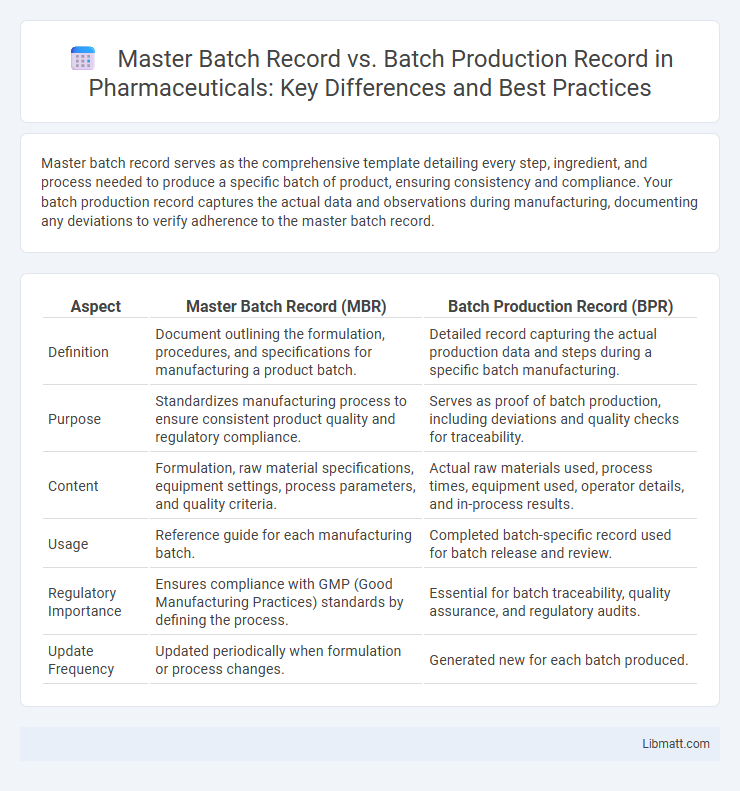
Master batch record serves as the comprehensive template detailing every step, ingredient, and process needed to produce a specific batch of product, ensuring consistency and compliance. Your batch production record captures the actual data and observations during manufacturing, documenting any deviations to verify adherence to the master batch record.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Master Batch Record (MBR) | Batch Production Record (BPR) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Document outlining the formulation, procedures, and specifications for manufacturing a product batch. | Detailed record capturing the actual production data and steps during a specific batch manufacturing. |
| Purpose | Standardizes manufacturing process to ensure consistent product quality and regulatory compliance. | Serves as proof of batch production, including deviations and quality checks for traceability. |
| Content | Formulation, raw material specifications, equipment settings, process parameters, and quality criteria. | Actual raw materials used, process times, equipment used, operator details, and in-process results. |
| Usage | Reference guide for each manufacturing batch. | Completed batch-specific record used for batch release and review. |
| Regulatory Importance | Ensures compliance with GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices) standards by defining the process. | Essential for batch traceability, quality assurance, and regulatory audits. |
| Update Frequency | Updated periodically when formulation or process changes. | Generated new for each batch produced. |
Introduction to Master Batch Record and Batch Production Record
Master Batch Record serves as a comprehensive blueprint detailing the standardized instructions, materials, and procedures required for producing a specific pharmaceutical product. Batch Production Record, derived from the Master Batch Record, documents the actual manufacturing process for a single batch, capturing data, deviations, and quality checks. Understanding the distinction between these records ensures Your manufacturing process maintains compliance and traceability within Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP).
Key Definitions: MBR vs BPR
Master Batch Record (MBR) serves as the comprehensive, standardized document outlining every process, formula, and specification necessary for manufacturing a product batch, ensuring consistent quality and compliance. Batch Production Record (BPR) is the detailed, real-time document capturing the actual execution data, observations, and deviations during the manufacturing of a specific batch, acting as a snapshot of production. Understanding the distinction between MBR and BPR is crucial for accurate documentation control, traceability, and regulatory compliance in your manufacturing process.
Purpose of Master Batch Record
The Master Batch Record serves as the comprehensive blueprint detailing the standardized procedures, materials, and specifications required to manufacture a pharmaceutical batch, ensuring consistent product quality and regulatory compliance. It outlines every step of the production process, including equipment settings, raw material quantities, and quality control tests. This document guides the creation of Batch Production Records, which capture the actual manufacturing data for individual batches.
Purpose of Batch Production Record
The Batch Production Record (BPR) provides detailed, step-by-step instructions to ensure consistent manufacturing and verification of each specific batch, serving as a real-time document during production. It captures actual data, materials used, equipment settings, and quality control results to verify compliance with established standards. Unlike the Master Batch Record (MBR), which serves as the standard template, the BPR functions as the definitive record validating that a batch was produced according to regulatory and company requirements.
Structural Differences Between MBR and BPR
Master Batch Record (MBR) serves as the comprehensive template detailing all necessary instructions, formulations, and quality standards required for manufacturing a specific batch. Batch Production Record (BPR) functions as the execution document that captures actual manufacturing data, including timestamps, operator signatures, and deviations during the production process. Structurally, MBR is standardized and static to ensure consistency across batches, whereas BPR is dynamic and customized per batch to record real-time production activities and variances.
Regulatory Requirements for MBR and BPR
Regulatory requirements for Master Batch Record (MBR) mandate detailed documentation of the standardized manufacturing process, ensuring consistent product quality and compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP). Batch Production Record (BPR) requirements emphasize precise real-time recording of each production batch, capturing deviations, equipment used, and operator details to validate traceability and accountability during manufacturing. Your pharmaceutical facility must rigorously maintain both MBR and BPR to meet stringent FDA and EMA regulations, minimizing risks of non-compliance and product recalls.
Role of MBR in Quality Assurance
The Master Batch Record (MBR) serves as the definitive blueprint for manufacturing processes, ensuring consistency, compliance, and regulatory adherence in pharmaceutical production. By standardizing all critical parameters and specifications, the MBR facilitates rigorous quality assurance and helps prevent deviations during batch production. It acts as a reference point against which Batch Production Records (BPRs) are reviewed to verify that each batch meets predefined quality standards.
How BPR Ensures Production Traceability
Batch Production Records (BPR) ensure production traceability by documenting each step of the manufacturing process, including raw material lot numbers, equipment used, and operator actions. This detailed record links every batch to its specific production parameters, enabling accurate tracking of product quality and deviations. Consequently, BPRs facilitate root cause analysis, regulatory compliance, and efficient recall management in pharmaceutical and manufacturing industries.
Common Errors in MBR and BPR Management
Common errors in Master Batch Record (MBR) management include inaccurate documentation of formulation details and failure to update records after process changes, leading to inconsistencies in production. In Batch Production Record (BPR) management, frequent mistakes involve incomplete raw material verification and omission of critical process parameters, which compromise batch traceability and product quality. Ensuring strict adherence to documentation protocols and real-time record validation significantly reduces discrepancies in both MBR and BPR processes.
Best Practices for Effective Recordkeeping
Master batch records provide standardized templates for batch production records, ensuring consistency and compliance in manufacturing processes. Effective recordkeeping involves accurately documenting each production batch against these templates, enabling traceability, quality control, and regulatory audits. Your best practices include maintaining detailed, legible entries, verifying data at each production stage, and regularly reviewing records for accuracy and completeness.
Master batch record vs batch production record Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com