, USP water for injection (WFI) variant exists | Pharmaceutical manufacturing, WFI compliant, sterile applications |
| Regulatory Acceptance | Accepted by FDA and US regulatory bodies | Accepted by European Medicines Agency (EMA) and EU regulators |
| Microbial Limits | Specified in USP chapters; stringent endotoxin levels | Specified in EP; often aligned with USP but may include additional microbial control requirements |
| Physical Characteristics | Clear, colorless, odorless water | Clear, colorless, odorless water |
Overview of USP and EP Pharmaceutical Water Standards
USP water standards for pharmaceutical use, established by the United States Pharmacopeia, emphasize purity levels necessary for drug formulation and manufacturing, including Purified Water and Water for Injection types. EP water standards, defined by the European Pharmacopoeia, also set stringent criteria for microbial limits, conductivity, and endotoxin levels to ensure safety and efficacy in pharmaceutical applications. Both USP and EP specify rigorous testing protocols and quality attributes to maintain water quality critical for compliance with global pharmaceutical regulations.
Key Differences Between USP Water and EP Water
USP water complies with the United States Pharmacopeia standards, primarily used in pharmaceutical and laboratory settings within the U.S., ensuring purity levels suitable for drug formulation. EP water meets the European Pharmacopoeia criteria, tailored for pharmaceutical applications in Europe, with specific microbial limits and chemical purity requirements. The key differences include regional regulatory standards, microbial limits, and testing methods that distinguish USP water from EP water in quality control and application.
Types of Pharmaceutical Water: USP vs EP
USP water and EP water are both essential types of pharmaceutical water used in drug manufacturing, formulated according to different pharmacopeial standards--the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) and the European Pharmacopoeia (EP). USP water, including Purified Water and Water for Injection, is primarily utilized in the U.S. while EP water meets stringent European regulatory criteria, emphasizing microbiological quality and endotoxin limits. Choosing the appropriate type ensures Your pharmaceutical processes comply with regional regulations and maintain product safety and efficacy.
Regulatory Bodies: USP vs EP Requirements
USP water and EP water adhere to distinct regulatory standards set by their respective governing bodies: the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) and the European Pharmacopoeia (EP). USP water standards emphasize criteria such as microbial limits, conductivity, and endotoxin levels tailored for the U.S. pharmaceutical market, while EP water requirements focus on similar quality parameters but with specific thresholds and testing methods aligned with European regulatory expectations. Compliance with USP or EP water specifications ensures pharmaceutical products meet regional safety, purity, and efficacy standards mandated by regulatory authorities like the FDA in the United States and the EMA in Europe.
Purity Specifications: Microbial and Chemical Limits
USP water adheres to strict purity specifications, maintaining microbial limits with a maximum of 100 CFU/mL and no detectable endotoxins, while chemical impurities must not exceed specified limits for heavy metals and organic compounds. EP water standards are similarly rigorous, imposing exact microbial count maximums and precise thresholds for chemical contaminants to ensure pharmaceutical-grade quality. Your choice between USP and EP water should consider these detailed purity specifications to meet regulatory and application-specific requirements.
Production Methods: USP Water vs EP Water
USP water is produced through highly controlled processes such as distillation, reverse osmosis, or deionization to meet stringent purity standards required for pharmaceutical applications. EP water is manufactured according to the European Pharmacopoeia guidelines, commonly involving methods like distillation or deionization, ensuring compliance with European regulatory criteria. Both USP and EP water undergo rigorous purification to achieve specific conductivity, total organic carbon (TOC), and microbial limits tailored to their respective pharmacopeial standards.
Applications in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
USP water and EP water are both critical in pharmaceutical manufacturing, but USP water is primarily used for general applications such as cleaning and formulation, while EP water meets stricter standards required for injectable products. USP water includes Purified Water and Water for Injection (WFI), with WFI being essential for producing sterile injectable drugs due to its higher purity and endotoxin limits. EP water, adhering to the European Pharmacopoeia guidelines, ensures compliance with European regulatory requirements, making it preferred in facilities manufacturing pharmaceuticals for the European market.
Testing and Quality Control Procedures
USP water undergoes rigorous testing for endotoxins, microbial contamination, and conductivity to ensure it meets strict pharmacopeial standards, while EP water is tested according to the European Pharmacopeia with similar parameters including total organic carbon (TOC) levels and sterility. Both types of water require stringent quality control procedures such as routine microbial bioburden testing, chemical purity assays, and validation of purification systems to confirm compliance with their respective pharmacopeial requirements. Continuous monitoring and documentation are critical to guarantee that USP and EP water maintain the high purity needed for pharmaceutical manufacturing and laboratory applications.
Global Compliance: Harmonization and Challenges
USP water and EP water standards aim for global compliance through harmonization with respective pharmacopoeias, ensuring consistent purity and quality for pharmaceutical use. Challenges arise from regional regulatory variations and differing test methods, which complicate mutual recognition and standardization efforts. Ongoing collaboration between USP and EP organizations seeks to align specifications, analytical techniques, and validation protocols to mitigate these discrepancies worldwide.
Choosing the Right Water Standard for Your Facility
Selecting between USP water and EP water standards depends on your facility's regulatory requirements and intended application, as USP water meets the United States Pharmacopeia criteria while EP water adheres to the European Pharmacopeia standards. Ensuring compliance with the specific pharmacopoeial standards guarantees the purity and quality necessary for pharmaceutical manufacturing, laboratory use, or formulation processes. Your choice impacts product safety, regulatory approval, and operational consistency within your facility.
USP water vs EP water Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com