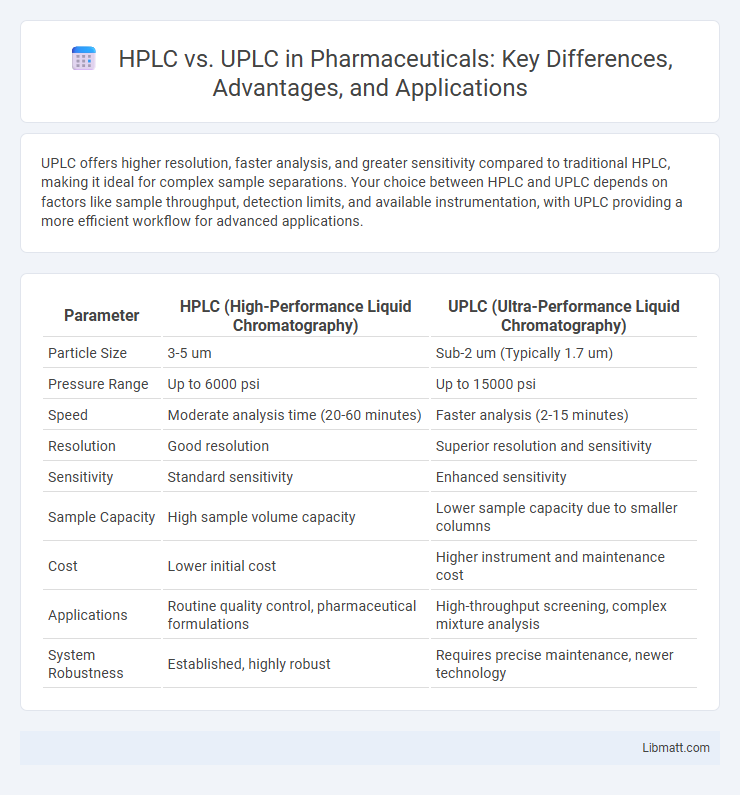
UPLC offers higher resolution, faster analysis, and greater sensitivity compared to traditional HPLC, making it ideal for complex sample separations. Your choice between HPLC and UPLC depends on factors like sample throughput, detection limits, and available instrumentation, with UPLC providing a more efficient workflow for advanced applications.
Table of Comparison
| Parameter | HPLC (High-Performance Liquid Chromatography) | UPLC (Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography) |
|---|---|---|
| Particle Size | 3-5 um | Sub-2 um (Typically 1.7 um) |
| Pressure Range | Up to 6000 psi | Up to 15000 psi |
| Speed | Moderate analysis time (20-60 minutes) | Faster analysis (2-15 minutes) |
| Resolution | Good resolution | Superior resolution and sensitivity |
| Sensitivity | Standard sensitivity | Enhanced sensitivity |
| Sample Capacity | High sample volume capacity | Lower sample capacity due to smaller columns |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher instrument and maintenance cost |
| Applications | Routine quality control, pharmaceutical formulations | High-throughput screening, complex mixture analysis |
| System Robustness | Established, highly robust | Requires precise maintenance, newer technology |
Introduction to HPLC and UPLC
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) and Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography (UPLC) are advanced techniques used for separating, identifying, and quantifying components in complex mixtures. HPLC operates at lower pressures with larger particle size columns, while UPLC employs smaller particle sizes and higher pressures, resulting in faster analysis and higher resolution. Both technologies are essential in pharmaceuticals, environmental analysis, and biochemistry for precise and efficient chemical separation.
Principles and Mechanisms of HPLC
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) operates on the principle of separating compounds based on their interactions between a stationary phase and a liquid mobile phase under high pressure. The mechanism relies on differences in analyte polarity, size, and affinity to the stationary phase to achieve separation. Your analytical goals can be optimized by understanding that HPLC uses larger particle sizes in the column compared to UPLC, resulting in longer run times but robust and reproducible separation.
Principles and Mechanisms of UPLC
UPLC (Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography) operates on principles similar to HPLC but utilizes smaller particle size columns (typically less than 2 um) that increase surface area and enhance separation efficiency. The high-pressure pumps in UPLC systems generate pressures up to 15,000 psi, enabling faster flow rates and reduced analysis time compared to traditional HPLC. UPLC's improved resolution and sensitivity result from optimized chromatographic mechanisms, including enhanced mass transfer and minimized peak dispersion.
Key Differences Between HPLC and UPLC
HPLC (High-Performance Liquid Chromatography) operates with larger particle sizes (3-5 um) and lower pressure limits (up to 6000 psi), whereas UPLC (Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography) utilizes smaller particle sizes (sub-2 um) and higher pressure capabilities (up to 15,000 psi), resulting in faster analysis times and higher resolution. UPLC offers enhanced sensitivity and better peak separation due to reduced dispersion, making it more suitable for complex sample matrices. Instrumentation costs for UPLC are typically higher, but the improved throughput and efficiency often justify the investment for high-performance analytical labs.
Resolution and Sensitivity Comparison
UPLC offers higher resolution than HPLC due to its use of smaller particle size columns, which enhances peak capacity and separation efficiency. Sensitivity in UPLC is significantly improved, as it allows for better detection of low-concentration analytes through sharper, more defined peaks. This combination of superior resolution and sensitivity makes UPLC the preferred choice for complex sample analysis requiring precise quantification.
Speed and Efficiency of Analysis
UPLC (Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography) offers significantly faster analysis times and higher resolution compared to traditional HPLC (High Performance Liquid Chromatography) due to its use of smaller particle size columns and higher system pressure. The increased efficiency of UPLC enables you to achieve sharper peaks and improved sensitivity, enhancing throughput and data quality in complex sample analysis. Speed and efficiency gains can reduce solvent consumption and operational costs while maintaining or improving chromatographic performance.
Sample Volume and Detection Limits
UPLC requires significantly lower sample volumes than HPLC, often in the microliter range, enabling more efficient use of precious or limited samples. Detection limits in UPLC are typically improved due to enhanced resolution and sensitivity, allowing for more accurate quantification of trace analytes. Optimizing your analytical method with UPLC can result in better detection performance while conserving sample material.
Instrumentation and Cost Considerations
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and ultra-performance liquid chromatography (UPLC) differ significantly in instrumentation; UPLC employs smaller particle size columns (sub-2 micron) and higher pressure limits (up to 15,000 psi) compared to HPLC's typical use of 3-5 micron particles and pressure up to 6,000 psi. The advanced technology in UPLC results in faster analysis times, higher resolution, and improved sensitivity, but requires more expensive pumps, detectors, and columns, increasing the initial capital investment. While HPLC systems are generally more affordable and suitable for routine analysis, UPLC offers enhanced performance with a higher cost, demanding consideration of budget constraints and throughput needs.
Applications in Pharmaceutical and Analytical Chemistry
HPLC (High-Performance Liquid Chromatography) and UPLC (Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography) are extensively used in pharmaceutical and analytical chemistry for drug development, quality control, and impurity profiling. UPLC offers higher resolution, faster analysis times, and enhanced sensitivity compared to traditional HPLC, making it ideal for complex sample matrices and trace-level quantification. Both techniques support regulatory compliance by accurately quantifying active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and detecting degradation products in stability studies.
Choosing Between HPLC and UPLC: Factors to Consider
Choosing between HPLC and UPLC depends on factors such as resolution, speed, and sample throughput requirements. UPLC offers higher resolution and faster analysis by operating at higher pressures with smaller particle sizes, ideal for high-throughput laboratories. HPLC remains suitable for routine analyses requiring lower operational costs and compatibility with a broader range of columns and equipment.
HPLC vs UPLC Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com