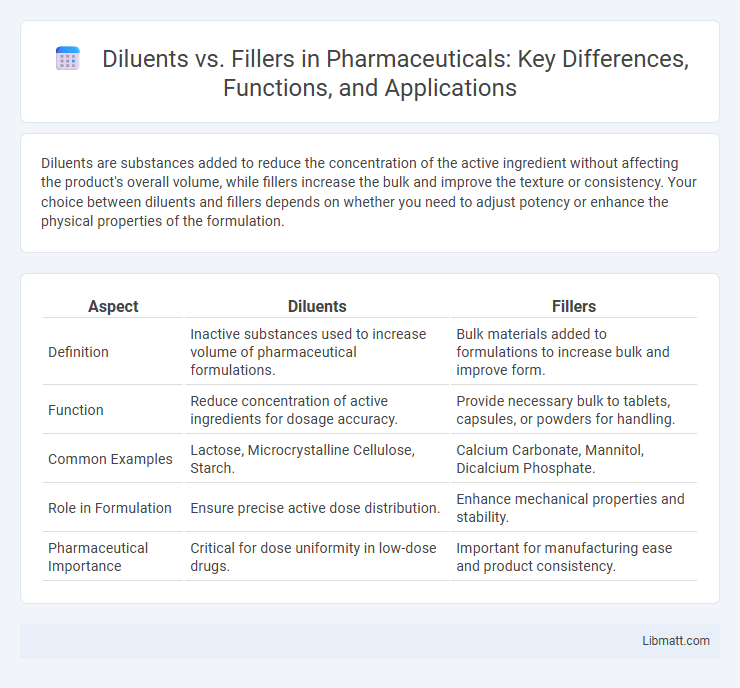
Diluents are substances added to reduce the concentration of the active ingredient without affecting the product's overall volume, while fillers increase the bulk and improve the texture or consistency. Your choice between diluents and fillers depends on whether you need to adjust potency or enhance the physical properties of the formulation.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Diluents | Fillers |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Inactive substances used to increase volume of pharmaceutical formulations. | Bulk materials added to formulations to increase bulk and improve form. |
| Function | Reduce concentration of active ingredients for dosage accuracy. | Provide necessary bulk to tablets, capsules, or powders for handling. |
| Common Examples | Lactose, Microcrystalline Cellulose, Starch. | Calcium Carbonate, Mannitol, Dicalcium Phosphate. |
| Role in Formulation | Ensure precise active dose distribution. | Enhance mechanical properties and stability. |
| Pharmaceutical Importance | Critical for dose uniformity in low-dose drugs. | Important for manufacturing ease and product consistency. |
Introduction to Diluents and Fillers
Diluents and fillers are commonly used substances in pharmaceutical and industrial formulations to modify texture, volume, and concentration without altering the active ingredient's properties. Diluents primarily reduce the concentration of active components to create the desired dosage, while fillers are added to increase bulk and improve manufacturing efficiency. Your understanding of the specific roles and compatibility of these excipients can optimize product performance and stability.
Definitions: What Are Diluents and Fillers?
Diluents are substances added to active pharmaceutical ingredients to reduce concentration without affecting therapeutic properties, optimizing dosage form consistency and ease of administration. Fillers, also known as bulking agents, increase the volume or mass of a formulation, ensuring uniformity and stability in tablets or capsules. Understanding the specific role of each helps you tailor formulation strategies for efficient drug delivery.
Key Differences Between Diluents and Fillers
Diluents primarily reduce the concentration or viscosity of active ingredients in formulations, whereas fillers mainly add bulk or volume without significantly altering the chemical properties. You should recognize that diluents are crucial in modifying the delivery or consistency of a product, while fillers enhance physical attributes such as size and texture. Understanding these key differences ensures precise formulation control and optimal performance in pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, or industrial applications.
Common Applications in Various Industries
Diluents and fillers are widely used across industries such as pharmaceuticals, construction, food processing, and cosmetics to modify product properties and improve performance. In pharmaceuticals, diluents act as inactive substances to bulk up formulations for tablets, while fillers in construction enhance texture or volume in materials like concrete and plaster. Your choice between diluents and fillers depends on the desired chemical interaction, physical characteristics, and end-use application.
Types of Diluents and Their Uses
Common types of diluents include lactose, microcrystalline cellulose, and starch, each serving specific purposes in pharmaceutical formulations. Lactose enhances powder flow and compressibility, microcrystalline cellulose provides excellent binding and disintegration properties, while starch acts as a disintegrant and filler. Your choice of diluent affects tablet consistency, dissolution rate, and overall drug efficacy.
Types of Fillers and Their Functions
Fillers such as calcium carbonate, talc, and silica enhance the volume and texture of products while improving stability and reducing production costs. Calcium carbonate acts as a cost-effective extender and improves bulk density, talc provides lubrication and improves flow properties, and silica enhances moisture resistance and anti-caking characteristics. These fillers optimize product performance in industries like pharmaceuticals, plastics, and cosmetics by modifying physical and mechanical properties without altering chemical composition.
Impact on Product Performance and Quality
Diluents primarily reduce the concentration of active ingredients without significantly altering the physical properties, ensuring consistent product performance and maintaining quality standards. Fillers, on the other hand, modify the texture, bulk, or structural integrity, which can enhance stability and ease of processing but may affect dissolution rates or bioavailability. Selecting appropriate diluents and fillers is critical to optimizing formulation efficacy, mechanical strength, and overall product consistency.
Selection Criteria: Choosing Diluents vs Fillers
Selection criteria for choosing diluents versus fillers depend on their functional roles in formulations; diluents primarily adjust viscosity and flow properties, while fillers enhance bulk and mechanical strength. Factors such as compatibility with active ingredients, desired texture, cost-effectiveness, and regulatory approval guide the decision-making process. Optimal selection balances formulation stability, processing efficiency, and end-product performance.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Diluents typically consist of substances designed to reduce viscosity or modify the physical properties of formulations with lower toxicity profiles, whereas fillers often include mineral-based materials that can pose inhalation hazards and environmental persistence concerns. The environmental impact of fillers, such as calcium carbonate or talc, involves potential ecosystem accumulation and disposal challenges, while diluents formulated with bio-based or biodegradable compounds offer improved sustainability and reduced ecological footprint. Safety measures for handling fillers must emphasize dust control and respiratory protection, contrasting with the generally safer handling protocols required for most diluents used in industrial and pharmaceutical applications.
Future Trends in Diluents and Fillers
Future trends in diluents and fillers emphasize the development of environmentally friendly and bio-based materials to meet sustainability goals in various industries. Innovations are driven by the demand for improved performance characteristics such as enhanced durability, reduced weight, and compatibility with advanced composites. Your choice of diluents and fillers will increasingly depend on regulatory compliance, eco-efficiency, and the ability to tailor properties for specific applications in automotive, construction, and packaging sectors.
Diluents vs Fillers Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com