Bulk production focuses on manufacturing large quantities of products efficiently, while fill finish specifically involves filling containers with a product, such as vaccines or pharmaceuticals, and sealing them for distribution. Ensuring your fill finish process is optimized can significantly impact the quality and safety of the final product before it reaches the market.
Table of Comparison
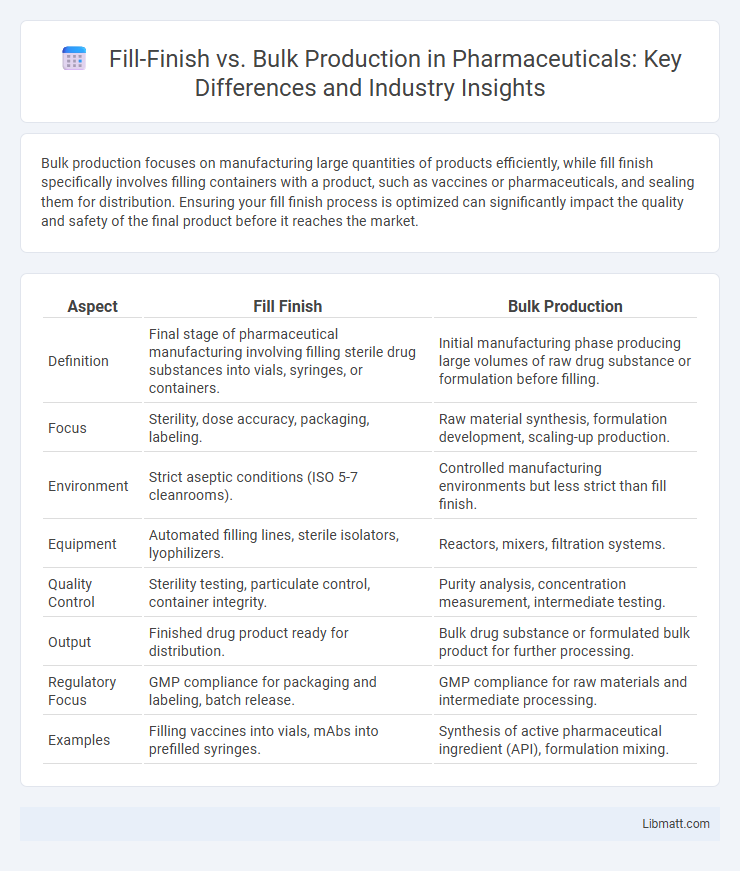
| Aspect | Fill Finish | Bulk Production |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Final stage of pharmaceutical manufacturing involving filling sterile drug substances into vials, syringes, or containers. | Initial manufacturing phase producing large volumes of raw drug substance or formulation before filling. |
| Focus | Sterility, dose accuracy, packaging, labeling. | Raw material synthesis, formulation development, scaling-up production. |
| Environment | Strict aseptic conditions (ISO 5-7 cleanrooms). | Controlled manufacturing environments but less strict than fill finish. |
| Equipment | Automated filling lines, sterile isolators, lyophilizers. | Reactors, mixers, filtration systems. |
| Quality Control | Sterility testing, particulate control, container integrity. | Purity analysis, concentration measurement, intermediate testing. |
| Output | Finished drug product ready for distribution. | Bulk drug substance or formulated bulk product for further processing. |
| Regulatory Focus | GMP compliance for packaging and labeling, batch release. | GMP compliance for raw materials and intermediate processing. |
| Examples | Filling vaccines into vials, mAbs into prefilled syringes. | Synthesis of active pharmaceutical ingredient (API), formulation mixing. |
Introduction to Fill Finish and Bulk Production
Fill finish refers to the final stage of pharmaceutical manufacturing where sterile drug products are filled into vials, syringes, or cartridges and sealed under aseptic conditions to ensure product safety and efficacy. Bulk production involves the large-scale synthesis and formulation of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) or drug compounds before they undergo the fill finish process. Efficient coordination between bulk production and fill finish is critical for maintaining product quality, regulatory compliance, and timely market supply.
Defining Fill Finish in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
Fill finish in pharmaceutical manufacturing refers to the critical process of aseptically filling vials, syringes, or bottles with the drug product and sealing them to ensure sterility and product integrity. This stage follows the bulk production phase, where the drug substance is synthesized and purified. Your choice between fill finish and bulk production impacts regulatory compliance, production timelines, and quality control measures in drug manufacturing.
What is Bulk Production?
Bulk production refers to the large-scale manufacturing process where raw pharmaceutical materials or drug substances are produced in bulk quantities before being processed into final dosage forms. This stage focuses on generating substantial volumes of the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or intermediate product under controlled conditions to ensure consistency, quality, and regulatory compliance. Bulk production is critical for meeting market demand and serving as the foundation for subsequent fill-finish operations.
Key Differences Between Fill Finish and Bulk Production
Fill finish involves aseptic filling of bulk drug substances into final containers such as vials, syringes, or bottles, emphasizing sterility and precise dosing. Bulk production refers to the large-scale synthesis and formulation of the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or drug substance before it is processed into final dosage forms. Key differences include the stage in the manufacturing process, where bulk production focuses on drug substance creation, while fill finish centers on packaging and preparing the drug for patient administration.
Advantages of Fill Finish Processes
Fill finish processes offer precise control over sterile product packaging, significantly reducing contamination risk during drug manufacturing. These processes ensure high accuracy in dosing and maintain product integrity, which is crucial for injectable pharmaceuticals. Leveraging advanced aseptic techniques and automation in fill finish enhances efficiency while complying with stringent regulatory standards.
Benefits of Bulk Production Methods
Bulk production methods offer significant cost-efficiency by manufacturing large volumes of pharmaceutical products in a continuous process, reducing per-unit expenses and minimizing waste. This approach enhances production scalability and consistency, ensuring uniform product quality across batches. Your facility can benefit from faster lead times and streamlined operations, supporting high-demand markets effectively.
Challenges in Fill Finish vs Bulk Production
Fill finish processes face challenges such as maintaining sterility, preventing contamination, and ensuring precise dosing, which require specialized equipment and strict regulatory compliance. Bulk production struggles with scaling up formulation consistency, managing raw material variability, and controlling large batch quality. Your manufacturing strategy must address these distinct hurdles to optimize efficiency and product integrity in both stages.
Regulatory Considerations for Both Approaches
Regulatory considerations for fill-finish and bulk production emphasize stringent compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and regulatory agency guidelines such as FDA and EMA standards. Fill-finish processes require validated aseptic techniques and environmental control to prevent contamination during vial filling, while bulk production demands robust process controls and thorough in-process testing to ensure product consistency. Both approaches must adhere to detailed documentation, batch record integrity, and comprehensive quality control to meet regulatory expectations for product safety and efficacy.
Industry Trends: When to Choose Fill Finish or Bulk Production
Industry trends reveal that fill finish is ideal for personalized therapies and small-batch biologics requiring sterile packaging and precision dosing, while bulk production suits high-volume vaccines and pharmaceuticals aiming for cost efficiency and faster scale-up. Advances in automation and single-use technologies are enhancing fill finish flexibility, aligning with personalized medicine demands. Your choice should depend on production scale, product type, and regulatory requirements to optimize quality and speed to market.
Conclusion: Selecting the Optimal Production Strategy
Selecting the optimal production strategy hinges on balancing quality control, scalability, and cost-efficiency. Fill finish processes excel in ensuring sterility and precision for high-value, sterile pharmaceuticals, while bulk production offers economies of scale for large-volume manufacturing. Your choice should align with product complexity, market demand, and regulatory requirements to maximize operational success.
Fill finish vs Bulk production Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com