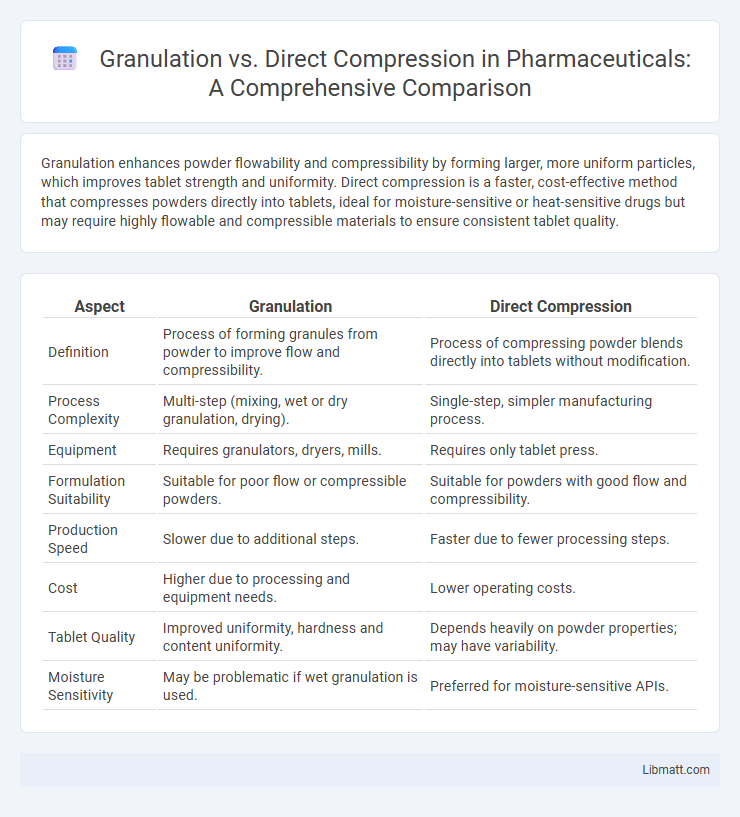
Granulation enhances powder flowability and compressibility by forming larger, more uniform particles, which improves tablet strength and uniformity. Direct compression is a faster, cost-effective method that compresses powders directly into tablets, ideal for moisture-sensitive or heat-sensitive drugs but may require highly flowable and compressible materials to ensure consistent tablet quality.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Granulation | Direct Compression |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of forming granules from powder to improve flow and compressibility. | Process of compressing powder blends directly into tablets without modification. |
| Process Complexity | Multi-step (mixing, wet or dry granulation, drying). | Single-step, simpler manufacturing process. |
| Equipment | Requires granulators, dryers, mills. | Requires only tablet press. |
| Formulation Suitability | Suitable for poor flow or compressible powders. | Suitable for powders with good flow and compressibility. |
| Production Speed | Slower due to additional steps. | Faster due to fewer processing steps. |
| Cost | Higher due to processing and equipment needs. | Lower operating costs. |
| Tablet Quality | Improved uniformity, hardness and content uniformity. | Depends heavily on powder properties; may have variability. |
| Moisture Sensitivity | May be problematic if wet granulation is used. | Preferred for moisture-sensitive APIs. |
Introduction to Oral Solid Dosage Forms
Oral solid dosage forms primarily include tablets and capsules, where granulation and direct compression are key manufacturing techniques. Granulation enhances powder flow and compressibility by forming aggregates, improving uniformity and tablet strength. Direct compression allows for faster production by compressing powders directly, requiring excipients with excellent flow and binding properties to ensure tablet integrity.
Understanding Granulation in Tablet Manufacturing
Granulation in tablet manufacturing involves forming powder particles into larger, free-flowing aggregates to improve compressibility and uniformity in dosage. This process enhances the physical properties of the powder blend, ensuring consistent tablet weight, strength, and dissolution rates compared to direct compression. Understanding granulation allows you to optimize tablet formulation for better handling and reliable drug delivery.
Overview of Direct Compression Technique
Direct compression is a pharmaceutical tablet manufacturing technique where powdered ingredients are compressed into tablets without any prior granulation. It requires powders with good flowability and compressibility, such as microcrystalline cellulose or lactose, to ensure uniformity and tablet integrity. This method offers advantages including reduced processing time, lower production costs, and minimal exposure to moisture or heat, making it ideal for moisture-sensitive formulations.
Key Differences Between Granulation and Direct Compression
Granulation involves agglomerating powder particles to improve flowability and compressibility, while direct compression blends powders that can be compressed directly into tablets without prior processing. Granulation typically requires multiple steps including mixing, wetting, and drying, whereas direct compression is a simpler, faster process with fewer manufacturing stages. Key differences include granulation's capacity to handle poor flow materials versus direct compression's reliance on excipients with excellent flow and compressibility properties.
Advantages of Granulation Method
Granulation offers improved powder flowability and uniformity, ensuring consistent dosage and content uniformity in tablet manufacturing. This method enhances the compressibility of active pharmaceutical ingredients, reducing the risk of segregation and improving tablet hardness and dissolution profiles. Your formulations benefit from better moisture control and reduced dust generation, making granulation ideal for handling sticky or cohesive powders.
Benefits of Direct Compression Process
Direct compression offers significant benefits such as reduced manufacturing time and lower production costs by eliminating the need for wet granulation or drying steps. This process ensures better content uniformity and improved product stability by minimizing exposure to heat and moisture. Additionally, direct compression is highly suitable for moisture-sensitive and heat-labile drugs, enhancing overall formulation efficiency and scalability.
Material Requirements for Each Method
Granulation requires materials with good binding properties and moisture content tolerance to form granules, making it suitable for powders that are cohesive or have poor flowability. Direct compression demands excipients with excellent flow and compaction characteristics, such as microcrystalline cellulose or lactose, designed for powders that can be compressed directly without prior treatment. Material selection is critical in each method to ensure tablet uniformity, stability, and dissolution profiles.
Common Applications in Pharmaceutical Industry
Granulation is widely applied in the pharmaceutical industry for producing tablets that require improved flowability, uniformity, and compressibility, especially for moisture-sensitive or poorly compressible drugs. Direct compression is favored for formulations with stable, free-flowing powders, allowing faster production of tablets without the need for additional processing steps. Both methods are crucial for manufacturing oral solid dosage forms, with granulation often used in controlled-release tablets and direct compression preferred for immediate-release products.
Factors Influencing Method Selection
Factors influencing the choice between granulation and direct compression include the properties of the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API), such as particle size, flowability, and compressibility. Your formulation's moisture sensitivity and required tablet strength also play critical roles, as granulation enhances cohesion and uniformity, whereas direct compression relies on excipients with good binding properties. Equipment availability and production scale further determine the most efficient and cost-effective manufacturing method.
Future Trends in Tablet Manufacturing Techniques
Future trends in tablet manufacturing emphasize continuous processing and advanced granulation technologies such as hot-melt extrusion and fluid bed granulation to enhance uniformity and bioavailability. Direct compression remains favored for its simplicity and cost-effectiveness, but innovations in excipient development and digital formulation design improve compressibility and stability. Integration of process analytical technology (PAT) and machine learning algorithms optimize both granulation and direct compression, driving precision, scalability, and real-time quality control in tablet production.
Granulation vs Direct Compression Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com