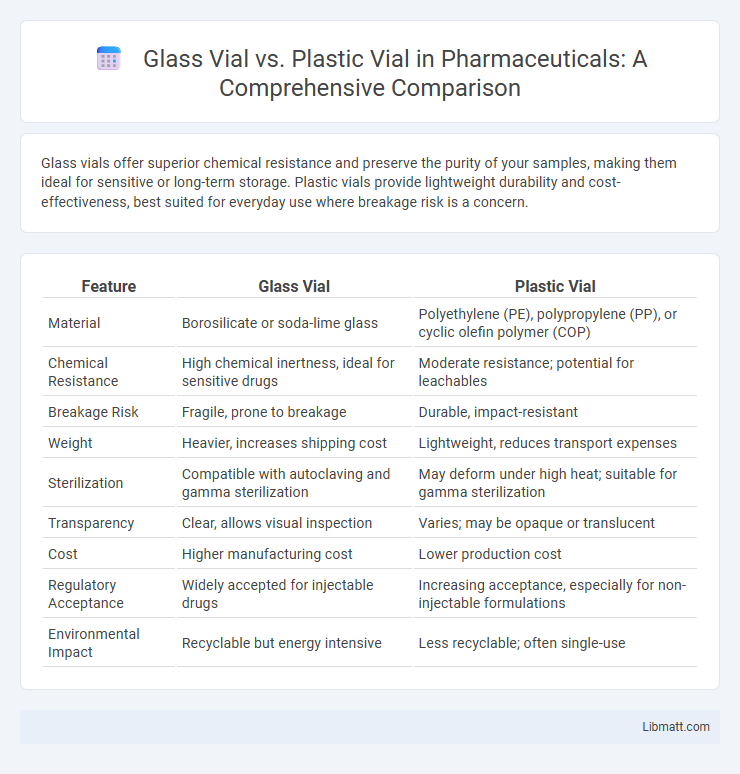
Glass vials offer superior chemical resistance and preserve the purity of your samples, making them ideal for sensitive or long-term storage. Plastic vials provide lightweight durability and cost-effectiveness, best suited for everyday use where breakage risk is a concern.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Glass Vial | Plastic Vial |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Borosilicate or soda-lime glass | Polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), or cyclic olefin polymer (COP) |
| Chemical Resistance | High chemical inertness, ideal for sensitive drugs | Moderate resistance; potential for leachables |
| Breakage Risk | Fragile, prone to breakage | Durable, impact-resistant |
| Weight | Heavier, increases shipping cost | Lightweight, reduces transport expenses |
| Sterilization | Compatible with autoclaving and gamma sterilization | May deform under high heat; suitable for gamma sterilization |
| Transparency | Clear, allows visual inspection | Varies; may be opaque or translucent |
| Cost | Higher manufacturing cost | Lower production cost |
| Regulatory Acceptance | Widely accepted for injectable drugs | Increasing acceptance, especially for non-injectable formulations |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable but energy intensive | Less recyclable; often single-use |
Introduction to Glass Vial vs Plastic Vial
Glass vials offer superior chemical resistance and airtight sealing compared to plastic vials, making them ideal for storing sensitive pharmaceuticals and laboratory samples. Plastic vials provide higher durability and shatter resistance, which is beneficial for handling and transportation in various medical and industrial applications. Choosing the right vial depends on your specific needs for chemical compatibility, durability, and storage stability.
Material Composition and Properties
Glass vials are made from silica-based materials, offering high chemical resistance, non-reactivity, and excellent clarity for visual inspection, making them ideal for storing sensitive pharmaceuticals. Plastic vials, typically composed of polypropylene or polyethylene, provide durability, flexibility, and impact resistance but may interact with certain chemicals and allow minimal permeability to gases. The choice between glass and plastic vials depends on the required barrier properties, chemical compatibility, and mechanical strength needed for specific applications.
Durability and Breakage Resistance
Plastic vials offer superior durability and breakage resistance compared to glass vials, making them ideal for environments requiring frequent handling or transport. Glass vials, while chemically inert and maintaining product purity, are more prone to cracking or shattering under impact or stress. Your choice between these materials should consider the balance between durability needs and the type of substance being stored to ensure safety and longevity.
Chemical Compatibility and Reactivity
Glass vials exhibit superior chemical compatibility and inertness, making them ideal for storing reactive or sensitive substances without risk of contamination or chemical interaction. Plastic vials, although lightweight and shatter-resistant, may leach additives or absorb certain chemicals over time, potentially compromising sample integrity. When selecting your vial, consider the chemical nature of your contents to ensure optimal stability and avoid unwanted reactions.
Sterility and Contamination Risks
Glass vials offer superior sterility due to their inert surface and resistance to chemical leaching, significantly reducing contamination risks in pharmaceutical and laboratory settings. Plastic vials, while lightweight and less fragile, are more susceptible to microbial contamination and chemical interactions that can compromise sample integrity. Choice between glass and plastic vials depends on stringent sterility requirements and the nature of the substances stored, with glass preferred for high-purity applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Glass vials demonstrate superior environmental sustainability due to their recyclability and inert nature, reducing chemical leaching and minimizing waste in landfills. Plastic vials, although lighter and less energy-intensive to produce, contribute significantly to microplastic pollution and often end up in non-biodegradable waste streams. Choosing glass vials supports circular economy practices and reduces the overall carbon footprint associated with pharmaceutical and laboratory packaging.
Cost Efficiency and Budget Considerations
Glass vials typically incur higher initial costs due to manufacturing and transportation expenses, whereas plastic vials offer a more cost-efficient option with lower production and shipping costs. Plastic vials also reduce budget strain by minimizing breakage risk during handling and storage, leading to fewer replacement expenses. However, long-term considerations should include the application requirements and potential regulatory compliance impacting overall cost efficiency.
Storage and Transportation Factors
Glass vials provide superior chemical resistance and maintain product integrity during extended storage, making them ideal for sensitive pharmaceuticals and biologics. Plastic vials are lighter, more impact-resistant, and reduce transportation costs by lowering overall package weight and minimizing breakage risks. Your choice between glass and plastic vials should consider the balance between durability, chemical compatibility, and logistical efficiency for optimal storage and transport outcomes.
Applications in Pharmaceuticals and Laboratories
Glass vials offer superior chemical inertness, making them ideal for storing sensitive pharmaceutical compounds and biologics without risk of contamination or reaction. Plastic vials provide enhanced durability and resistance to breakage, which is preferred in high-throughput laboratory environments where handling efficiency and safety are critical. Your choice between glass and plastic vials should consider factors like drug stability, sterility requirements, and the specific use case in pharmaceutical formulation or laboratory testing.
Choosing the Right Vial: Key Considerations
Choosing the right vial depends on factors such as chemical compatibility, durability, and cost-effectiveness; glass vials offer superior chemical resistance and are ideal for storing pharmaceuticals or sensitive samples, while plastic vials provide impact resistance and are suitable for general laboratory use. Consider the sample's nature, storage conditions, and potential interaction with container materials to ensure sample integrity and avoid contamination. Cost and environmental impact also influence vial selection, with glass being more recyclable and plastic offering lighter weight and reduced shipping costs.
Glass Vial vs Plastic Vial Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com