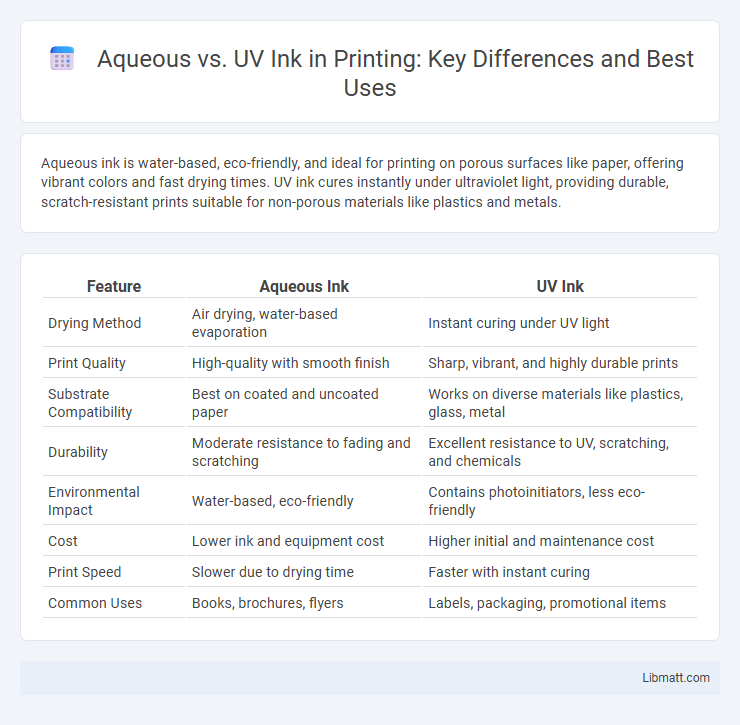
Aqueous ink is water-based, eco-friendly, and ideal for printing on porous surfaces like paper, offering vibrant colors and fast drying times. UV ink cures instantly under ultraviolet light, providing durable, scratch-resistant prints suitable for non-porous materials like plastics and metals.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Aqueous Ink | UV Ink |
|---|---|---|
| Drying Method | Air drying, water-based evaporation | Instant curing under UV light |
| Print Quality | High-quality with smooth finish | Sharp, vibrant, and highly durable prints |
| Substrate Compatibility | Best on coated and uncoated paper | Works on diverse materials like plastics, glass, metal |
| Durability | Moderate resistance to fading and scratching | Excellent resistance to UV, scratching, and chemicals |
| Environmental Impact | Water-based, eco-friendly | Contains photoinitiators, less eco-friendly |
| Cost | Lower ink and equipment cost | Higher initial and maintenance cost |
| Print Speed | Slower due to drying time | Faster with instant curing |
| Common Uses | Books, brochures, flyers | Labels, packaging, promotional items |
Introduction to Aqueous and UV Inks
Aqueous inks are water-based formulations known for their eco-friendly properties and vibrant color output, commonly used in inkjet printing and packaging applications. UV inks, cured instantly by ultraviolet light, offer superior durability, abrasion resistance, and fast drying times, ideal for high-quality industrial and commercial printing on diverse substrates. Both ink types serve distinct purposes based on environmental impact, substrate compatibility, and production speed requirements.
Composition and Chemical Properties
Aqueous ink is primarily composed of water-based solvents and dyes or pigments that are designed to evaporate easily, offering low toxicity and minimal environmental impact. UV ink contains photoinitiators and pigments that cure instantly under ultraviolet light through a polymerization process, resulting in a durable and chemically resistant finish. Your choice between these inks depends on the required drying time, adhesion properties, and environmental considerations for your printing project.
Printing Process Differences
Aqueous ink relies on water-based solutions that dry through absorption into paper fibers, resulting in a slower drying process suitable for uncoated papers. UV ink cures instantly when exposed to ultraviolet light, forming a durable, vibrant layer on a variety of substrates including plastics and metals. Your choice between these inks will impact print speed, substrate compatibility, and environmental considerations in the printing process.
Substrate Compatibility
Aqueous inks are compatible with porous substrates such as paper and cardboard, offering excellent absorption and vibrant color reproduction, while UV inks are ideal for non-porous materials like plastics, glass, and metals due to their rapid curing under ultraviolet light. UV inks bond strongly to a wide range of surfaces, providing superior durability and resistance to scratching and fading, making them suitable for outdoor applications. Your choice between aqueous and UV ink should depend on the specific substrate to ensure optimal adhesion and print quality.
Drying and Curing Mechanisms
Aqueous ink dries through evaporation of water, requiring air circulation and longer drying times, which makes it suitable for porous materials like paper. UV ink undergoes a polymerization process triggered by ultraviolet light exposure, instantly curing the ink to create a durable and chemical-resistant finish on non-porous surfaces. The drying speed and adhesion properties of UV ink are superior due to its instant curing mechanism compared to the slower evaporation-based drying of aqueous ink.
Color Vibrancy and Print Quality
UV ink offers superior color vibrancy due to its ability to cure instantly under ultraviolet light, producing sharp, bright, and highly saturated prints. Aqueous ink, while providing good color accuracy, often results in less vivid tones and a more muted finish because it relies on water-based pigments that can absorb into the substrate. For high-quality prints demanding intense color brilliance and fine detail, UV ink stands out as the preferred choice in commercial printing.
Environmental Impact and Safety
Aqueous inks are water-based, making them environmentally friendly due to low volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and easier disposal, reducing air and water pollution. UV inks cure instantly under ultraviolet light, producing minimal waste and no solvents, which lowers hazardous emissions but involve chemicals that can require careful handling to avoid health risks. Both options reduce environmental footprints compared to solvent-based inks, but aqueous inks tend to have a safer profile for workers and ecosystems due to their biodegradable properties and lower toxicity.
Durability and Resistance Factors
Aqueous inks offer moderate durability and resistance, making them suitable for indoor applications where exposure to moisture and abrasion is limited. UV inks cure instantly under ultraviolet light, creating a robust, resilient print resistant to water, chemicals, and fading, ideal for outdoor and high-contact surfaces. The chemical composition of UV inks contributes to their superior hardness and longevity compared to the water-based formulation of aqueous inks.
Cost Considerations
Aqueous inks generally have lower upfront costs and are more affordable for short print runs due to simpler drying requirements and compatibility with digital printers. UV inks, while more expensive initially, offer cost benefits over time through faster curing, enhanced durability, and reduced post-print processing. Choosing between aqueous and UV ink depends on budget constraints, production volume, and desired print longevity.
Choosing the Right Ink for Your Application
Aqueous ink offers eco-friendly, water-based printing ideal for vibrant, high-resolution images on coated and uncoated papers, making it perfect for brochures and photographic prints. UV ink cures instantly under ultraviolet light, providing superior durability, scratch resistance, and adherence on a wide range of substrates, including plastics and metal, ideal for outdoor signage and packaging. Selecting the right ink depends on the material compatibility, required print longevity, and desired environmental impact for your specific application.
aqueous vs UV ink Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com