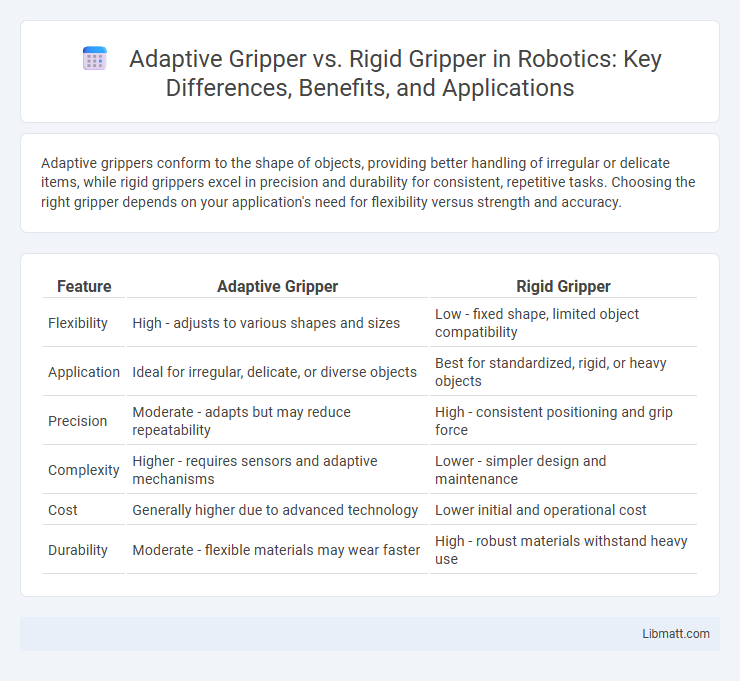
Adaptive grippers conform to the shape of objects, providing better handling of irregular or delicate items, while rigid grippers excel in precision and durability for consistent, repetitive tasks. Choosing the right gripper depends on your application's need for flexibility versus strength and accuracy.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Adaptive Gripper | Rigid Gripper |
|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | High - adjusts to various shapes and sizes | Low - fixed shape, limited object compatibility |
| Application | Ideal for irregular, delicate, or diverse objects | Best for standardized, rigid, or heavy objects |
| Precision | Moderate - adapts but may reduce repeatability | High - consistent positioning and grip force |
| Complexity | Higher - requires sensors and adaptive mechanisms | Lower - simpler design and maintenance |
| Cost | Generally higher due to advanced technology | Lower initial and operational cost |
| Durability | Moderate - flexible materials may wear faster | High - robust materials withstand heavy use |
Introduction to Industrial Grippers
Industrial grippers are essential tools in automation for handling and manipulating objects with precision and efficiency. Adaptive grippers automatically conform to the shape of various workpieces, improving versatility and reducing the need for multiple end-effectors, while rigid grippers maintain a fixed structure designed for specific tasks requiring high repeatability and strength. Your choice between adaptive and rigid grippers depends on the application's flexibility, load requirements, and object variability.
What is an Adaptive Gripper?
An Adaptive Gripper is a robotic end-effector designed to conform to the shape of various objects, providing versatile and secure handling without requiring precise object positioning. Unlike Rigid Grippers, which have fixed gripping surfaces ideal for consistent shapes, Adaptive Grippers use flexible materials or mechanical adaptations to accommodate irregular or delicate items. Your automation processes can benefit from increased efficiency and reduced damage risk when employing Adaptive Grippers for diverse and unpredictable workloads.
What is a Rigid Gripper?
A rigid gripper is a mechanical end-effector designed with fixed, solid components that provide precise and stable gripping for objects with consistent shapes and sizes. Unlike adaptive grippers, rigid grippers lack flexibility, making them ideal for repetitive tasks in manufacturing where high accuracy and strength are crucial. Your choice between rigid and adaptive grippers depends on the application's need for precision versus adaptability.
Key Differences Between Adaptive and Rigid Grippers
Adaptive grippers utilize flexible materials and compliant mechanisms to conform to various object shapes, enhancing versatility and reducing the risk of damage during handling. Rigid grippers rely on fixed, inflexible structures designed for precise, repeatable gripping of uniform objects, providing higher accuracy in industrial automation tasks. The key differences lie in adaptability for complex geometries versus stability and precision for consistent shapes, impacting their suitability across different manufacturing environments.
Application Scenarios: When to Use Adaptive Grippers
Adaptive grippers excel in handling irregular, fragile, or delicate objects in applications such as food processing, electronics assembly, and small parts manufacturing, where variable shapes and sizes are common. They provide enhanced flexibility and reduce the risk of damage during gripping, making them ideal for delicate handling tasks. Rigid grippers are better suited for stable, uniform objects in high-precision, repeatable industrial tasks like automotive parts assembly or heavy machinery handling where consistency and strength are paramount.
Application Scenarios: When to Use Rigid Grippers
Rigid grippers excel in applications requiring high precision and strong gripping force, such as industrial automation in automotive assembly and heavy machining. They are ideal for handling uniform, rigid objects with consistent geometry, ensuring reliable and repeatable performance in repetitive tasks. Industries involving metal parts, electronics manufacturing, and packaging often rely on rigid grippers for their stability and durability.
Performance Comparison: Flexibility and Precision
Adaptive grippers offer superior flexibility by conforming to various shapes and sizes, enabling efficient handling of irregular or delicate objects without causing damage. Rigid grippers excel in precision and repeatability for tasks requiring consistent, firm grasps on uniform parts, making them ideal for high-volume manufacturing with minimal variation. Your choice depends on whether flexibility in diverse applications or precise, reliable grasping for standardized items is the priority.
Cost Considerations and ROI Analysis
Adaptive grippers typically incur higher upfront costs due to advanced materials and sensor integration, yet they reduce operational expenses by minimizing product damage and increasing handling versatility across varied applications. Rigid grippers present lower initial investment and maintenance costs but may result in higher long-term expenses from frequent manual adjustments and part-specific tooling requirements. Evaluating ROI, businesses benefit from adaptive grippers in dynamic production environments through faster changeovers and decreased downtime, while rigid grippers yield better ROI in high-volume, uniform product lines with predictable handling needs.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Gripper Type
Adaptive grippers face challenges in maintaining precision and repeatability due to their flexible materials, which can lead to inconsistent gripping forces and difficulty handling very small or delicate objects. Rigid grippers, while offering high precision and strength, struggle with adaptability to varied object shapes and sizes, often requiring multiple gripper designs or complex tooling changes. The limitations of adaptive grippers include lower load capacity and wear issues, whereas rigid grippers are limited by lack of compliance, increasing the risk of object damage and reduced versatility in unstructured environments.
Future Trends in Robotic Gripping Technologies
Future trends in robotic gripping technologies emphasize the integration of adaptive grippers, which offer enhanced flexibility and the ability to handle a wide range of objects with varying shapes and textures, overcoming limitations of traditional rigid grippers. Advances in sensor technology and artificial intelligence enable adaptive grippers to improve precision and responsiveness, positioning your automated systems for greater efficiency and versatility in complex environments. The growing demand for collaborative robots in manufacturing and healthcare further accelerates the adoption of adaptive gripping solutions, driving innovation in materials and control algorithms.
Adaptive Gripper vs Rigid Gripper Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com