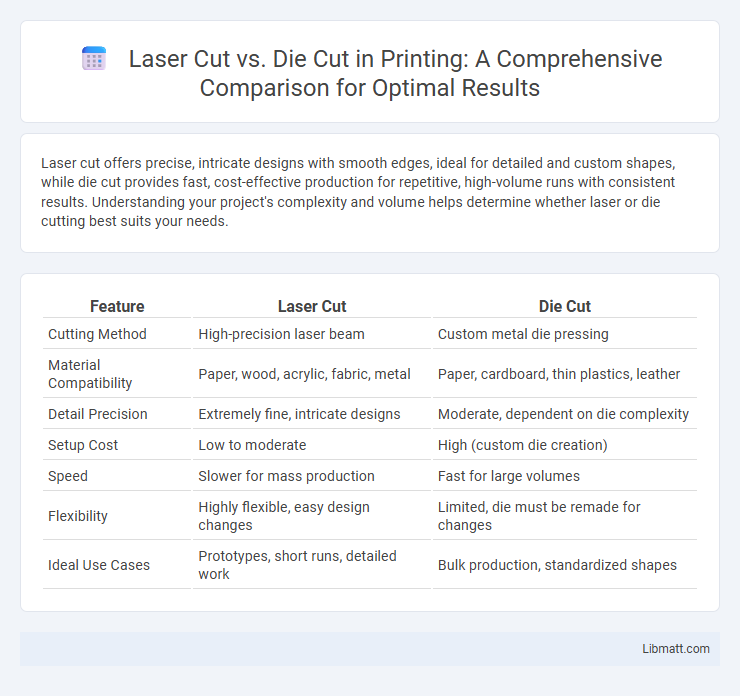
Laser cut offers precise, intricate designs with smooth edges, ideal for detailed and custom shapes, while die cut provides fast, cost-effective production for repetitive, high-volume runs with consistent results. Understanding your project's complexity and volume helps determine whether laser or die cutting best suits your needs.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Laser Cut | Die Cut |
|---|---|---|
| Cutting Method | High-precision laser beam | Custom metal die pressing |
| Material Compatibility | Paper, wood, acrylic, fabric, metal | Paper, cardboard, thin plastics, leather |
| Detail Precision | Extremely fine, intricate designs | Moderate, dependent on die complexity |
| Setup Cost | Low to moderate | High (custom die creation) |
| Speed | Slower for mass production | Fast for large volumes |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible, easy design changes | Limited, die must be remade for changes |
| Ideal Use Cases | Prototypes, short runs, detailed work | Bulk production, standardized shapes |
Introduction to Laser Cutting and Die Cutting
Laser cutting uses a high-powered laser beam to precisely cut or engrave materials such as wood, acrylic, and metal with minimal waste and complex detail. Die cutting employs a custom-shaped steel blade to stamp out patterns from materials like paper, fabric, and leather, ideal for high-volume production runs. Both techniques serve different industrial needs, with laser cutting excelling in accuracy and versatility, while die cutting offers speed and efficiency for repetitive shapes.
How Laser Cutting Works
Laser cutting operates by directing a focused laser beam onto materials to precisely vaporize or melt specified areas, allowing intricate designs and fine details to be achieved without physical contact. The process utilizes computer-controlled movements to guide the laser, ensuring high accuracy and consistency for varying materials such as wood, acrylic, or metal. Your projects benefit from the non-contact nature of laser cutting, which reduces material distortion and offers superior edge quality compared to traditional die cutting.
How Die Cutting Works
Die cutting works by using a custom-made steel rule die to precisely cut, score, or emboss materials such as paper, cardboard, or plastic sheets. The die, shaped like a cookie cutter, is pressed into the material with controlled pressure to create consistent shapes and designs quickly and efficiently. Your choice of die cutting ensures sharp, repeatable results ideal for high-volume production runs and complex, intricate patterns.
Key Differences Between Laser Cut and Die Cut
Laser cut technology uses a focused laser beam to precisely cut or engrave materials with high accuracy and flexibility, ideal for intricate designs and custom shapes. Die cutting employs a pre-made metal die to stamp out shapes consistently, making it cost-effective for large-volume runs but less adaptable to changes. Your choice depends on the project's complexity, production volume, and budget, with laser cutting favored for detailed, small-batch work and die cutting suited for repetitive, high-volume tasks.
Material Compatibility: Laser Cut vs Die Cut
Laser cutting offers superior material compatibility, efficiently handling a wide range of materials including wood, acrylic, fabric, and metal with precision and minimal waste. Die cutting performs best on softer, thinner materials like paper, cardstock, and foam, but struggles with thick or rigid substrates due to its reliance on physical pressure. Your choice depends on the material type and project requirements, as laser cutting provides greater flexibility while die cutting excels in high-volume, simpler shapes.
Cost Comparison: Laser Cutting vs Die Cutting
Laser cutting typically incurs higher initial costs due to advanced machinery and slower processing speeds, making it less cost-effective for large production runs. Die cutting offers lower per-unit costs and faster throughput, especially suitable for high-volume projects with repetitive shapes. Your choice depends on budget constraints and production scale, where laser cutting excels in customization and die cutting is ideal for mass manufacturing.
Precision and Edge Quality: Which is Better?
Laser cut technology offers superior precision and cleaner edge quality due to its ability to burn through material with minimal mechanical force, resulting in sharp, intricate designs and smooth finishes. Die cut processes rely on a physical blade to stamp out shapes, which may cause slight edge roughness and less accuracy in complex patterns. Your choice should consider that laser cutting excels in detailed, high-precision applications, while die cutting is effective for simpler, high-volume jobs.
Speed and Production Efficiency
Laser cut technology offers superior speed and production efficiency for complex and small-batch projects due to its non-contact process and minimal setup time. Die cutting excels in high-volume production with consistent output, benefiting from faster cycle times once the die is created and optimized. Businesses prioritize laser cutting for rapid prototyping and custom designs, while die cutting remains efficient for mass production runs with repetitive shapes.
Best Applications for Laser Cut and Die Cut
Laser cut technology excels in producing intricate, precise designs on materials like wood, acrylic, and fabric, making it ideal for custom signage, detailed art pieces, and prototype development. Die cut is best suited for high-volume production of uniform shapes, such as packaging, labels, and stickers, where speed and cost-efficiency are critical. Choosing the right method depends on whether your project prioritizes customization and detail or volume and consistency.
Choosing the Right Cutting Method for Your Project
Laser cut offers precise, intricate designs perfect for detailed projects with complex patterns, while die cut excels in high-volume production with consistent shapes and faster turnaround. Material compatibility varies; laser cutting suits a wider range including acrylic, wood, and fabric, whereas die cutting is often preferred for paper, cardboard, and thin plastics. Evaluating project scale, design complexity, material type, and budget helps determine the ideal cutting method for optimal results.
Laser Cut vs Die Cut Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com