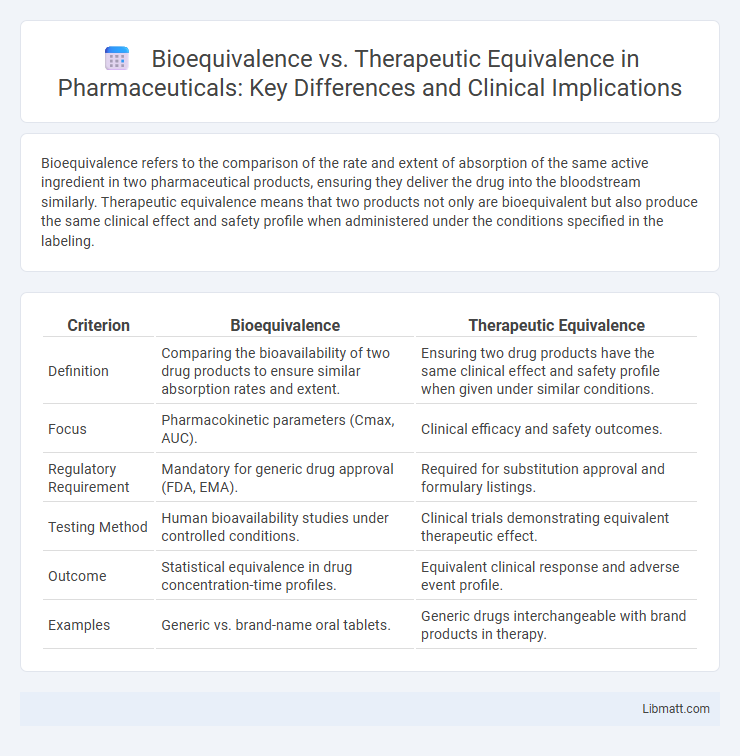
Bioequivalence refers to the comparison of the rate and extent of absorption of the same active ingredient in two pharmaceutical products, ensuring they deliver the drug into the bloodstream similarly. Therapeutic equivalence means that two products not only are bioequivalent but also produce the same clinical effect and safety profile when administered under the conditions specified in the labeling.
Table of Comparison
| Criterion | Bioequivalence | Therapeutic Equivalence |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Comparing the bioavailability of two drug products to ensure similar absorption rates and extent. | Ensuring two drug products have the same clinical effect and safety profile when given under similar conditions. |
| Focus | Pharmacokinetic parameters (Cmax, AUC). | Clinical efficacy and safety outcomes. |
| Regulatory Requirement | Mandatory for generic drug approval (FDA, EMA). | Required for substitution approval and formulary listings. |
| Testing Method | Human bioavailability studies under controlled conditions. | Clinical trials demonstrating equivalent therapeutic effect. |
| Outcome | Statistical equivalence in drug concentration-time profiles. | Equivalent clinical response and adverse event profile. |
| Examples | Generic vs. brand-name oral tablets. | Generic drugs interchangeable with brand products in therapy. |
Introduction to Bioequivalence and Therapeutic Equivalence
Bioequivalence refers to the comparison of the bioavailability of two pharmaceutical products, ensuring that they release the active ingredient into the bloodstream at the same rate and extent. Therapeutic equivalence indicates that pharmaceutical products are pharmaceutically equivalent and expected to have the same clinical effect and safety profile when administered under the conditions specified. Regulatory agencies require demonstration of bioequivalence as a critical step to establish therapeutic equivalence for generic drug approval.
Defining Bioequivalence: Key Concepts
Bioequivalence refers to the absence of a significant difference in the rate and extent of absorption of the active pharmaceutical ingredient between two drug products under similar conditions. Key concepts include pharmacokinetic parameters such as Cmax, Tmax, and AUC, which are measured to ensure comparable plasma concentration profiles. Demonstrating bioequivalence is critical for generic drug approval, indicating that the generic product delivers the same therapeutic effect as the reference brand.
Understanding Therapeutic Equivalence
Therapeutic equivalence ensures that two drugs not only have the same active ingredients and bioavailability but also produce the same clinical effect and safety profile when administered under recommended conditions. It confirms that your medication will perform identically in terms of efficacy and side effects, regardless of the manufacturer. Understanding therapeutic equivalence is crucial for selecting appropriate generic alternatives that guarantee consistent treatment outcomes.
Regulatory Standards and Guidelines
Regulatory standards for bioequivalence emphasize pharmacokinetic parameters such as Cmax and AUC to ensure generic drugs exhibit comparable absorption rates and extents to reference products. Therapeutic equivalence standards, governed by agencies like the FDA and EMA, require both bioequivalence and pharmaceutical equivalence, confirming that generic drugs have the same clinical effect and safety profile. Guidelines outlined in documents like the FDA's Orange Book and EMA's bioequivalence guidelines provide specific protocols and acceptance criteria to validate these equivalences for market approval.
Comparative Evaluation Methods
Comparative evaluation methods for bioequivalence involve pharmacokinetic studies measuring drug concentration in plasma to ensure similar absorption rates between generic and brand-name drugs. Therapeutic equivalence assessment requires clinical trials evaluating safety, efficacy, and therapeutic outcomes to confirm that different drug formulations produce the same clinical effect. Your choice between these methods depends on regulatory requirements and the complexity of the drug's therapeutic profile.
Clinical Relevance of Bioequivalence
Bioequivalence ensures that two pharmaceutical products release the same active ingredient at the same rate and extent, which is critical for predicting similar clinical outcomes. Therapeutic equivalence extends this concept by requiring similar safety and efficacy profiles in clinical use, confirming that substituting one product for another will not affect the clinical result. The clinical relevance of bioequivalence lies in its regulatory role for generic drug approval, ensuring that generics provide the same therapeutic benefits as branded drugs without direct clinical trials.
Therapeutic Equivalence in Drug Substitution
Therapeutic equivalence ensures that substituted drugs are pharmaceutically equivalent and expected to have the same clinical effect and safety profile when administered under the same conditions. Regulatory agencies require evidence of therapeutic equivalence before approving generic drugs for substitution to guarantee that your treatment remains consistent and effective. Understanding this concept helps optimize medication management by ensuring substituted drugs deliver the same therapeutic benefits without compromising patient outcomes.
Challenges in Assessment and Interpretation
Bioequivalence assessment faces challenges due to variability in pharmacokinetic parameters and the influence of formulation differences on drug absorption. Therapeutic equivalence evaluation is complicated by patient-specific factors, clinical endpoint variability, and differences in therapeutic outcomes beyond mere bioavailability. Your accurate interpretation requires understanding these complexities to ensure safe and effective substitution between drug products.
Implications for Healthcare Providers and Patients
Bioequivalence ensures that generic drugs have the same rate and extent of absorption as their brand-name counterparts, providing confidence for healthcare providers in prescribing cost-effective alternatives. Therapeutic equivalence goes further by confirming that these drugs produce the same clinical effect and safety profile, which is crucial for patient outcomes and treatment consistency. Understanding the distinction aids healthcare providers in making informed decisions, optimizing medication efficacy, and enhancing patient trust in generic substitution.
Future Trends and Research Directions
Future trends in bioequivalence research emphasize advances in pharmacokinetic modeling and the integration of real-world evidence to enhance generic drug evaluation. Emerging techniques such as physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modeling and biomarker-driven studies aim to refine therapeutic equivalence assessments beyond traditional metrics. Research directions increasingly focus on personalized medicine and digital health technologies to ensure more precise bioequivalence and therapeutic outcomes.
Bioequivalence vs Therapeutic equivalence Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com